Editing and data compilation > COGO
An overview of COGO |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified November 10, 2008 |



Print all topics in : "COGO" |
- Common COGO workflows
- About COGO descriptions
- Reporting COGO descriptions
- Adding COGO fields to a feature class
- Applying a ground to grid correction
- Using the Curve Calculator command
- Using the COGO Area command
- Splitting features into COGO lines
- Splitting line features
- Creating lines with the Traverse window
- Creating lines with the 2-Point Line window
- Creating lines with the Offset Line window
- Creating cul-de-sac lines
When surveyors or civil engineers need to record the location of human-made features, such as land parcels, road centerlines, utility easements containing transmission lines, oil and gas leases, and so on, they typically provide the results on a survey plan that describes the location of features relative to each other. Below is an example survey plan that diagrammatically shows a road centerline and the edge of the land properties adjoining the road. The road centerline and parcel boundaries comprise a number of straight and curved lines.
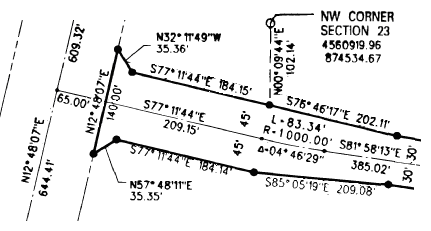
Each line has measurements that describe it. A straight line has a direction and distance, while a curved line has a radius, angle, arc length, direction, and so on. These measurements are coordinate geometry (COGO) descriptions. You can use these COGO descriptions to accurately re-create the features the surveyor captured. The survey plan also includes references to existing locations that help you to tie these new features into your GIS database. The reference could be the coordinates for a point or a measurement to a well known location such as a control point, a road intersection, or an existing parcel corner.
Building blocks for COGO
The basic building blocks for COGO are:
- Points—Survey plans can describe point features such as control points, section corners, monuments, and so on. You can use a simple point feature class to represent these features.
- Lines—You use a simple line feature class to represent these features. You can optionally add COGO fields to your line feature class, and measurements you enter are recorded on the features. There are three types of lines found on survey plans:
- Straight lines—Straight lines are the predominant type of lines on a survey plan, they are used to represent all types of features.
- Curved lines—A typical use for curved lines is to smoothly change direction on a road centerline. Parcel boundaries are usually parallel to the road centerline, so boundaries adjacent to a curved centerline are also curved. Curves are used in a number of other situations; in cul-de-sac parcels to provide a large turning circle for vehicles and on parcels at an intersection to provide greater visibility.
- Spirals—Spirals are not as common as the other types of lines. Spirals typically provide a transition to and from circular curves. Spirals are used in roadway and railroad design, where a high speed vehicle or train must be eased into or out of a circular path from or to a straight tangent. Creating and modifying spirals is not supported.
- Polygons—Polygon features are used to represent the parcel areas formed by your COGO line features. You usually don't directly create polygons with the ArcMap COGO functionality, more typically you derive polygons from your lines. For example, you can use the Construct Features command on the Topology toolbar to creates polygons from selected lines.
- Traverses—Much of the data that is entered using COGO descriptions is entered from traverses. A traverse is simply an ordered collection of COGO descriptions that are used to create either a line or a polygon. Each individual line is referred to as a Course. Traverses are not stored in the GIS; however, you can save a traverse to a text file and recall it later.
Creating features from COGO descriptions
The commands and dialog boxes in the ArcMap editing environment for creating features from COGO descriptions are integrated into the editing experience. The common commands and dialog boxes you will use include:
- Traverse window—Create an edit sketch from a traverse description.
- 2-Point Line window—Quickly create a feature from a single COGO description.
- Offset Line window—Create an edit sketch from a strip description, a type of survey plan used for realigning road centerlines.
- Cul-de-sac command—Create a cul-de-sac from a selected road centerline.
These are just some of the commands and dialog boxes available for creating features in ArcGIS. Refer to Common COGO workflows to understand how you can use these and other commands to build and maintain your land parcels.
When you are creating features, you still need to set the target layer so ArcMap knows which layer you want to update. For the Traverse and Offset Line windows, you also need to set the edit task to either Create New Feature or Create 2-Point Line Features.
