Getting started > Introducing ArcGIS Desktop
Workspace and dataset management with ArcCatalog |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified May 27, 2009 |



Print all topics in : "Introducing ArcGIS Desktop" |
In ArcGIS applications, you work with multiple data sources—datasets, relational databases, and file types and schemas. ArcGIS allows you to work with geographic information in many forms including relational databases, files, ArcGIS documents, and remote GIS Web services.
ArcCatalog helps you by providing an integrated and unified view of these various sources of information. The ArcCatalog application helps you organize and manage all your geographic information, such as maps, globes, datasets, models, metadata, and services. It includes tools to
- Browse and find geographic information.
- Record, view, and manage metadata.
- Define, export, and import geodatabase data models.
- Search for and discover GIS data on local networks and the Web.
- Administer an ArcGIS server.
You can employ ArcCatalog to find, organize, and use GIS data as well as to document data holdings using standards-based metadata.
A GIS database administrator uses ArcCatalog to define and build geodatabases. A GIS server administrator uses ArcCatalog to administer his ArcGIS server framework.
Workspaces and geodatabases
Workspaces and geodatabases provide the primary containers to store and manage geographic information for ArcGIS.
Workspaces are directories (file folders on disk) that hold numerous GIS datasets and a series of ArcGIS documents. Workspaces can contain external datasets in many file formats as well as references to geodatabases. For example, you can work with file geodatabases, connect to ArcSDE geodatabases, and work with folders containing numerous data files—such as ESRI shapefiles and coverages, JPEG images, DXF CAD files, dBASE tables, Excel spreadsheets, and GML data files.
You organize your datasets and ArcGIS documents into a series of file system folders (often referred to as ArcGIS workspaces) and in geodatabases.
Organizing datasets by workspaces and in geodatabases is useful because it provides a mechanism to
- Control access to datasets.
- Provide a transaction framework for updating and sharing datasets.
- Organize, document, and catalog numerous geographic datasets.
Typical contents in a workspace can include
- ArcGIS documents, such as ArcMap documents (.mxd), layer files (.lyr), ArcGlobe documents (.3dd), and Python scripts (.py)
- Any number of external datasets
- Subfolders containing file geodatabases
- Microsoft Access files (.mdb) containing personal geodatabases
A geodatabase is a collection of geographic datasets of various types used for representing features, images, tabular data, and other data types managed in either a file structure or a multiuser relational database. It is the native data source for ArcGIS and is used for editing and data automation in ArcGIS.
ArcGIS documents
In ArcGIS, you work with system documents and files such as
- ArcMap documents (.mxd)
- ArcGlobe documents (.3dd)
- Layer files (.lyr)
- Python scripts (.py)
- AML scripts (.aml)
ArcGIS applications use a series of documents for saving work created in ArcGIS. These documents define how maps, map elements, map layers, globes, globe elements, and geoprocessing models are managed and used within the software. For example, a map document specifies the set of map elements contained in a map along with the map layers and their display properties used to present GIS datasets. Once you create a map document, you can use it simply by selecting the document and opening it. This will launch the ArcMap application for the selected map.
Each ArcGIS document is saved as a file in a disk folder.
| Document type | How it is used | Filename extension | Notes |
| ArcMap document
|
Double-click to start ArcMap | .mxd
|
A file containing a map, its layers, display information, and other elements used in ArcMap.
|
| ArcGlobe document
|
Double-click to start ArcGlobe | .3dd
|
A file containing a globe, its layers, and 3D display properties for use in ArcGlobe. Part of the 3D Analyst extension.
|
| ArcScene document
|
Double-click to start ArcScene | .sxd
|
A file containing a 3D scene, its layers, and 3D properties for use in ArcScene. Part of the 3D Analyst extension.
|
| ArcGIS Layer file
|
Drag-and-drop into ArcMap, ArcGlobe, or ArcScene | .lyr
|
A layer is a set of rules for displaying and working with datasets in ArcMap and ArcGlobe. Layer definitions include symbol assignments, classifications, labeling rules, and other map use properties.
|
| Published Map File for ArcReader
|
Double-click to start ArcReader | .pmf
|
A read-only map file created using the ArcGIS Publisher extension. Read-only maps can be used in ArcReader and ArcMap. They can also be served on the Web.
