Mapping and visualization > Page layout and map composition > Map output
Advanced PDF features |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified April 24, 2009 |



Print all topics in : "Map output" |
Note:
This topic was updated for 9.3.1.
PDFs exported from ArcMap can include advanced functionality in addition to their usage as a graphic interchange format. PDFs can contain layers from the ArcMap TOC so that users can enable and disable the visibility of layers and graphic elements in the layout. Additionally, ArcMap PDFs can contain attribute information that users can query and identify using the Object Data tool in Adobe Reader and Adobe Acrobat. The following sections contain information about these advanced features and their usage.
PDF layers
ArcMap PDF exports can contain layers that users can control the visibility of in Adobe Acrobat and Reader 6.0 and higher. To enable layers in a PDF export, select the Export PDF Layers Only option or the Export PDF Layers and Feature Attributes option under the Layers and Attributes drop-down menu on the export dialog box Advanced tab:

The Export PDF Layers Only option will add PDF layers without adding attributes.
Most ArcMap TOC layers, data frames, and layout elements will be included as separate layers in the export. However certain types of symbology may affect the presentation of a layer in the finished PDF. Refer to the graphic below for an outline of the PDF layer creation from within ArcMap.

This graphic shows the correlation between the ArcMap table of contents (right) and the PDF layers (left).
Below are some facts and tips concerning PDF layer creation from ArcMap.
- Each data frame will have its own folder in the tree view of the PDF which contains all the layers and the data frame graphics (neatline, background, etc.) associated with it.
- Text, picture, or north arrow elements added to a layout become part of a layer called Other. It contains all the graphics and marginalia that are not part of a data frame.
- Each group layer will be represented as a folder in the tree view, and the contents of the group layer will be presented within the group layer.
- Layers that cause rasterization, such as transparent layers or layers that use a picture fill symbology, consolidate all the layers below them into a single Image layer.
- If a layer contains picture marker or picture fill symbology, use the option Vectorize picture markers/fills, found on the Format tab of the export options dialog box. This prevents rasterization of layers below picture markers and fills.
- Raster layers, such as orthophotos, consolidate all layers below them into a single Image layer. Place raster layers lower in the ArcMap table of contents to avoid this problem.
- Graphic or text elements added to the data frame's default graphics layer from data view become a layer called <Default>. These display above the layers in the data frame. If multiple annotation groups exist (check this on the Drawing toolbar under Drawing > Active Annotation Target) and their contents are in the data view, each individual annotation group becomes a separate layer above the <Default> layer. This is a good way to add focus areas or graphics that emphasize or mask certain features in the data view.
- Backgrounds or drop shadows added to the data frame may become separate graphic elements and may be rendered multiple times as graphics. For example, if a data frame has a colored background, and the layout has a different colored background, the data frame's background may be rendered once to the data frame's "Graphics" or "ArcGIS Layer" and again to the layout's "Graphics" layer or "ArcGIS Layer".
- Dynamic labels (not using annotation) in each data frame are rendered separately as part of a layer called Labels.
- Geodatabase annotation displays as a separate layer in the PDF. Map annotation is consolidated into the layer for the annotation group in which it belongs.
- When labels are converted to annotation, they are automatically placed in their own named annotation group and so will render separately from the <Default> group.
- Data frames and other layout elements are rendered in draw order when exported to PDF. Therefore, the topmost layout element in the map will be the first element in the resultant PDF table of contents.
PDF attributes
PDF exports from ArcGIS 9.3 can include feature attributes from the feature's attribute table using functionality built in to Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader. This option can be enabled by choosing the Export PDF Layers and Feature Attributes option from the Advanced tab of the Export Map dialog box:

The Export PDF Layers and Feature Attributes option enables both PDF layers and the export of attributes based on options chosen in the Fields tab of the Layer Properties dialog box.
The visibility of fields in the feature's attribute table determines what fields will be exported in the resulting PDF. To turn these fields on and off, go to the Layer Properties dialog boxFields tab. The check boxes determine the visibility of the given layer. Check or uncheck the check boxes to expose more or fewer attributes in the resultant PDF.

The Fields tab on the Layer Properties dialog box, showing visibility of attribute table fields
Alternatively, the visibility of the fields can be controlled in the attribute table view by right-clicking the heading to disable and choosing the Turn Field Off option:

The Turn Field Off context menu option also toggles field visibility, disabling its export in the PDF attributes.
Exporting attributes to PDF can lead to performance problems when viewing the file in supported PDF readers. If possible, limit exported fields to one layer per map. To suppress field export, turn off field visibility in the Fields tab of the Layer Properties dialog box.
People using your PDF can access these attributes in Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader using the Object Data tool (see Tools > Object Data in either of those programs).
PDF map georeference
Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader 9 support a new version of PDF that allows for encoding of map coordinate system and georeference information inside the PDF file. Exporting a map with the Export Map Georeference Information option enabled will record each data frame's georeference information inside the PDF. When the georeferenced PDF is opened in a compatible viewer, such as Adobe Reader 9, the user can access geospatial functions such as coordinate readout and find XY.
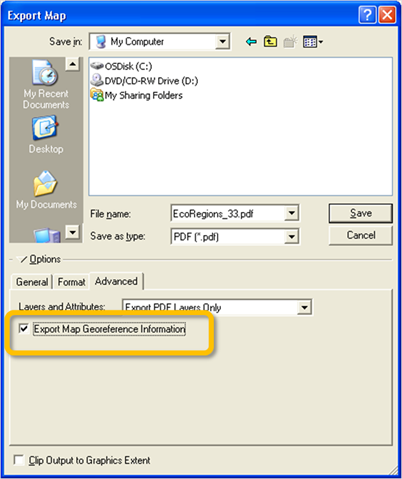
The Export Map Georeference Information check box on the Advanced tab of the Export Map dialog box.
The geospatial functionality available to Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader users depends on which Acrobat 9 product they are using. When a PDF exported from ArcMap is used directly in the free Adobe Reader 9 product, tools for coordinate readout and find XY will be available. If that same PDF is opened in any of the purchased Acrobat products, an extended geospatial toolset is provided including coordinate readout, find XY, geodesic measurement, and georeferenced markup. This same extended toolset can be accessed in the free Adobe Reader if the PDF has first been resaved in Adobe Acrobat 9 Pro or Pro Extended using the Enable for Commenting and Analysis in Adobe Reader command.
The georeference information saved inside the PDF file contains the following for each data frame on the page layout: corner coordinates of the data frame's boundary both in latitude and longitude and in PDF page units (points), and a string describing the data frame's coordinate system as defined in the data frame properties coordinate system options. When a map is exported from data view instead of layout view, the PDF will contain a single map image along with its corresponding georeference information.
PDF files containing georeference information are still compatible with earlier (pre-Acrobat 9) versions of Adobe Acrobat and Adobe Reader. Files will open without problems, but the coordinate-related functions will not be available. Exporting to PDF with the Georeference option enabled does not negatively impact performance. Export takes the same amount of time with the option on or off. With these facts in mind, you may wish to keep the option enabled for all map exports. However, if you desire to not have the georeference information included in the PDF file, uncheck the Export Map Georeference Information check box to suppress export of georeference information.
Note: PDF Map Georeference export functionality is not present in the initial ArcGIS 9.3 installation. It must be enabled via installation of a free general patch on top of 9.3, available from http://support.esri.com, entitled "ArcGIS (Desktop, Engine, Server) 9.3 map export patch to support Adobe Acrobat 9 PDF".
The ArcGIS 9.3 Service Pack, once released, will also enable this functionality.