Extensions > Spatial Analyst > Spatial Analyst functional reference > Surface (Spatial Analyst)
Aspect |
|
|
Release 9.2
Last modified January 3, 2008 |



Print all topics in : "Surface (Spatial Analyst)" |
Derives aspect from a raster surface.
Aspect identifies the downslope direction of the maximum rate of change in value from each cell to its neighbors. Aspect can be thought of as the slope direction. The values of the output raster will be the compass direction of the aspect.
Learn more about how Aspect works
Illustration
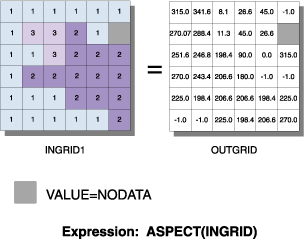
Usage tips
-
Aspect is the direction of the maximum rate of change in the z-value from each cell in a raster surface.
-
Aspect is expressed in positive degrees from 0 to 359.9, measured clockwise from north.
-
Cells in the input raster of zero slope — for example, flat — are assigned an aspect of -1.
-
If the center cell in the immediate neighborhood (3 x 3 window) is NoData, the output is NoData.
-
If any neighborhood cells are NoData, they are assigned the value of the center cell; then the aspect is computed.
-
Aspect is expressed in positive degrees from 0 to 359.9, measured clockwise from north.
-
Cells in the input raster of zero slope (flat) are assigned an aspect of -1.
-
If the center cell in the immediate neighborhood (3 x 3 window) is NoData, the output is NoData.
-
If any neighborhood cells are NoData, they are assigned the value of the center cell; then the aspect is computed.
-
Learn more about how to specify the input raster dataset in the Map Algebra expression of Raster Calculator.
-
Aspect is expressed in positive degrees from 0 to 359.9, measured clockwise from north.
-
Cells in the input raster of zero slope (flat) are assigned an aspect of -1.
-
If the center cell in the immediate neighborhood (3 x 3 window) is NoData, the output is NoData.
-
If any neighborhood cells are NoData, they are assigned the value of the center cell; then the aspect is computed.
-
Valid input for the geoDataset to ArcObjects is a Raster, RasterDataset, RasterBand, or RasterDescriptor.
-
The output from the ArcObjects method is a raster object.
Command line and Scripting
Map Algebra
ArcObjects
Command line syntax
An overview of the Command Line window
Aspect_sa <in_raster> <out_raster>
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
| <in_raster> |
Input raster. |
Composite Geodataset |
| <out_raster> |
The raster to be created. |
Raster Dataset |
Command line example
Aspect_sa C:/data/dem C:/data/aspect
Scripting syntax
About getting started with writing geoprocessing scripts
Aspect_sa (in_raster, out_raster)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
| in_raster (Required) |
Input raster. |
Composite Geodataset |
| out_raster (Required) |
The raster to be created. |
Raster Dataset |
Data types for geoprocessing tool parameters
Script example
# Aspect_sample.py
# Description:
# Derives aspect from a raster surface.
# Requirements: None
# Author: ESRI
# Date: Sept 6, 2005
# Import system modules
import arcgisscripting
# Create the Geoprocessor object
gp = arcgisscripting.create()
try:
# Set local variables
InRaster = "C:/data/dem"
OutRaster = "C:/data/aspect"
# Check out ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
gp.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Process: Aspect
gp.Aspect_sa(InRaster, OutRaster)
except:
# If an error occurred while running a tool, then print the messages.
print gp.GetMessages()
Map Algebra syntax
Aspect(<grid>)
| Parameter | Explanation |
| <grid> | Any valid combination of rasters, numbers, operators, and functions that produces an output raster. |
Map Algebra example
aspect(ingrid) aspect(ingrid) * 5 aspect(ingrid1 + ingrid2)
ArcObjects syntax
ISurfaceOp::Aspect (geoDataset As IGeoDataset) As IGeoDataset
| Parameter | Explanation |
| geoDataset | An input Raster, RasterDataset, RasterBand, or RasterDescriptor. |
ArcObjects example
' Create the RasterSurfaceOp object
Dim pSurfaceOp As ISurfaceOp
Set pSurfaceOp = New RasterSurfaceOp
' Declare the input raster object
Dim pInputDataset As IGeoDataset
' Calls function to open a raster dataset from disk
Set pInputDataset = OpenRasterDataset ("D:\SpatialData", "inputraster")
' Declare the output raster object
Dim pOutputRaster As IGeoDataset
' Calls the method
Set pOutputRaster = pSurfaceOp.Aspect (pInputDataset)