Managing CAD data in ArcCatalog |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified August 15, 2007 |



|
This section describes how you can work with CAD data in ArcCatalog beyond the standard file management operations such as move, copy, and delete.
File management
In addition to the CAD drawing file, you can have up to two additional files that are associated with CAD drawings. These are the projection (.prj) and world files (.wld). A .prj file contains coordinate system information that is defined with a CAD drawing file. Projection files can only be created in ArcGIS. A world file contains coordinate values that define a two-point similarity transformation. This file can be created in ArcGIS or outside ArcGIS using a text editor. Both of these files are text files. When you copy a CAD drawing in ArcCatalog, the .prj and .wld files will also be copied if they exist. Conversely, when you delete a CAD drawing, its .prj and .wld files will also be deleted if they exist.
Learn more about world files
Learn more about projection files
File extensions
By default, file extensions are hidden. When working with CAD data, it may be helpful to show file extensions so that you can quickly differentiate between different CAD file formats when browsing data in the catalog (for example, .dwg, .dgn, and .dxf). You can change this setting on the General tab of the Options dialog box in ArcCatalog.
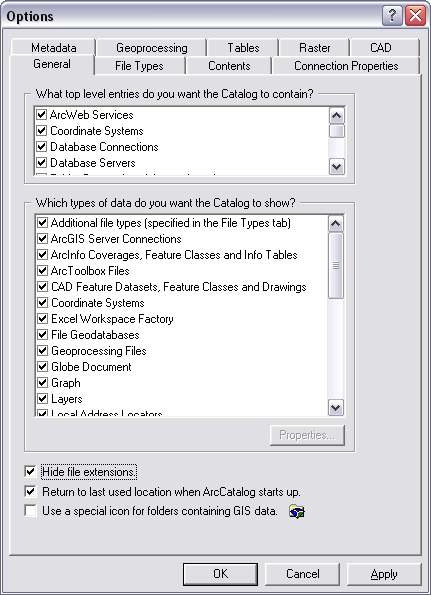
File types
If you want to see projection files and/or world files displayed in the Catalog tree among your CAD drawings, you can add them to the catalog view. You can do this by adding the .prj and/or .wld file type via the File Types tab. The example below shows the addition of the world file type.
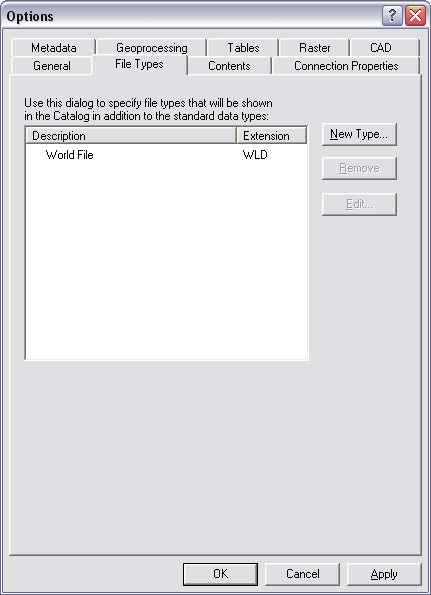
You can add a new file type by clicking New Type. On this dialog box, you specify the file extension and a description. The example below shows the addition of the .wld file extension.
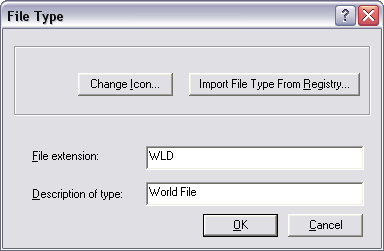
Options
ArcGIS has the ability to recognize MicroStation design files that possess unique file extensions. By default, MicroStation design files use the .dgn file extension (for example, roads.dgn). However, MicroStation supports the use of unique file extensions. Therefore, to support design files with unique file extensions, ArcCatalog provides an option to examine all file extensions for .dgn compliance. This option is located on the CAD tab of the Options dialog box (shown below).

By checking the Examine all file extensions box, ArcGIS will search for MicroStation design files regardless of their file extension. Design files that use more or less than three characters for their file extension will be ignored. For example, the following design files will be recognized by ArcGIS when the Examine all file extensions box is checked:
- roads.abc
- roads.123
- roads.xy9
- roads.98a
- roads.ab
- roads.9876
- roads.design
Metadata
Metadata is critical for sharing tools, data, and maps and for searching to see if the resources you need already exist. Metadata describes GIS resources the same way a card in a library's card catalog describes a book. Once you've found a resource with a search, its metadata will help you decide whether it suits your purpose. To make this decision, you may need to know how accurate or current the resource is and if there are any restrictions on how it can be used. Metadata can answer these questions.
Any item in ArcCatalog, including folders and file types such as CAD drawings, can have metadata. Once created, metadata is copied, moved, and deleted along with the item when it is managed with ArcCatalog or ArcInfo Workstation.
Learn more about metadata