|
| ArcGIS Style file
|
Open in ArcMap to assign symbols for markers, lines, fills, and text | .style
|
A predefined set of colors, symbols, and graphical elements used for displaying and representing geographic datasets according to a mapping standard.
|
| ArcGIS Address Locator file
|
Used for geocoding in ArcGIS | .loc
|
A Locator dataset and rules used for geocoding addresses in ArcGIS. Locators are types of geodatabase datasets and can be saved independently of the geodatabase as a disk file for sharing and use.
|
| Metadata files
|
Used to document all information sets. Viewed and edited in ArcCatalog | .xml
|
Metadata documents for individual file-based datasets are stored in XML files and often managed in ArcGIS workspace folders.
|
| ArcGIS models, toolsets, and geoprocessing tools
|
Used in the geoprocessing framework | .tbx
|
Collections of geoprocessing models saved using toolbox files.
|
| Map projection file
|
Saved with each dataset as its coordinate system | .prj
|
Coordinate system and map projection information for a dataset.
|
| Geoprocessing scripts | Used in the geoprocessing framework | .py.
aml |
Python (.py) and ArcInfo Workstation AML scripts used for geoprocessing in ArcGIS |
ArcCatalog
ArcCatalog provides an integrated and unified view of all the data files, databases, and ArcGIS documents available to you. ArcCatalog is also used to document and manage metadata and to define the schemas of geodatabases.
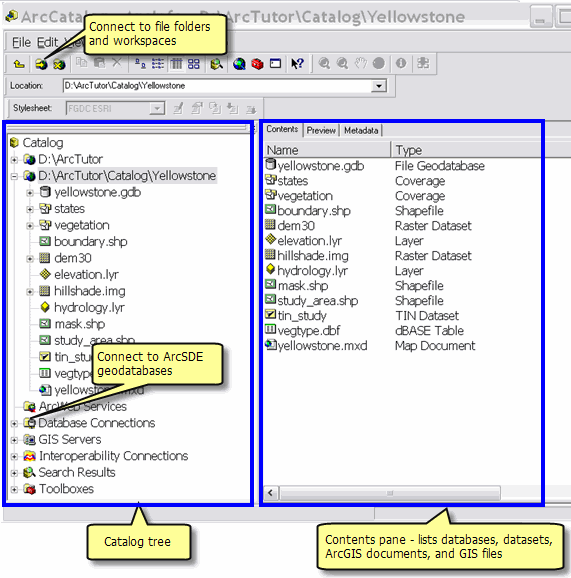
The Catalog tree
A key step in ArcGIS is to establish a connection to file folders and geodatabases that you plan to use.
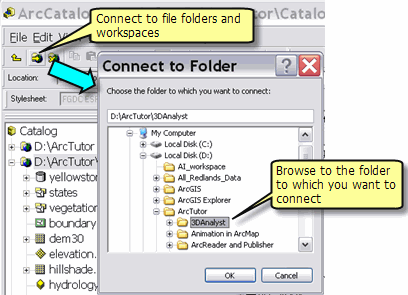
Once connected, ArcCatalog helps you manage all your geographic information sets using the Catalog tree to view your disk files and database connections. The ArcCatalog user interface presents the Catalog tree in the left-hand panel. By selecting an element in the Catalog tree, you can read its various properties and views in the right-hand panel. You can edit the Catalog tree, make new connections, add new elements (such as datasets), and remove elements.
