Mapping and visualization > Navigating and interacting with maps > Interacting with maps
Identifying features |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified January 9, 2008 |



Print all topics in : "Interacting with maps" |
About identifying features
When you want information about a feature displayed in ArcMap, you can use the Identify tool ![]() on the Tools toolbar. The Identify tool allows you to see the attributes of your data and is an easy way to learn something about a location in a map. Clicking the Identify tool on a location inside a data frame will present the attributes of the data at that location. When identifying features with the Identify tool, the attributes are presented in a feature-by-feature, layer-by-layer manner in the Identify window.
on the Tools toolbar. The Identify tool allows you to see the attributes of your data and is an easy way to learn something about a location in a map. Clicking the Identify tool on a location inside a data frame will present the attributes of the data at that location. When identifying features with the Identify tool, the attributes are presented in a feature-by-feature, layer-by-layer manner in the Identify window.
The Identify tool can be customized to narrow down the amount of data you see by either filtering the layers you are interested in or by customizing the field properties of those layers. By reducing the number of layers the Identify tool works with, you can quickly focus on what is important to you when exploring a map. By customizing which fields are shown and setting field aliases, you can ensure that the Identify tool returns only the most appropriate fields, using field names that are easy to understand. In particular, the Primary Display Field, which is a layer property on the Fields tab of the Layer Properties dialog box, is used to determine the text in the left panel of the Identify window. It's a good practice to test the results of your formatting with the Identify tool before sharing a map document or publishing a map.
Accessing the Identify tool
The Identify tool can be accessed in a number of ways. The most popular is to click it on the Tools toolbar but you can also access it by right-clicking
- The map in data view
- Aresult listed in the Find dialog box
- A record in the table window
When you click the Identify tool on the Tools toolbar in ArcMap, the Identify window immediately appears, enabling you to choose which layers you want to identify before you click the map to identify a feature. This makes the Identify tool more convenient if you don't want to use the default topmost layer setting. It also enables you to position the window conveniently on the screen so it doesn't cover up the map area you're viewing. In ArcCatalog, the Identify tool doesn't open the Identify window when it's selected because you normally only work with one layer at a time in the ArcCatalog Preview window.
Choosing which layers to identify
When you use the Identify tool, it defaults to identifying the topmost layer in your map. If you click a location and do not find that the topmost layer interests you, you can use the Layers drop-down list at the top of the Identify window to choose from specific layers in your map or generic layer settings.
The Identify tool will act on whichever option you choose in the Layers drop-down list:
-
Topmost layer: Identify will give you the attributes of the feature or features from the layer that is uppermost in the drawing hierarchy—in other words, highest in the table of contents Display tab—at the location you click. This option won't identify features in a layer that is turned off in the table of contents or currently not being drawn because of the scale of the map. With this setting, you'll usually get the attributes of the feature you click without getting the attributes of features in other layers that are drawn underneath that feature.
- Visible layers: Identify will give you the attributes of the features belonging to all layers that are currently drawn on the map at the location you click.
- Selectable layers: Identify will give you the attributes of the features belonging to layers at the location you click that are checked on in the table of contents Selection tab or the Set Selectable Layers dialog box. If a layer is selectable, its features will be identifiable even if the layer is not currently drawn on the map. The Selectable layers option can be useful as your default because it restricts Identify to the same set of layers on which interactive selection operates.
- All layers: Identify will give you the attributes of the features from all the layers at the location you click. This includes layers that are not currently drawn on the map. This setting is useful if you want to get a cross-section of all the attributes of all layers at a particular location.
In addition, you can choose a specific layer in your map to identify. If you choose a particular layer name rather than a generic option, its features will be identifiable even if the layer is not currently drawn on the map.
Why does Identify let you identify a feature that's not drawn on the map? This is because in some situations you may want to be able to access a layer's attributes without drawing its features. For example, you may want to be able to find out what ZIP Code a particular street segment is located in without drawing the ZIP Code boundaries on your street map. In this case, you would choose the ZIP Code layer from this drop-down list but turn this layer off in the table of contents. Clicking a street with the Identify tool will give you the attributes of the ZIP Code layer at the location you clicked.
Working in the Identify window
The results of an identify displays in the window and shows three categories of information: a list of features that have been identified, the attributes belonging to each identified feature, and location coordinates.
