Data management with ArcCatalog > Working with metadata
About metadata |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified April 3, 2008 |



Print all topics in : "Working with metadata" |
Metadata is critical for sharing tools, data, and maps and for searching to see if the resources you need already exist. Metadata describes geographic information system (GIS) resources in the same way a card in a library's card catalog describes a book. Once you've found a resource with a search, its metadata will help you decide whether it's suitable for your purposes. To make this decision, you may need to know how accurate or current the resource is and if there are any restrictions on how it can be used. Metadata can answer these questions.
Any item in ArcCatalog, including folders and file types such as Word documents, can have metadata. Once created, metadata is copied, moved, and deleted along with the item when it is managed with ArcCatalog or ArcInfo Workstation.
How metadata is organized
In ArcCatalog, metadata is divided into properties and documentation. Properties, such as the extent of a shapefile's features, are derived from the item by ArcCatalog and added to the metadata. Documentation is descriptive information supplied by a person using a metadata editor, for example, a description of and legal information about using the resource. With the default settings in ArcCatalog, all you have to do to create metadata is click the item in the Catalog tree and click the Metadata tab—properties will be added to the metadata automatically.
Each GIS resource has its own discrete metadata document. Metadata documents describing related resources are not interconnected. Metadata for a feature class describes only that feature class—it does not inherit any metadata from the feature dataset in which the feature class is stored.
Similarly, metadata for a layer file or an ArcIMS Image Service should describe only the layer file or image service and the information it portrays, not the data sources it consumes. If a shapefile contains an entire suite of demographic data, its metadata should describe the values in each attribute column and its coordinate system since that is where those properties are defined and stored. Several layers may portray different aspects of the shapefile's data: one layer might show population growth, while another shows the ratio between the retired and working population. The layer file's metadata should describe what the layer shows; how the data was classified, normalized, and symbolized; and any joins or relates that are defined in the layer—not all the details of the data.
How metadata is stored
Metadata created with ArcCatalog is stored as XML data, either in a file alongside the item, or within its geodatabase. In a geodatabase, metadata is stored in the GDB_UserMetadata table as a BLOB of XML data.
XML is a markup language similar to HTML. HTML defines both the data and how it's presented. XML, on the other hand, lets you define data using tags that add meaning. Stylesheets are created using XSL.
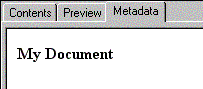
For example, in a metadata XML document, a title may be stored as follows: <title>My Document</title>. The XSL stylesheet selects the title and defines how to display it in HTML format as follows: <P><B><xsl:value-of select="title" /></B></P>. The metadata would then appear in the Metadata tab like this:
Learn more about viewing metadata using stylesheets
Metadata in ArcGIS is required to be well-formed XML. Metadata in ArcGIS is not required to comply with an XML Schema or Document Type Definition (DTD). However, you may have your own requirements to create metadata that is compliant with a specific standard.
Metadata in ArcGIS is stored in an ESRI-defined XML format that combines elements defined in the esriprof80 and ESRI_ISO1 DTDs published on the ESRI Metadata Web site. The esriprof80.dtd file defines the storage format for metadata adhering to the ESRI Profile of the Content Standard for Digital Geospatial Metadata. The ESRI_ISO1.dtd file defines the ESRI-ISO format for metadata adhering to the ISO 19115 standard, Geographic Information—Metadata.
Learn about metadata standards and the ArcGIS metadata XML format
XML has become an industry standard for storing data and transferring it across the Internet. Because ArcGIS metadata is stored as standard XML, any XML editing application can be used to view or edit metadata XML files.
Learn more about XML documents