Show Navigation
|
Hide Navigation
Feature data |
|
|
Release 9.1
Last modified April 26, 2005 |
|
Related Topics
 Geodatabase feature datasets
Geodatabase feature datasets
Geodatabase feature datasets reside inside geodatabases, personal or ArcSDE. They contain a collection of geodatabase feature classes that share the same extent and coordinate system.
The following geoprocessing tools accept geodatabase feature datasets as input or output: Create Feature Dataset, Copy, Delete, Rename, and Project.
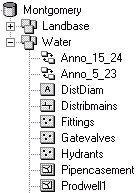
 Geodatabase feature classes
Geodatabase feature classes
You can perform geoprocessing tasks on the feature classes contained within a geodatabase feature dataset. Geodatabase feature classes store geographic features represented as points, lines, polygons, annotation, dimensions, and multipatches and their attributes. They store simple features, so they can be organized inside or outside a feature dataset, but always inside a geodatabase, personal or ArcSDE. Simple feature classes that are outside a feature dataset are called standalone feature classes. Feature classes that store topological features must be contained within a feature dataset to ensure a common coordinate system.
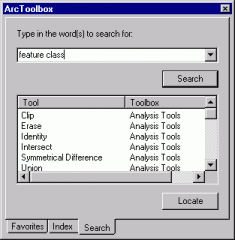
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "feature class" to locate tools that accept geodatabase feature classes as input or output.
 Shapefile datasets
Shapefile datasets
A shapefile dataset (.shp) is stored in a folder, is composed of geographic features and their attributes, and contains one feature class. Geographic features in a shapefile can be represented with points, lines, or polygons (areas).

Since shapefile datasets contain one feature class, you can use them like any other feature class.
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "feature class" to locate tools that accept shapefiles as input or output.
 Coverage datasets
Coverage datasets
A coverage is stored in a workspace that is a folder in your file system. It contains an integrated set of feature classes that represent geographic features.
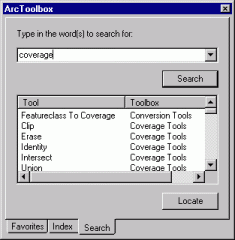
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "coverage" to locate tools that accept coverages as input or output.
 Coverage feature classes
Coverage feature classes
Coverage feature classes can store a set of points, lines (arcs), polygons (areas), regions, routes, tics, links, and annotation (text). They can also have topology, which determines the relationships between features that are within or between feature classes.
A coverage feature class can be used as input to tools that produce a distinct output or to tools that update the attributes of the input feature class. They cannot be used by those tools that update the geometry of the input.
If you want to update the geometry of a coverage feature class, export it to a geodatabase feature class and perform updates to the geometry of the geodatabase feature class.
In the Conversion Tools toolbox, click the To Geodatabase toolset and use the Feature Class To Geodatabase tool to convert coverage feature classes into geodatabase feature classes.
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "feature class" to locate tools that work with coverage feature classes.
 CAD feature datasets
CAD feature datasets
A CAD feature dataset is the ArcGIS feature representation of a CAD file. A CAD feature dataset is composed of five read-only feature classes: points, polylines, polygons, multi-patches, and annotation.
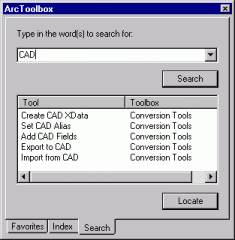
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "CAD" to locate all tools that accept CAD feature datasets as input or output.
Supported CAD file formats include DWG (AutoCAD), AutoDesk Drawing Exchange Format (DXF), and DGN (the default MicroStation file format). If the extension of your CAD file is not .dwg, .dxf, or .dgn, you will not see its feature dataset representation in the ArcCatalog tree. Use the File types tab in the Options dialog box (accessed via the Tools menu) to add the file extension of your CAD file so its feature dataset representation is displayed in the ArcCatalog tree.