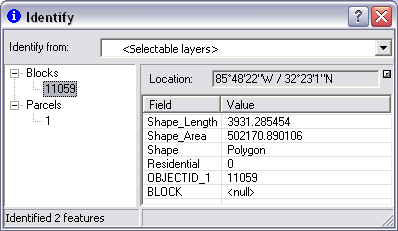
The left side of the window lists each feature that has been identified. Features are listed using the value of the layer's Primary Display Field, under the name of the layer to which they belong. You'll see multiple layers listed if you have identified features from more than one layer.
The right side of the window shows the attributes of the feature you identified. When you have identified features, you can click a particular feature in the list on the left and see its attributes in the right panel. In this way, you can compare attributes for different features. You can interact with the attributes of identified features by right-clicking within the attributes panel.
The x,y coordinates for the location you clicked are displayed on the right side of the window above the attributes panel. When you click an identified feature from the list on the left, the location box will display the x,y coordinates of that feature's location (if it is a point feature) or centroid (if it is any other type of feature). You can also choose the units with which these coordinates are displayed and you can select the coordinates and copy them.
Working with Identify results
You can interact with identified features by right-clicking a feature in the list on the left side of the window. This menu allows you to do a number of actions with the identified feature, including selecting, flashing, zooming, and panning to it. You can also manage and access hyperlinks set for the feature, create spatial bookmarks based on the extent of the identified feature, organize the list of identified features, and copy the feature's attributes.
The Identify window is one way of viewing related information about the feature you identified. Related information is data that has been expressly associated with the geographic feature you clicked by either a geodatabase relationship class or by a relate in ArcMap. For example, if you have a table of landowners that is related to a parcel feature class, you can identify a parcel feature, then view the related attributes in the owner table. You can use the expansion controls to navigate any related information.
Learn more about working with spatial bookmarks
Learn more about adding hyperlinks to features
Working with the attributes of identified features
By clicking or right-clicking the right side of the Identify window, you can interact with the attributes of identified features. Some of the tasks you can perform include accessing hyperlinks and rasters, managing fields, and copying field names or attribute values. When you have hyperlinks or rasters available, you'll see their icons in the Value column.
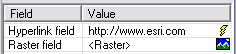
- Accessing hyperlinks: A field that contains a text value that is a full URL or full path can be used to link to either a Web site (URL) or launch a document. This enables you to link from fields in the Identify window without defining a hyperlink field in the layer's properties.
- Viewing images in a field of type raster: The attribute tables of geodatabase feature classes and standalone tables in geodatabases can contain a field of type raster. These fields can contain any supported image or raster file, such as a photo of a feature. When you identify a feature containing a raster field, a small icon appears next to the raster field if a picture exists for the record. Clicking it opens the raster in a new window.
Learn more about fields of type raster
- Managing fields: You can hide, show, sort, and select fields by right-clicking the right side of the Identify window. You can also sort the attribute list by clicking either the Field or Value title bar above the results.
- Copying fields and values: To copy all the field names and attribute values, right-click the left side of the window and use the Copy Record command. You may want to hide the fields you don't want to copy. To copy individual field names or individual values, right-click the right side and click Copy. For a field/value pair, right-click the right side and click Copy Selected Fields.
These hyperlinks do not support the hyperlink base property on the Document Properties dialog box; they must be complete URLs or paths. URLs must start with either http:// or https://, and paths must start with a disk drive or be a full UNC path. Windows environment variables are recognized as hyperlinks as long as they are defined at the system or current user level. You can have as many fields as you want that contain URLs or paths to documents, and values for a field can include both URLs and paths. The logic for recognizing the values as clickable links is built into the Identify window, and you don't need to set any layer or document properties.
Learn more about adding hyperlinks to features
How to identify features
Identifying features
- Click the Identify tool
 on the Tools toolbar.
on the Tools toolbar.
The Identify window opens. - Click the mouse pointer over the map feature you want to identify.
The features in the topmost layer (by default) under the pointer will be identified. - Right-click the left side of the window to interact with the identified features, or the right side to work with their attributes.
| Tips |
|
Changing the search tolerance of the Identify tool
- Click Selection on the Main menu and click Options.
- Type a new selection tolerance. The default is 3 pixels.
- Click OK.
| Tips |
|
Changing the default layer of the Identify tool
- Click Tools on the Main menu and click Options.
- Click the General tab.
- Click the Default Layer Option drop-down and click the layer type you want to use.
- Click OK.
| Tip |
|
Changing the units of the x,y coordinates displayed
- On the right side of the Identify window, click the small arrow next to the location information.
- Click the units you want to use.
| Tip |
|