Image and raster data management > Properties of raster data
Raster dataset statistics |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified November 12, 2009 |



Print all topics in : "Properties of raster data" |
About statistics
Note:
This topic was updated for 9.3.1.
Statistics are required for a raster dataset to perform some geoprocessing operations or certain tasks in ArcMap or ArcCatalog such as applying a contrast stretch or classifying data.
Statistical information for the raster dataset is stored in an associated auxiliary file, if it cannot be stored internally. Once the auxiliary file has been created, the statistics within it will be reused for future procedures that require statistical information.
It is not essential to always calculate statistics; however, statistics need to be calculated before performing some geoprocessing analysis operations. In ArcMap and ArcCatalog, if statistics are not calculated, they will be calculated automatically when they are needed. For example, in ArcMap, when a raster dataset without statistics is first added to the data frame and statistics are needed to render the raster correctly, ArcMap functions will calculate default statistics and place these into an auxiliary file. Creating statistics for rasters in ArcCatalog prior to their use in ArcMap is recommended so that you don't have to wait for the statistics to be calculated when displaying the raster dataset in ArcMap.
Learn more about auxiliary files.
The default display of a raster in ArcMap or ArcCatalog will be improved in most cases if statistics have already been calculated because a standard deviation stretch is applied to the raster if statistics are present. In other cases, if the data to be displayed shouldn't be displayed with stretch by default, it would be appropriate not to calculate statistics for the dataset.
If the statistics do not exist, they can be created in ArcCatalog or by using the Calculate Statistics tool. There are two parameters you can specify when calculating statistics: a skip factor and values to ignore. Setting a skip factor speeds up the process of calculating statistics by skipping pixels. The default is a skip factor of 1 for both row and column, which means that every cell in the raster will be used in the calculation, resulting in the most accurate statistics. A skip factor is not used with all raster formats. The raster formats that will calculate statistics and take advantage of the skip factor include TIFF, IMG, NITF, DTED, RAW, ADRG, CIB, CADRG, DIGEST, GIS, LAN, CIT, COT, ERMapper, personal and file geodatabase, and ArcSDE. Values to ignore are the cell values you do not want used when calculating statistics such as background values (for example, the edges of some satellite data) or NoData values.
The statistics for a raster dataset can be viewed on the Raster Dataset Properties dialog box. Below is an example showing the statistics for a thematic raster dataset such as a land-use dataset. Statistics are calculated for each band; if there is more than one band in the raster datasets, the statistics for each band are present. You can see that the parameters used to build the statistics are listed. The statistics that are calculated include the minimum and maximum pixel values as well as the mean and standard deviation of the calculated pixel values, and if the dataset is thematic, the number of classes is listed. If your dataset is continuous, there will be no classes.
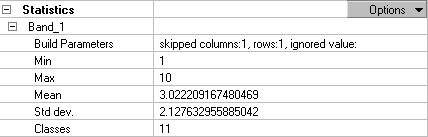
You cannot recalculate statistics on a grid dataset, because they are stored within that file format and are always present. The statistics are calculated using every cell in the grid except for cells with the value of NoData.
Learn more about NoData in raster datasets.
How to calculate statistics
Calculating statistics in ArcCatalog
- In ArcCatalog, navigate to the raster dataset for which you want to calculate statistics.
- Optionally, choose skip factors to use while calculating statistics.
A skip factor of 1 for both row and column means every cell in the raster will be used in the calculation, resulting in the most accurate statistics. - Optionally, type a value you want to ignore when calculating statistics.
This is frequently the background value, which is often a value of 0. Eliminating such a value can result in a more accurate, and perhaps more representative, calculation of statistics. If your raster dataset contains a NoData value, you will not be able to specify an ignore value. - Click OK.
| Tips |
|
Calculating statistics using the Calculate Statistics tool
- In any of the ArcGIS Desktop programs, click the Show/Hide ArcToolbox window button
 to open the ArcToolbox window if it is not already open.
to open the ArcToolbox window if it is not already open.
- Expand the Data Management Tools.
- Expand the Raster toolset.
- Expand the Raster Properties toolset.
- Double-click Calculate Statistics.
- Optionally, type values in each of the parameters.
- Click OK.
| Tip |
|
Setting the statistics settings for the geoprocessing environment
- Click Tools on the Main menu of the application you are using and click Options.
- Click the Geoprocessing tab.
- Click the Environments button.
- Click Raster Storage Settings.
- The Calculate statistics check box is checked by default. If you previously unchecked it, check it.
- Type a value for the skip factor in the x and y direction.
If, for instance, you type a value of 2 for both, every other pixel will be skipped while calculating statistics. A skip factor of 1,1 ensures full, accurate statistics. - If there are values in the raster that you want to ignore while calculating statistics for the raster, type their values, separated by a semicolon (;).
These values are frequently background values, which often have a value of 0. Eliminating such a value can result in a more accurate, and perhaps more representative, calculation of statistics. If your raster dataset contains a NoData value, you will not be able to specify an ignore value. - Click OK to close the Environment Setting dialog box, and click OK to close the Options dialog box.
| Tip |
Viewing the statistics
In ArcCatalog
- Right-click the raster dataset and click Properties.
- Expand Statistics on the Raster Dataset Properties dialog box.
- Right-click the raster dataset in the table of contents and click Properties.
- Click the Source tab.
- Scroll to the Statistics section.