Show Navigation
|
Hide Navigation
You are here:
Extensions > Military Overlay Editor > Getting started with MOLE
Extensions > Military Overlay Editor > Getting started with MOLE
Symbol ID code |
|
|
Release 9.1
Last modified March 30, 2006 |
Print all topics in : "Getting started with MOLE" |
Related Topics
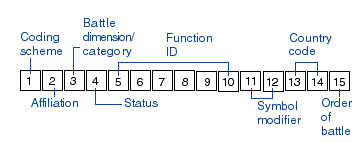
Central to MIL-STD-2525B—and, therefore, MOLE—is the Symbol ID code, a 15-character identifier. The characters and numbers that make up the code provide critical information about the war fighting elementthe code represents: how big the unit is, if it has mobility, if it is hostile, and so on. MOLE takes the information provided in the code and any additional information you provide in attributes and renders the war fighting element as a symbol in ArcGIS.
The presence of this code in a field named Symbol_ID in a dataset allows you to open and use the dataset in MOLE.
How MOLE renders the symbol based on the Symbol ID code
Each character or group of characters in the Symbol ID code gives information about, an attribute of, the war fighting element. For example, the second character in the code tells whether the war fighting element is friendly or hostile.
Each of these attributes has a corresponding visual component that can be drawn or rendered on a map. For example, if the second character is F, the war fighting element is friendly, and MIL-STD-2525B says friendly should be represented by a blue fill. When several of these components are rendered by MOLE for one war fighting element, they make a complete symbol.
To illustrate, the following image provides a complete symbol with its visual, or graphic components, described.

If you saw the above symbol on a map, you’d know that it represents
a present, friendly, subsurface force element. The valid values for these attributes (for example, F is a valid value for the affiliation attribute) are given in MIL-STD-2525B but are also excerpted from MIL-STD-2525B in the following tables.
MOLE allows you to manually add or edit Symbol ID codes in the attribute table of the MOLE feature or, if the MOLE layer is a shapefile or a feature class stored in a geodatabase, you can use the MOLE Symbol Editor to add or edit symbols.
Attribute values for force element graphics
| Coding scheme | Affiliaton | Battle dimension | Status |
| S: war fighting
G: tactical graphics W: METOC I: intelligence M: mapping (for future use) O: military operations other than war |
P: pending
U: unknown A: assumed friend F: friend N: neutral S: suspect H: hostile J: joker K: faker O: none specified |
P: space
A: air G: ground S: sea surface U: sea subsurface F: SOF X: other (no frame) |
A: anticipated/planned
P: present |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Function ID | Symbol modifier | Country code |
Order of battle
|
| Describes the specific function of a symbol. See MIL-STD-2525B for values. | Describes echelon, mobility, equipment, or installation characteristics of a symbol. See MIL-STD-2525B for specific values. | See FIPS Pub series 10. | A: air
E: electronic C: civilian G: ground N: maritime S: strategic force related |
Attribute values for tactical graphics
| Coding scheme | Affiliation | Category | Status |
| S: C2 symbology: units, equipment, and installations
G: C2 symbology: military operations W: METOC I: signals intelligence M: mapping (for future use) O: military operations other than war |
P: pending
U: unknown A: assumed friend F: friend N: neutral S: suspect H: hostile J: joker K: faker O: none specified |
T: tasks
G: C2 and general maneuver M: mobility/survivability F: fire support S: combat service support O: other |
A: anticipated/planned
P: present |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Function ID | Echelon/size | Country code | Order of battle |
| See MIL-STD-2525B for values. | See MIL-STD-2525B for values. | See FIPS Pub series 10. | X: control markings |
Special considerations for attribute values
- MOLE handles the Function ID attribute differently for force element graphics than it does for tactical graphics. For more information, see the MOLE developer documentation.
- MIL-STD-2525B often uses one or more asterisks (*) in sample Symbol ID codes to signify that any valid MIL-STD-2525B character can be used in that location. For example, S F G * * * * * * * * * * * *. It is important to keep in mind that these are sample codes only; neither MIL-STD-2525B nor MOLE supports use of asterisks in Symbol ID codes. MOLE does not recognize an asterisk as a valid character. If you want to indicate that a character in the Symbol ID is unknown, use a hyphen (-) instead. For example, if you know the coding scheme is S, affiliation is F, battle dimension is G, and no other properties, you’d use hyphens for the other characters so your Symbol ID code would be:
S F G - - - - - - - - - - - -