Data support in ArcGIS > Terrains > Building terrain datasets
Importing terrain dataset source measurements |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified April 28, 2009 |



Print all topics in : "Building terrain datasets" |
About importing terrain dataset source measurements
One of the most important processes when creating a terrain dataset is to import source measurements correctly into a geodatabase feature dataset. Terrain datasets can be generated from several different types of data. Such data can include lidar and sonar points, breaklines and points derived from stereo photography, and other forms of survey data. The feature class geometry types supported for terrain datasets include points, multipoints, polylines, and polygons. Source data used to generate a terrain dataset will come in either ASCII or LAS file formats.
The ASCII 3D to Feature Class and the LAS to Multipoint geoprocessing tools are the two geoprocessing tools offered to import terrain source data into desired feature classes. These tools are available with the 3D Analyst toolbox. To ensure the toolbox is available, make sure 3D Analyst is installed and enabled via the Tools > Extensions dialog box. Both geoprocessing tools can be found in the From File tools of the 3D Analyst Conversion toolset. The image below displays the location of the terrain dataset import tools in ArcToolbox.
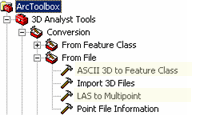
Terrain Source Data Import Tools
3D ASCII source data
ASCII source data can be imported into feature classes using the ASCII 3D to Feature Class geoprocessing tool. The ASCII 3D to Feature Class geoprocessing tool imports 3D features from one or more ASCII files into a new output feature class. The input format may be set to either XYZ or 3D GENERATE.
XYZ file format is the same for points, lines, and polygons in that each row of the source data file(s) is organized as x, y, z. The x-, y-, and z-values are double-precision floating point. Values can be space or comma delimited. Spaces are recommended. Header lines are permitted. The first line encountered where the first three tokens are numeric will be considered the beginning of the point records. Alphanumeric items following x-, y-, and z-coordinates are permitted, but they won't be used for anything. Only individual polylines and polygons can be represented in an XYZ file, and they can only be single part. Polygons must close, with the last vertex equal to the first, and must not self-intersect.
The 3D GENERATE format for points is the same as XYZ with the exception that no header lines are permitted and points are prefaced with IDs, and the last line of the file is optionally noted using the END keyword. The 3D GENERATE format for lines and polygons supports multiple features per file. Therefore, a feature can have several points along a vertex. The END keyword signals the end of a feature. Two END keywords in a row indicate the end of the file. Polylines and polygons can only be single part. Polygons must close, with the last vertex equal to the first, and must not self-intersect.
LAS Source Data
The LAS file format is a public file format for the interchange of lidar data. The LAS file format is a binary file format that maintains specific information related to lidar data. It is a way for vendors and clients to interchange data and maintain all information specific to that data. The LAS to Multipoint geoprocessing tool imports one or more LAS files into a multipoint feature class. Both LAS file format versions 1.0 and 1.1 are supported. Each LAS file contains metadata of the lidar survey in a header block followed by individual records for each laser pulse recorded. The header portion of each LAS file holds attribute information on the lidar survey itself. Information such as: data extents, flight date, flight time, number of points records, number of points by return, any applied data offset, and any applied scale factor is held within the header of each LAS file. The following lidar point attributes are maintained for each laser pulse of a LAS file: x, y, z location information; intensity; return number; number of returns; point classification values; scan angle; and scan direction.
Using geoprocessing tools to import source measurements
How to use the ASCII 3D to feature class geoprocessing tool
- In ArcToolbox, expand 3D Analyst Tools, expand the Conversion tools, then expand the From File tools.
- Double-click the ASCII 3D to Feature Class tool to open the geoprocessing tool. The ASCII 3D to Feature Class dialog box is displayed below.
- To determine the input files, click the Browse for drop-down arrow and chose either Folders or Files.
- Click the Input browse button
 to navigate to the ASCII files you want to import.
to navigate to the ASCII files you want to import.
- Highlight the ASCII files or folder you want to import into a feature class and click Open. You can use the Shift or Ctrl key to select more than one ASCII file.
