Mapping and visualization > Adding graphics and text to maps > Working with text
Displaying labels |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified September 29, 2009 |



Print all topics in : "Working with text" |
About displaying labels
Labeling is an easy way to add descriptive text to features on your map. Labels are dynamically placed, and label text strings are based on feature attributes. You can turn labels on or off or lock them so their locations stay fixed as you zoom or pan on your map.
You can use dynamic labeling for all features in a layer, or you can use label classes to specify different labeling properties for features within the same layer. For example, in a layer of cities, you might label those with a population greater than 100,000 with a larger font size and those with a population less than 100,000 with a smaller font size. In addition, if the features in your layer are symbolized with different symbols, you can create label classes from your symbology classes. Building your label classes from your symbol classes is a fast way to create maps with a consistent look.
The Labeling toolbar, Label Manager, and Label class summary dialog box
The Labeling toolbar is where you start labeling in ArcMap. From here you can control the labeling process and open the Label Manager, which lets you view and change labeling properties for all the labels in your map. By clicking the Summary button on the Label Manager you can access the Label class summary dialog box. This dialog box presents a general overview of the labeling classes in the data frame for quality assurance and performance checks.
General label settings
In addition to the parameters you can set to control the labeling of individual label classes, ArcGIS has global parameters you can use to control how labels are placed for all layers. These include
- Setting the color of unplaced labels
- Controlling whether or not the labels rotate with the data frame
- Setting the orientation of vertical labels
Because these are global parameters, you set them from the Labeling Options dialog box, which you can open from the Labeling menu.
Learn more about General label settings
Label symbols and styles
You control the appearance of dynamic labels by changing the label symbol. The label symbol is a text symbol that is used for all the labels in a layer or label class. Text symbols have basic properties such as font, size, and color. You can also work with more advanced text symbol properties to add callouts, leader lines, shadows, halos, and other effects to your labels.
Learn more about creating text symbols
To change the appearance of your labels, you can either change the properties of the existing label symbol or choose a different text symbol from a style file. For instance, on a map of European capital cities, if you want to use a bold font, you can change the properties of the existing label symbol to be bold. Or since the ESRI style contains a number of text symbols that are useful for labeling, you can choose the Capital symbol from this style and use it to label the European capitals.
To reuse any text symbol for labeling, save that symbol to a style. Then, you can use the saved text symbol for labeling, or any other purpose, in another map.
Learn more about modifying symbols and map elements
Another option for changing the appearance of your labels is to choose a label style. A label style consists of both a text symbol and label placement options. You can change the appearance and positioning of labels by choosing a label style for your layer or label class. The ESRI style contains a number of useful label styles for labeling points, lines, and polygons; they are stored in the Labels style category. If you choose label style, its text symbol will replace any text symbol currently set for your label symbol.
Learn more about label placement options
Showing unplaced labels
Often there is not quite enough room to place the labels for all the features on your map. You can view the labels that were not placed by clicking the View Unplaced Labels button located on the Labeling toolbar.
Unplaced labels appear in red by default, although you can change the color of unplaced labels on the Labeling menu’s Options dialog box located on the Labeling toolbar.
How to display labels
Adding the Labeling toolbar and opening the Label Manager
- Click the View menu, point to Toolbars, and click Labeling.
- Click the Label Manager button.
Using the Label Manager
- Click the Label Manager button
 on the Labeling toolbar.
on the Labeling toolbar.
- Check the box next to the layer you want to label.
- Choose a label class under the layer.
- Click the Label Field drop-down arrow and click the attribute field you want to use as a label.
- Click OK.
| Tips |
|
Opening the Label class summary dialog box
- Click the Label Manager button
 on the Labeling toolbar.
on the Labeling toolbar.
- Click the Summary button.
Turning labels on or off for a layer
- Right-click the layer in the table of contents and check Label Features to turn dynamic labels on.
- Check Label Features to turn labels on; uncheck Label Features to turn labels off.
| Tip |
|
Using label classes to label features from the same layer differently
- Open the Label Manager.
- Click the layer in the Label Classes box for which you want to create label classes.
- Type a name for your new label class in the Enter label name box and click Add.
- Uncheck the Default label class to avoid labeling some features twice.
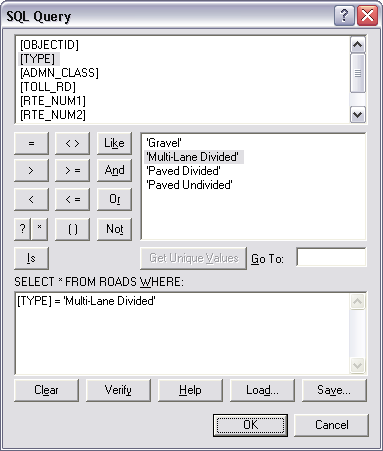
- Right-click the new label class in the Label Classes list and click SQL Query.
- Click the operators to build an expression that identifies the subset of features you want to label.
- Click OK.
- Click the Label Field drop-down arrow and click the attribute field you want to use as a label.
- Click the buttons and drop-down menus to define the symbol and placement properties of your labels.
- Repeat steps 2 through 9 if you want to create additional label classes.
- Click OK.
| Tips |
|
Building label classes from symbology classes
- Open the Label Manager.
- Click a layer in the Label Classes list.
- Check the box next to the symbology class or classes in the Select Symbol Categories box that you want to use to make a new label class or classes.
- Click the Add button.
- Click Yes or No on the Overwrite label classes dialog box depending on what you want to do with your existing label classes.
- Click OK.
| Tips |
|
Changing the appearance of labels by changing the label symbol
- Open the Label Manager.
- Click a label class in the Label Classes list.
- Click the buttons and drop-down menus in the Text Symbol box to set the font, size, color, or other symbol properties of your labels.
Optionally, click the Symbol button to change other properties or to choose an existing text symbol for your labels. - Click OK.
Changing the appearance of labels by choosing a label style
- Open the Label Manager.
- Click a label class in the Label Classes list.
- Click the Label Styles button.
- Click a standard label style from the left pane of the Symbol Selector dialog box.
Optionally, modify the properties of a label style and click Save to save your current settings as a new label style in your personal style folder. - Click OK on the Symbol Selector dialog box.
- Click OK on the Label Manager dialog box.
| Tips |
|
How to show unplaced labels
- Click the View Unplaced Labels button on the Labeling toolbar.
The unplaced labels appear in red. - When you want to hide the unplaced labels, click the View Unplaced Labels button again.