Another representation of a CAD file in ArcGIS is the CAD drawing dataset, which is a pictorial representation of an entire CAD file. The symbology in a CAD drawing dataset mimics the symbology of the originating CAD file. It is useful to display the CAD drawing dataset in any ArcGIS application with a display, but for geoprocessing purposes you'll generally use the CAD dataset or feature classes as input to geoprocessing tools.
 CAD feature classes
CAD feature classes
A CAD feature class is a read-only, in-memory member of a CAD feature dataset. CAD feature classes include points, polylines, polygons, multipatches, or annotation.
A CAD feature class is the result of a direct file read into memory of the objects contained within a single CAD drawing file of a specific geometric type. The feature attribute table of a CAD feature class is a virtual table composed of select read-only CAD graphic properties and any existing block or cell attribute values.
Since they are read-only, CAD feature classes can only be used by geoprocessing tools that produce a distinct output. They cannot be used by tools that alter the geometry or attributes of the input feature class. To alter the geometry or attributes of a CAD feature class, export the feature class to a geodatabase feature class and perform the alteration on the geodatabase feature class.
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "feature class" to locate tools that accept CAD feature classes as input or output.
 SDC datasets
SDC datasets
A Smart Data Compression dataset contains read-only feature classes, all of which have the same attribute information but with different levels of generality in the shapes. SDC data is encrypted and highly compressed. This format is used by ESRI to provide StreetMap data and also by commercial data vendors who distribute street data for geocoding and routing with various ESRI software products.
The following geoprocessing tools accept SDC datasets as input or output: Copy, Delete, and Rename.
 SDC feature classes
SDC feature classes
SDC feature classes can store a set of points, lines and polygons. They can also have topology, which determines the relationships between features that are within or between feature classes.
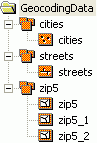
SDC feature classes differ in respect to other ArcGIS feature classes because they support multiple geometries for a single record. This design feature allows the storage of generalized versions of detailed geometry with only one set of attribute information. They support a licensing mechanism which can be used to bind access to a specific ArcGIS application, such as ArcReader or to a specific extension such as ArcGIS Business Analyst.
SDC feature classes are created using ESRI's Data Development Kit Professional (DDKP). They are composed of an SDC file that stores both geometry and data, a spatial index (.sdi) file that represents the spatial index, an attribute index descriptor (.idi) file that is a pointer to attribute indexes, and any number of attribute indexes that are defined in the IDI file. Filename extensions for individual attribute indexes are open as long as they are correctly defined in the IDI file.
SDC feature classes can only be used as input to geoprocessing tools that produce a distinct output or tools that update attributes. They cannot be used by those tools that update the geometry of the input.
If you want to update the geometry of an SDC feature class, export it to a geodatabase feature class and perform updates to the geometry of the geodatabase feature class. In the Conversion Tools toolbox, click the To Geodatabase toolset and use the Feature Class To Feature Class tool or the Feature Class to Geodatabase tool (for multiple inputs) to convert SDC feature classes into geodatabase feature classes.
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "feature class" to locate tools that work with SDC feature classes.
 VPF datasets
VPF datasets
The VPF dataset is a U.S. Department of Defense military standard that defines a standard format, structure, and organization for large geographic databases. A VPF dataset contains read-only feature classes.
You can export from VPF to coverage and vice versa. In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "VPF" to locate all tools that accept VPF datasets as input or output.
 VPF feature classes
VPF feature classes
A VPF feature class is a collection of features (primitives) that have the same attributes. Each feature class contains point (node), line (edge), polygon (face), or annotation features and has an associated feature attribute table. VPF feature classes are read-only. They can only be used by geoprocessing tools that produce a distinct output. They cannot be used by tools that alter the geometry or attributes of the input feature class.
In the Search tab of the ArcToolbox window, type "feature class" to locate tools that accept VPF feature classes as input or output.
If you want to alter the schema of a VPF feature class, you must export the feature class to a geodatabase feature class. In the ArcToolbox window, under Conversion Tools, click the To Geodatabase toolset and use the Feature Class To Feature Class tool or the Feature Class to Geodatabase tool (for multiple inputs) to convert VPF feature classes into geodatabase feature classes.