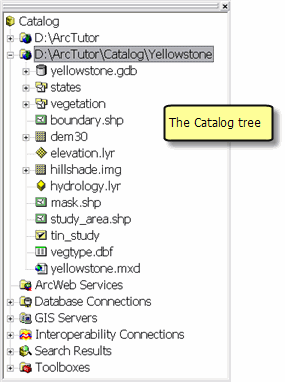
Some of the elements commonly shown in the Catalog tree include
- Folders—Connections to workspaces holding datasets and ArcGIS documents
- Database connections—ArcSDE geodatabase connections
- Address locators—Address geocoding files used in ArcGIS
- Coordinate systems—Map projection and coordinate system definitions used to georeference datasets
- GIS Servers—A list of the ArcGIS servers that can be managed with ArcCatalog
- Toolboxes—Geoprocessing tools used in ArcGIS
- Styles—Contains map symbols such as Marker (point) symbols, Line symbols, Pattern fill symbols (for polygons), and Text symbols used for map labels
- Map Templates—Map styles that you can use as a starting point in ArcMap
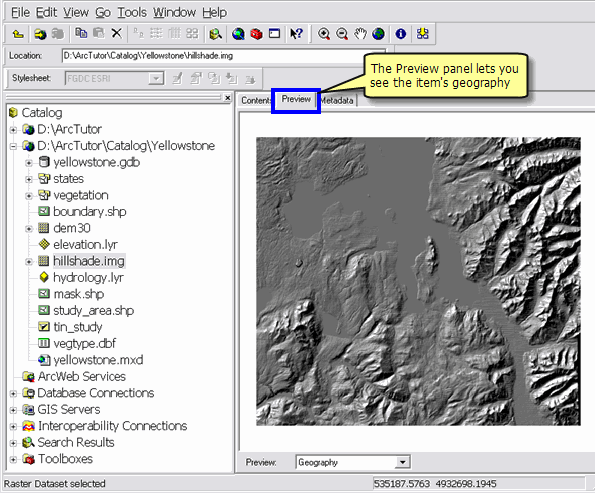
The Preview panel
You can see the geographic content of an item that is selected (and highlighted) in the Catalog tree using the Preview panel.
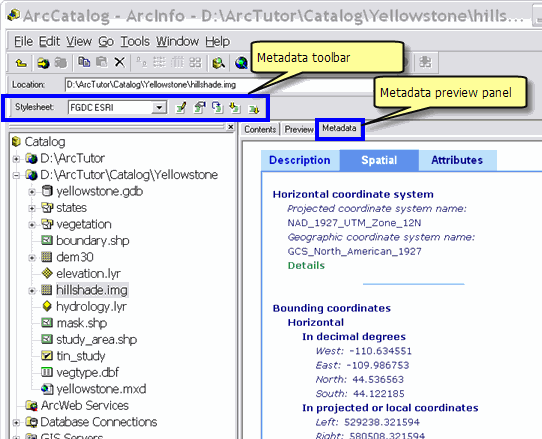
Metadata in ArcCatalog
Metadata documents can be created, edited, and viewed in ArcCatalog.
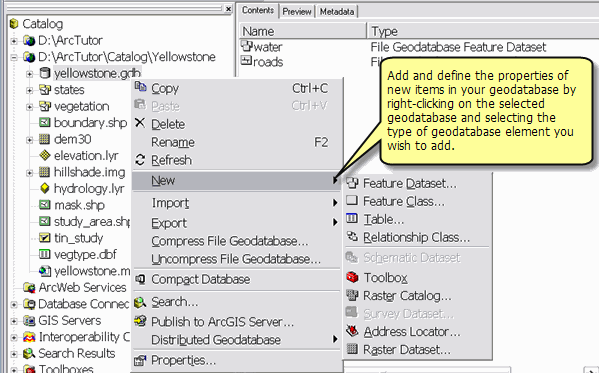
Creating and managing geodatabase schemas in ArcCatalog
Database administrators can create and manage the schemas of their geodatabases using ArcCatalog.
Toolbars in ArcCatalog
ArcCatalog contains a number of toolbars that are used to view datasets and perform a number of workspace and information management tasks in ArcGIS. For example, you can use the Preview panel to view your data in a map view and use the Geography toolbar to zoom and pan across of your dataset. Here is a quick review of some of the commonly used toolbars in ArcCatalog.
-
Standard toolbar—Typically appears at the top of the ArcCatalog application window and is used to navigate between workspaces, to set the viewing properties of your folder and dataset contents, for starting related ArcGIS applications, and more.
-
Metadata toolbar—Used to edit, share, and import standards-based metadata documents.
-
Geography toolbar—Used with the Preview panel for navigating within a map view of a selected dataset, identify features, and create a thumbnail picture for metadata in ArcCatalog.
-
ArcGIS Server Administrator toolbar—Used by ArcGIS Server administrators to start, stop, and pause server objects.