Data support in ArcGIS > Raster data > Properties of raster data
Raster dataset colormaps |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified September 22, 2008 |



Print all topics in : "Properties of raster data" |
A colormap is a set of values that are associated with colors. Colormaps are used to display a single band raster consistently with the same colors. Each pixel value is associated with a color, defined as a set of red, green, and blue (RGB) values. Since each value has a distinct color associated with it, it will always display the same way each time you open it up in a program that can read a raster with a colormap. Colormaps are capable of handling up to 8-bit data (256 colors).
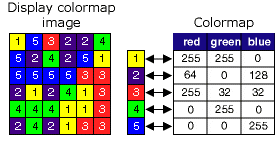
By default, a raster dataset with a colormap will always be displayed using the associated colormap. If you want to change the raster dataset's appearance, use the Unique Renderer (accessible on the raster dataset's Layer Properties dialog box on the Symbology tab) to redefine the colors to apply. See Displaying rasters to learn more about the different types of renderers.
The easiest way to see if your raster dataset has a colormap associated with it is to open the Raster Dataset Properties (in ArcCatalog) or the Layer Properties (in ArcMap); the colormap property will be present if there is a colormap associated with the raster dataset.
Colormaps are associated with the raster dataset in different ways, depending on the raster format. Some raster formats, such as .bil, .bip, or .bsq, have the colormap information stored in an auxiliary file next to the raster. Other formats, such as .img, .tif, or ArcSDE, will have the colormap information stored internally within the raster dataset itself.
The available geoprocessing tools allow you to copy a colormap or delete a colormap for a raster dataset. The Add Colormap tool allows the user to copy the colormap schema from an existing color-mapped raster dataset to another raster dataset. The Delete Colormap tool allows the user to delete the colormap from an existing raster dataset. Not all raster formats are applicable for these two geoprocessing tools. Please refer to the technical specifications, to see which formats can support colormaps. For more control over colormaps, you can use ArcObjects programming.
NOTE: Applying these two geoprocessing tools to an IMG or TIFF file will not work when the colormap is internally stored in the attribute table. If the attribute table contains the fields "Red", "Green", and "Blue", that means these tool cannot be used.