Text |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified November 7, 2007 |



|
Text can be used in a variety of ways to enhance the information on a map. Maps convey information about geographic features, yet displaying only features on a map—even with symbols that convey their meaning—isn't always enough to make your point. Adding text to your map improves the visualization of geographic information.
There are various uses for text that is added to your map. Descriptive text can be placed near individual map features. For example, you might add the name of each major city in Africa to your map. You can add text to draw attention to an area of the map, such as the general location of the Sahara. You can also add text that improves the presentation of your map. For example, a map title provides context; you might also consider adding other information such as map author, data source, and date.
Because text serves so many different mapping purposes, ArcGIS offers several different types. In ArcGIS, label, annotation, and graphic text have more specific meanings than they have in the general cartographic world. ArcGIS differentiates these terms by their function and storage models. All types of text are based on the same text symbol, therefore they support the same graphic abilities but they are each tailored to different situations. It is important to know the differences between these types of text when considering adding text to a map.
Labels
In ArcGIS, a label is a piece of text that is automatically positioned and whose text string is based on feature attributes. Labels offer the fastest and easiest way to add descriptive text for individual features to your map. For example, you can turn on dynamic labeling for a layer of major cities to quickly add all the city names to your map.
Automatic label positioning is performed by a label engine. The ESRI Standard Label Engine is provided with all license levels of ArcGIS. The Maplex for ArcGIS extension provides the ESRI Maplex Label Engine for advanced cartographic labeling. With labels, each time you draw your map document (for example, pan, zoom, and so on), label text is generated on-the-fly following the labeling properties you establish for each map layer.
To label your features, the first step is to add the Labeling toolbar. Use this toolbar to set various labeling options and to choose your desired labeling engine. If you have ArcInfo or if you have the Maplex for ArcGIS extension, you can choose Maplex as your labeling engine in the Labeling menu.
Learn more about the tools on the Labeling toolbar
Next, use the Label Manager to set up labeling properties and rules for all layers you want to label within the data frame. Choose the attribute field that will be used as the source for the label text, set the properties of the text symbol, and establish placement rules and priorities for placing text labels on your map.
View a diagram of the Label Manager

Using Maplex for ArcGIS
NOTE: Maplex for ArcGIS is included as part of an ArcInfo license of ArcGIS Desktop. It is available as an optional extension for ArcView and ArcEditor.
Maplex for ArcGIS adds advanced label placement and conflict detection to ArcMap for automating many of the cartographic tasks used in high-end mapping. Maplex can save significant production time by automating much of the work of manual label placement. Maplex will place more text labels onto your map using automated procedures as well as to help you create a more useful map product. This saves time and money and can also help you to create higher quality maps regardless of your cartographic abilities.
Annotation
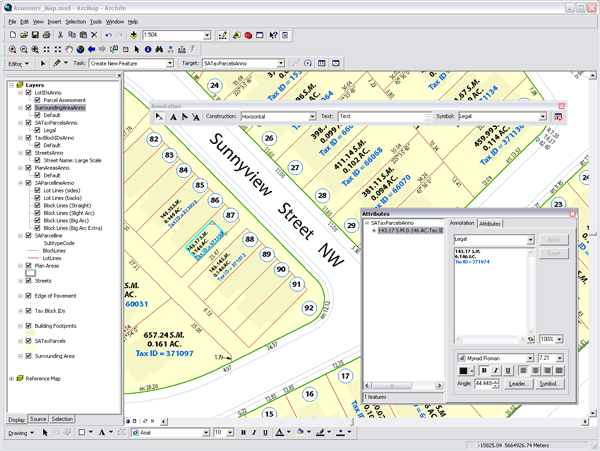
Annotation can be used to describe particular features or add general information to the map. You can use annotation like labels, to add descriptive text for map features, or just add a few pieces of text manually to describe an area on your map. Unlike labels, each piece of annotation stores its own position, text string, and display properties. Compared to labels, annotation provides more flexibility over the appearance and placement of your text because you can select individual pieces of text and edit their position and appearance. You can use ArcMap to convert labels to annotation. Annotation can be further divided based on where it is stored: in a geodatabase, in a map document, or in one of the read-only formats that ArcGIS supports.
Geodatabase annotation is the native annotation type of ArcGIS. With this type, pieces of text or graphics are stored as features in a geodatabase annotation feature class. The text positions are stored in spatially referenced coordinates and are sized graphically according to the reference scale. Geodatabase annotation is fully editable using the ArcGIS editing tools. There are two types of geodatabase annotation. Standard annotation is geodatabase annotation that does not have a maintained link to any features. The other type, feature-linked annotation, is a special type of geodatabase annotation that is directly linked to features and has special updating behavior when the linked features are updated.
Map annotation consists of text or graphics stored in the map document. With this type of annotation, pieces of text or graphics are stored as elements in a map's annotation group. A map can have multiple annotation groups to aid with organization. The text positions are stored in spatially referenced coordinates and are sized graphically according to the map scale or, optionally, a reference scale. Map annotation is fully editable using the ArcGIS graphic tools.
ArcGIS supports a variety of other annotation types as read-only data sources. These types include ArcInfo Workstation coverage, PC ARC/INFO coverage, Spatial Database Engine (SDE) 3.x, computer-aided design (CAD), and Vector Product Format (VPF) annotation. ArcGIS provides tools to convert them to geodatabase annotation or map document annotation, both of which are editable formats.
Graphic text
Text is also a fundamental part of page design in the page layout view in ArcMap. This type of text is called graphic text and is useful for adding information on and around your map that exists in page space—as opposed to annotation, which is stored in geographic space. Graphic text editing is performed using the graphic editing tools and can only be added to ArcMap in layout view. Some examples of graphic text include titles and explanatory paragraphs, and notes, such as the projection used, date, author, and data source.
Learn more about the tools on the Draw toolbar
Learn more about adding text to a map
Common tasks with text
| Common task | Where to go for more information |
| Creating text symbols and styles (used throughout ArcGIS, in labels, annotation, graphic text, legends, and so on) | Creating text symbols |
| Adding labels to a map |
Displaying labels
Prioritizing and positioning labels |
| Creating annotation from labels | Converting labels to annotation |
| Adding titles and other text to a layout |
Adding new text to a map
Working with titles |
| Creating new annotation | Creating new annotation features |
| Working with feature-linked annotation |
Using feature-linked annotation
Editing feature-linked annotation |
| Importing other annotation formats into ArcGIS |
Importing coverage or CAD annotation into geodatabase annotation
Importing SDE 3, VPF, or PC ARC/INFO coverage annotation |
In addition, see Common text related tasks for a description of how to perform a task using different types of text in ArcGIS.