- From the Input File Format drop-down menu, choose either XYZ or Generate to specify the input file format of the source measurements.
- Click the Output Feature Class browse button
 to set the location of the output feature class. All feature classes contributing to a terrain dataset must reside in the same feature dataset. It is recommended to set the output feature class to be the feature dataset where the terrain dataset will be created.
to set the location of the output feature class. All feature classes contributing to a terrain dataset must reside in the same feature dataset. It is recommended to set the output feature class to be the feature dataset where the terrain dataset will be created.
- Optionally, type a number for a Z Factor to be set.
- Optionally, specify an Input Coordinate System.
- Optionally, type a number for the Average Point Spacing.
- Optionally, set the File Suffix.
- Optionally, set the Decimal Separator.
- Click OK.
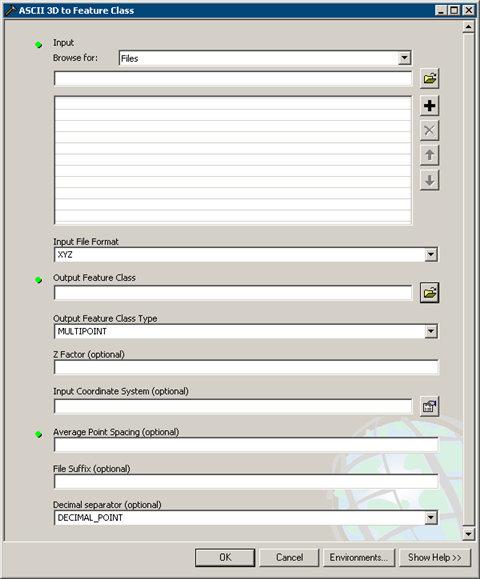
ASCII 3D to Feature Class Geoprocessing Tool
| Tips |
|
How to use the LAS to multipoint tool
- In ArcToolbox, expand 3D Analyst Tools, expand the Conversion tools, then expand the From File tools.
- Double-click the LAS to Multipoint tool to open the geoprocessing tool. The LAS to Multipoint dialog box is displayed below.
- From the Input Browse for drop-down menu, choose either Folders or Files.
- Click the Input browse button
 to navigate to the LAS files you want to import.
to navigate to the LAS files you want to import.
- Highlight the LAS files you want to import and click Open. You can use the Shift or Ctrl keys to select more than one LAS file.
- Click the Output Feature Class browse button
 to set the location of the output feature class. All feature classes contributing to a terrain dataset must reside in the same feature dataset. It is recommended to set the output feature class to be the feature dataset where the terrain dataset will be created.
to set the location of the output feature class. All feature classes contributing to a terrain dataset must reside in the same feature dataset. It is recommended to set the output feature class to be the feature dataset where the terrain dataset will be created.
- Set the average point spacing for the input LAS data.
- Optionally, specify an Input Class Code.
- Optionally, type an Input Return Value.
- Optionally, specify Input Atribute Names.
- Optionally, specify an Input Coordinate System.
- Optionally, set the File Suffix.
- Click OK.
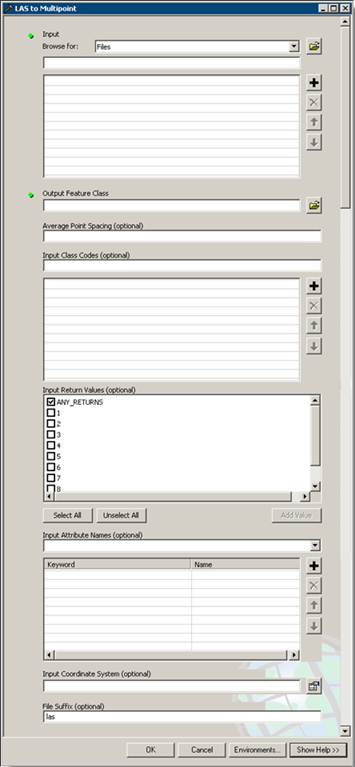
LAS to MULTIPOINT Geoprocessing Tool
| Tips |
|