Working for an organization that manages geographic information, you're faced with the challenge of sharing your collection of geographic information to people within your organization and to those outside as well. ArcGIS Server provides the platform for sharing your GIS resources, such as maps, with your user community, whether they're sitting in the same office using ArcGIS Desktop or sitting across the country accessing and viewing maps from across the Internet.
ArcGIS Server allows you to share your GIS resources across an enterprise and across the Web. GIS resources are the maps, globes, address locators, and geodatabases that you want to share with others. You share these resources by first hosting them on your ArcGIS Server system, or GIS server, and then allowing client applications to use and interact with the resources. The main advantages of sharing your GIS resources on a GIS server are the same as sharing any data through any kind of server technology for instance, the data is centrally managed, supports multiple users, and provides clients with the most up-to-date information.
You might ask, why do I need a GIS server for this, wouldn't any server technology work? Well, in addition to providing access to particular GIS resources, the GIS server also provides access to the GIS functionality that the resource contains. For example, you might be able to share a map with someone through a server, but it would be even better if that person could also interact with the map, like find the closest hospital, restaurant, or bank and then get directions to it from their location. Thus, the GIS server not only allows you to share resources, like maps, but also allows you to access the embedded GIS functionality in them.
How people use the GIS resources on the server depends on who they are. Some people will be fully aware of GIS servers and also of the particular resources on a given server because they need to use them directly. For example, a GIS analyst might author a map that contains a layer that references a map resource on a GIS server. Or a developer may build a Web application that uses a map and an address locator to schedule and route delivery trucks.
For other people, the details about GIS servers and GIS resources will be completely hidden from them. For example, the members of a city council may explore a map through a Web application, for instance, finding locations suitable for redevelopment, before they make a decision that affects the community they live in. For them, the Web application simply provides the tools and information to help them make their decision. The fact that the Web application they're using to explore the map is accessing a particular map resource hosted on a GIS server is of no concern.
Let's take a look at some examples of how people use the GIS resources on a GIS server.
The GIS Server and Web application users
It is now commonplace to see maps or other geographic information integrated seamlessly into Websites. ArcGIS Server helps you put your geographic information on the Web, whether you need an application that simply displays a map or a more sophisticated one that incorporates specialized GIS tools. Access to the GIS server is embedded inside the Web application and typically hidden from the user of the application.
When you create web applications with ArcGIS Server, you can integrate content from your own server with content from other GIS servers. For example, suppose you’re a retailer with data about how products are selling across your store locations. You might overlay your data with demographic data from a different source to see how sales at each store location compare to the population around them. This way, you can tailor the products at the stores to the community they serve.
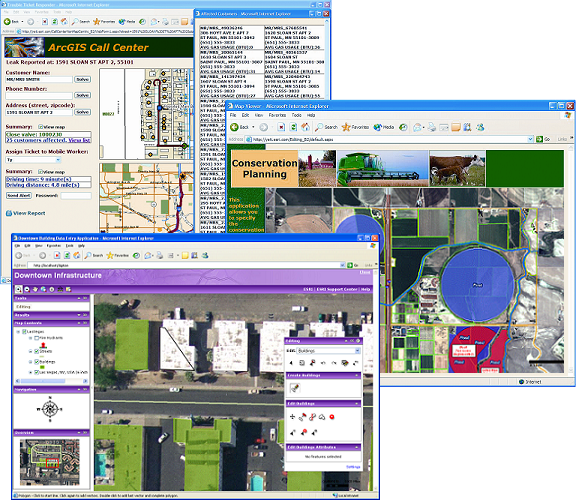
The GIS Server and ArcGIS Explorer users
Perhaps one of the easiest ways to access the GIS resources you host on your GIS server is through ArcGIS Explorer. Included with ArcGIS Server, ArcGIS Explorer is a geospatial information viewer that provides an easy way to view the geographic information running on a GIS server.
With ArcGIS Explorer, you can:
- Seamlessly explore data for the entire world in two and three dimensions.
- Fuse your local data with data and services from ArcGIS Server, ArcIMS, Open Geospatial Consortium WMS, and ESRI-hosted ArcWeb Services.
- Perform GIS analysis tasks (e.g., visibility, direction finding, and proximity search).
