Mapping and visualization > Working with layers
Saving a layer to disk |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified October 5, 2010 |



Print all topics in : "Working with layers" |
About saving a layer to disk
Note:
This topic was updated for 9.3.1.
One of the main features of a layer is that it can exist outside your map as a file on disk. This makes it easy for others to access the layers you've built.
There are two ways to save and share map layers:
- As layer files
- As layer packages
Layer files
Layer files (layer_name.lyr) include all map display properties for symbolization and labeling. However, layers do not usually contain the actual datasets. Instead, they typically reference a data source that resides in another location.
Layer packages: Saving layers with their data
A map layer and its data contents can be saved and shared using a layer package. A layer package is saved as a special file (layer_name.lpk) that contains the map layer, a copy of its data, and an XML file that has a brief description of the layer. Layer packages contain all the information necessary for users to put them to work in their own ArcGIS software installation. They are supported in ArcMap, ArcGlobe, and ArcGIS Explorer.
Layer packages make it easy to share your map layer display along with the underlying data with other users. For example, users of ArcGIS Explorer can add a new layer to their maps and easily begin using the information that you shared with them as a layer package. You can upload layer packages into to ArcGIS Online by visiting the ArcGIS.com website. This enables anyone using the ArcGIS Explorer desktop client or ArcGIS Desktop 9.3.1 or more recent to access your data. When you upload a layer package into ArcGIS Online, you can choose to make it publically available or you can restrict access to the members of particular ArcGIS Online groups. Please see the ArcGIS.com site for more details.
Pathnames to data sources
The layer file that is created will reference its data source using the Data Source Options setting currently specified for the map on the Document Properties dialog box (accessed from the ArcMap File menu). By default, this setting specifies that data sources will be referenced with their full path.
If the folder connection through which the data was accessed connects to a disk using a drive letter, such as C:\ or N:\, others won't be able to access the data or preview the layer's contents unless they also access the same disk using the same drive letter. If the folder connection was created from the Network Neighborhood, the path will include the name of the computer and the share name such as \\Blues\Shared Data. Others will be able to access the data and preview the layer's contents. However, if the data is renamed or moved, the layer files must be updated to use the new path.
Similar problems can be encountered with database connections and the layers that access data in the geodatabase. If the geodatabase is moved to a new machine or the database administrator changes the user names and passwords for accessing the geodatabase, you must update the source information for layers and database connections.
An alternative for referencing a layer's data source is to use a relative path. Suppose a folder named Forest contains both a layer and a subfolder named Data. The layer's data source is located within the data folder. With a relative path, the layer will start looking for the data source from the location in which the layer is stored. The layer will continue to work even if the Forest folder is relocated or renamed. To create a layer that uses relative paths in ArcMap, you must set the map's properties so that it uses relative paths for all layers. For more information, see Referencing data in the map.
Once you've saved the layer file, you can't change the data source options from absolute to relative or vice versa. The layer will always maintain the data source option that was set for the map document at the time you saved the layer.
How to save layers to disk
Saving a layer to disk in ArcMap
- Right-click the layer in the table of contents and click Save As Layer File.
- Click the Look in drop-down arrow and navigate to the location where you want to save the layer.
- Type a file name.
- Optionally, click the Save as type drop-down arrow and click 8.3 Layer files, 9.0/9.1 Layer files, or 9.2 Layer files to save a layer to a previous version of ArcGIS.
If you choose Layer files (the option without a version number), the layer will be saved in the current version of the software. - Click Save.
| Tips |
When you save a layer to disk, you are only saving a reference to the data source, not the data itself. When saving a layer to a previous version, keep in mind that older versions of ArcGIS may be unable to access newer data sources. For example, you can save a layer that points to any ArcGIS 9 geodatabase as an ArcGIS 8.3 layer and you'll be able to add the layer to a map in ArcGIS 8.3. However, the link to the data source will be broken because ArcGIS 8.3 can't access the newer geodatabase. In addition, older versions of the software won't be able to support some of the functionality and properties that have been added in later versions. Learn more about saving to previous versions of ArcGIS |
Saving a layer package
- Right click on a layer or group layer in ArcMap or ArcGlobe, and click 'Create Layer Package …'.
- Navigate to the folder location where you want to save the layer along with its data, and enter the file name.
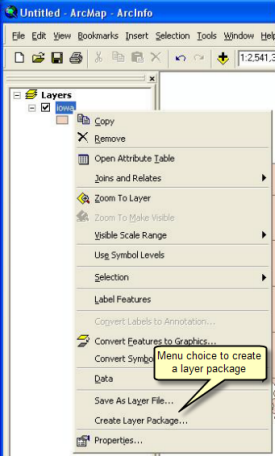
| Tips |
|
Saving a layer package with 3D properties
- To add 3D properties to a map layer, we suggest that you first create a map layer in ArcMap, and save it.
- Start ArcGlobe, and add the map layer (or layer package) that you created in ArcMap.
- Set the desired 3D properties for this map layer (e.g., setting height properties to extrude features in 3D, setting the distance range for a map layer's visibility in 3D, and so on).
- Right-click on the layer in ArcGlobe, and click 'Create Layer Package …'.
| Tip |
|
Creating a layer from existing data in ArcCatalog
- Right-click the data source from which you want to create a layer.
- Click Create Layer.
- Navigate to the folder in which you want to save the layer.
- Type a name for the layer file.
- Click Save.
The layer file appears in the folder's contents.
| Tip |
|
Creating a new, empty layer in ArcCatalog
- In the Catalog tree, select the folder in which you want to store the new layer.
- Click the File menu, point to New, then click Layer.
- Type a name for the new layer.
- Click the Browse button.
- Navigate to and click the geographic data source for which you want to create the layer.
- Click Add.
- If you don't want ArcCatalog to create a thumbnail representing the entire layer, uncheck Create thumbnail.
- If you don't want the layer to store the full path identifying the location of the data, check Store relative path name.
The location of the data will be recorded in relation to where the layer itself is stored. - Click OK.
The new layer appears in the folder's contents.