Correcting for differences between the survey plan and GIS data
When you are using the COGO descriptions from a survey plan, you are using measurements the surveyor took on the ground and possibly adjusted to some coordinate system. However, a GIS stores coordinates relative to a projections coordinate grid. You can use the ground to grid correction to adjust the geometry of the features you create.
Reporting COGO descriptions
Before you begin adding features from COGO descriptions, you may need to investigate and understand how the new features will fit compared to the existing features. You can use the COGO Report dialog box to measure directions and distances between points you click on the map as well as query the COGO descriptions for line feature in your database. You can also use the COGO Area command to calculate the legal area of selected line features, useful when deciding which approach to use when modifying features.
Storing COGO attributes on line features
In ArcMap, you can store the COGO values that you enter when creating features as an attribute of the line feature. One reason to do this is to keep a record of the original COGO description of the line features. This is useful if you need to research the original value when you are modifying the line feature in the future.
Not every command and tool in ArcMap updates the COGO attributes of a line feature. The Traverse window, 2-Point Line window, Cul-de-sac command, and Proportion command are examples of those that do update. For a complete list, see About COGO descriptions. To get this behavior, you need a line feature class with the appropriate COGO attributes. You can use the Create COGO fields command in ArcCatalog to do this.
How is COGO different from other ESRI COGO capabilities?
The COGO functionality provided when editing in ArcMap with the COGO toolbar allows you to create and maintain your land parcels and other surveyed features in a geodatabase. There is other ESRI functionality that provides similar capabilities, such as the Survey Analyst extension to ArcGIS and the COGO extension to ArcInfo Workstation.
ArcGIS Survey Analyst and Cadastral Editor
ArcGIS Survey Analyst is an extension to ArcGIS that allows you to capture and maintain survey information collected from field notes, data collectors, and record information submitted by surveyors to public authorities. You can use this survey information to incrementally improve the accuracy of GIS feature geometry in the geodatabase. See the Survey Analyst documentation for more information.
Survey Analyst is comprised of a Survey Editor and Cadastral Editor. The Cadastral Editor provides a new cadastral fabric dataset, job tracking, and workflow functionality for maintaining a land records database.
How does this differ from COGO?
- Availability of functionality—COGO in ArcGIS is available with an ArcEditor or ArcInfo license. Similar to the COGO extension for ArcInfo Workstation, Survey Analyst requires an extension license. The Survey Analyst extension works with ArcView, ArcEditor, and ArcInfo.
- Maintaining your features over time—When you create line and polygon features with COGO functionality in ArcGIS, you cannot go back and change the measurements and re-adjust the features. For example, if you use the Traverse window to create a parcel boundary and realize later you made an error, you must delete the parcel boundaries and create them again. Using the Cadastral Editor, the parcel record information is stored in the cadastral fabric so you can reapply the measurements and adjust the fabric.
- Adjustment of the parcels—With COGO, as new parcels are added, you need to decide how those new parcels integrate into the existing parcel layers. You may need to delete some lines or modify or re-create others. Cadastral Editor uses a least squares adjustment that defines a best fit for your new parcels. As you add new parcels, they are seamlessly integrated into the cadastral fabric. Old record information is not deleted, it is kept as a historical record and can continue to contribute to the coordinate accuracy of the fabric.
- Tracking history of parcels—The geodatabase allows you to archive data so you can model your parcel data over time. This works for the parcels created with COGO. The Cadastral Editor provides additional functionality to geodatabase archiving where you can store incremental changes to the parcels in a cadastral fabric.
COGO extension for ArcInfo Workstation
The COGO extension for ArcInfo Workstation provides functionality for capturing and maintaining land records data in a coverage. How does this differ from COGO in ArcGIS?
- Availability of functionality—COGO is available with an ArcEditor or ArcInfo license. The COGO extension for ArcInfo Workstation requires an additional extension license.
- Similar functionality—COGO in ArcGIS provides similar functionality to the COGO extension for ArcInfo Workstation. Refer to Common COGO workflows to understand what capabilities are available.
- No COGO point feature class—COGO in ArcGIS doesn't have an explicit COGO point feature class
- Support for spiral curves—Creating and modifying spirals is not supported in ArcGIS.
- Stationing is not supported in ArcGIS.