- Answer geographic questions and get answers you can share with others.
- Use maps and data from your own GIS servers.
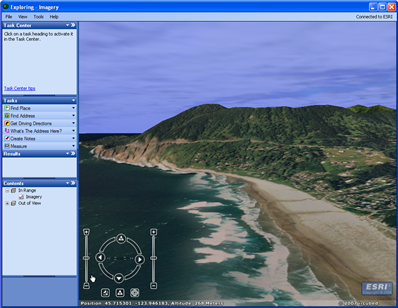
Use ArcGIS Explorer to view GIS resources running on your GIS server.
The GIS Server and ArcGIS Desktop users
The ArcGIS Desktop suite of applications (e.g., ArcCatalog, ArcMap, and ArcGlobe) provides access to the GIS resources on the GIS server. ArcGIS Desktop users can be divided into two groups: those that simply use the GIS resources hosted on the GIS server and those that are actively involved with creating and managing the GIS resources. Thus, ArcGIS Desktop applications can serve as clients and they are also the tools you'll use to create the resources that you host on your GIS server. For instance, you'll build maps in ArcMap and build globes in ArcGlobe, then use ArcCatalog to put them on your GIS server.
Here's a brief overview of how you can use the desktop applications with the GIS server.
- In ArcCatalog, connecting to a GIS server is similar to connecting to a local folder on your computer or to a database server. Once connected, you have access to all the resources available on the GIS server. You can use these resources just as you would use any resource, for example, adding a map service as a layer in an ArcMap map. If you also have administrative access to the GIS server, you'll also see additional tools that let you manage the server. You'll be able to configure the server, add and remove resources, and monitor it to make sure it's working properly.
- You'll use ArcMap to author the map resources you host on your GIS server. ArcMap can also function as a client application that simply consumes the resources running on the GIS server. For example, you can add layers to your map based on map services, find addresses based on geocoding services, and perform data management tasks, such as geodatabase syncronization using geodata services.
- You'll use ArcGlobe to author globe documents that you host on your GIS server. You can also use ArcGlobe as a client application and add layers to your globe document that reference globe services running on the GIS server.
- ArcToolbox supports the GIS server by providing the tools you need to create cached map services. A cached map service serves a collection of tiled map image created in advance at fixed scales and stored on the server. Client applications that access a cached map service draw maps very fast because the GIS server simply returns a precreated image to the client.

You can use ArcGIS Desktop applications to create and view resources hosted on a GIS server.
The GIS Server and Developers
Application developers can also make use of the GIS resources to create custom applications that focus on the requirements of a particular user in their user community. Typically, the end user of a custom application that incorporates GIS functionality has little or no knowledge that this functionality is being provided by the GIS server.
The following sections describe how a developer might use GIS resources to build various kinds of applications.
Web applications
Developers can build Web applications that end users access through Web browsers. Again, the developer accesses one or more GIS resources on the GIS server and incorporates its functionality into the Web application.
Web services
Unlike Web applications, Web services are not consumed by people, but by software applications. Thus, Web services don't have any user interface; it's up to the application that uses the Web service to provide the interface. Usually, the fact that an application uses a Web service is completely hidden to any user of the application. ArcGIS Server Web services are no different. They provide GIS functionality to applications that need it, with the expectation that those applications will provide the necessary user experience that exposes the functionality.
ArcGIS Server Manager lets you create Web services that access the GIS server and provide GIS functionality to other applications. You can create map, geocode, globe, geodata, geoprocessing, mobile data, network analysis, OGC Web Mapping Services (WMS), and Keyhole Markup Language (KML) Web services.
Desktop applications
Developers can build desktop applications that work with the GIS server in a client/server mode. These applications can be built using the ArcGIS Server application developer framework (ADF) or with the ArcGIS Engine Developer Kit.
The software developer kit (SDK) included with ArcGIS Server includes the libraries, samples, diagrams, and help you need to develop applications that make use of the server.
Java Enterprise applications
In the Java Enterprise world, an enterprise application is a complete, deployable unit of application components, often consisting of Enterprise JavaBeans(tm) (EJBs), JSP-based Web applications or Web services that consume the EJB services , and any other application resources that run in a standards-based J2EE application server.