Geoprocessing tool reference > Analysis toolbox > Overlay toolset > Tools
Intersect (Analysis) |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified January 13, 2009 |



Print all topics in : "Tools" |
Computes a geometric intersection of the Input Features. Features or portions of features which overlap in all layers and/or feature classes will be written to the Output Feature Class.
Learn more about how Intersect works
Illustration
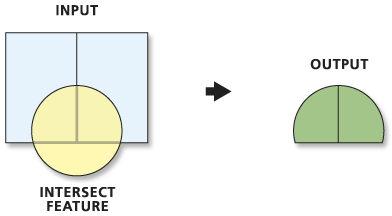
Usage tips
-
The Input Features must be simple features: point, multipoint, line, or polygon. The inputs cannot be complex features like annotation features, dimension features, or network features.
-
If the inputs have different geometry types (that is, line on poly, point on line, and so on), the Output Feature Class geometry type will default to be the same as the Input Features with the lowest dimension geometry. For example, if one or more of the inputs is of type point, the default output will be point; if one or more of the inputs is line, the default output will be line; and if all inputs are polygon, the default output will be polygon.
-
The Output Type can be that of the Input Features with the lowest dimension geometry or lower. For example, if all the inputs are polygons, the output could be polygon, line, or point. If one of the inputs is of type line and none are points, the output can be line or point. If any of the inputs are point, the Output Type can only be point.
-
Output may be multipart. If multipart features are not desired, use the Multipart to Singlepart tool on the output.
-
When processing datasets that contain any individual feature with a very large number of vertices (e.g., hundreds of thousands to millions of vertices within a single feature), some geometric processing operations may run out of memory. For more details, see Geoprocessing with large datasets.
-
With ArcView and Editor licenses, the number of input feature classes or layers is limited to two.
-
The following environment settings affect this tool: Coordinate system, Extent, XY Tolerance, Z Tolerance, M Tolerance, XY Resolution, Z Resolution, M Resolution, Output XY domain, Output Z domain, Output M domain, Output has M values, Output has Z values, Default Z value, Configuration keyword, Output Spatial Grid.
Command line syntax
An overview of the Command Line window
Intersect_analysis <in_features {Ranks};in_features {Ranks}...> <out_feature_class> {NO_FID | ONLY_FID | ALL} {cluster_tolerance} {INPUT | LINE | POINT}
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
| <in_features {Ranks};in_features {Ranks}...> |
A list of the input feature classes or layers. When the distance between features is less than the cluster tolerance, the features with the lower rank will snap to the feature with the higher rank. The highest rank is one. For more information, see Priority ranks and Geoprocessing tools. With ArcView and Editor licenses, the number of input feature classes or layers is limited to two. |
(Feature Layer Long; Feature Layer Long;...) |
| <out_feature_class> |
The feature class to which the results will be written. |
Feature Class |
| {NO_FID | ONLY_FID | ALL} |
Determines which attributes from the Input Features will be transferred to the Output Feature Class.
|
String |
| {cluster_tolerance} |
The minimum distance separating all feature coordinates (nodes and vertices) as well as the distance a coordinate can move in X or Y (or both). You can set the value to be higher for data that has less coordinate accuracy and lower for datasets with extremely high accuracy. |
Linear unit |
| {INPUT | LINE | POINT} |
Choose what type of intersection you want to find.
|
String |
Command line example
workspace d:\data\RedRiver_basin.mdb intersect_analysis (vegetation_stands ; road_buffer200m ; water_buffer100) mysites ALL # # intersect_analysis (vegetation_stands 2; road_buffer200m 1; water_buffer100 2) mysites_ranked ALL # #
Scripting syntax
About getting started with writing geoprocessing scripts
Intersect_analysis (in_features, out_feature_class, join_attributes, cluster_tolerance, output_type)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
| in_features (Required) |
A list of the input feature classes or layers. When the distance between features is less than the cluster tolerance, the features with the lower rank will snap to the feature with the higher rank. The highest rank is one. For more information, see Priority ranks and Geoprocessing tools. With ArcView and Editor licenses, the number of input feature classes or layers is limited to two. |
(Feature Layer Long; Feature Layer Long;...) |
| out_feature_class (Required) |
The feature class to which the results will be written. |
Feature Class |
| join_attributes (Optional) |
Determines which attributes from the Input Features will be transferred to the Output Feature Class.
|
String |
| cluster_tolerance (Optional) |
The minimum distance separating all feature coordinates (nodes and vertices) as well as the distance a coordinate can move in X or Y (or both). You can set the value to be higher for data that has less coordinate accuracy and lower for datasets with extremely high accuracy. |
Linear unit |
| output_type (Optional) |
Choose what type of intersection you want to find.
|
String |
Data types for geoprocessing tool parameters
Script example
# Purpose: Determine the type of vegetation within 100 meters of all stream crossings
# Create the Geoprocessor object
import arcgisscripting
gp = arcgisscripting.create()
try:
# Set the workspace (to avoid having to type in the full path to the data every time)
gp.Workspace = "c:/projects/RedRiverBasin/data.mdb"
# Process: Find all stream crossings (points)
gp.Intersect_analysis("roads ; streams ", "stream_crossings", "#", 1.5, "point")
# Process: Buffer all stream crossings by 100 meters
gp.Buffer("stream_crossings","stream_crossings_100m", "100 meters")
# Process: Clip the vegetation feature class to stream_crossing_100m
gp.Clip("vegetation", "stream_crossings_100m", "veg_within_100m_of_crossings")
# Process: Summarize how much (area) of each type of vegetation is found within 100 meter of the stream crossings
gp.Statistics("veg_within_100m_of_crossings", "veg_within_100m_of_crossings_stats","shape_area sum","veg_type")
except:
# If an error occurred while running a tool print the messages
print gp.GetMessages()