Types of GIS map applications |
|
|
Release 9.3
Last modified August 13, 2008 |



|
Many types of map applications can be used with ArcGIS
The full range of GIS map application types can be built and deployed using ArcGIS. Each type of ArcGIS map (or other) application is suitable for certain user audiences and supports selected work flows and user scenarios. GIS professionals design and create map documents for use in these systems and then deploy these map layers within a suitable application framework to support each map type.
In this context, end users identify with the particular GIS map application that they use for conducting their work.
"I use ArcGIS Explorer."
"I use the City Web GIS application."
While it may be important for you to identify, design, and implement the larger aspects of these GIS applications, it is not essential for your end users to know much more than what application they use for their work. They do not need to know about the larger, more complete system (e.g., the data, the maps, the tools, the Web services, etc.). They do not have to know about all the map application choices you have to choose from to build their solution. They can focus solely on using the chosen GIS map application to help them do their work.
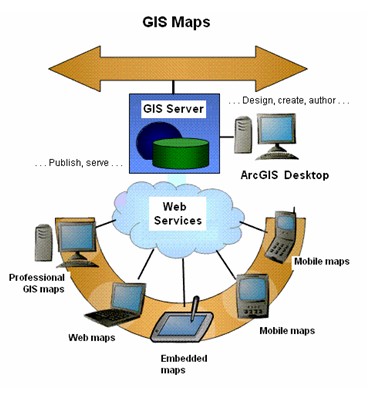
In ArcGIS, the vast majority of GIS maps are designed, created, and saved as a series of ArcMap documents or ArcGlobe documents, which can then be published using ArcGIS Server and accessed as an element of the appropriate GIS mapping application.
It's important to choose a GIS map application suitable for use by your intended audience. The right choice can depend on many factors -- for example:
- Requirements for and the size of the map display window
- The end user's knowledge about GIS
- Intended tasks to be performed
- Administration and application delivery requirements
- Costs to deploy the application
Here's a quick rundown of some common ArcGIS application choices.
Professional GIS maps
ArcGIS Desktop users (i.e., users of ArcView, ArcEditor, ArcInfo, and often custom ArcGIS Engine applications) employ a rich set of mapping applications such as ArcMap to perform their daily work.
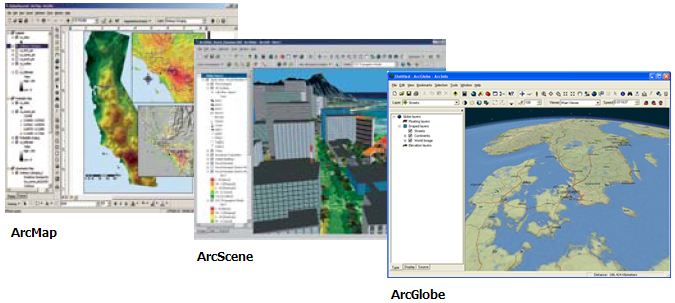
ArcGIS Desktop provides a rich set of professional GIS applications for map authoring and map use, 3D scene and globe authoring and use, data compilation, analysis and geoprocessing, and publishing of GIS information products for use by others in your organization.
| Usage notes | ArcMap is the primary application in a professional GIS desktop.
ArcGIS Desktop is used by GIS analysts to perform a broad range of GIS tasks - map authoring, editing and data compilation, GIS-centric workflow automation, and the analysis and visualization of results ArcGIS Desktop is the authoring environment used to create GIS maps and tools for use across all of the other mapping applications. |
| Who uses this application type? |
|
| Typical tasks |
|
JavaScript(TM) applications and Web mashups with Google Maps(TM) and and Microsoft Virtual Earth(TM)
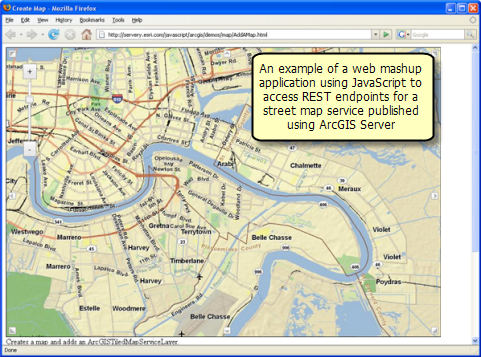
Using ArcGIS Server, you can develop and deploy custom JavaScript™ applications powered by back end REST services hosted on by ArcGIS Server. You can mashup your ArcGIS services with other web services plus content from ArcGIS Server content, ArcGIS Online, Google Maps™, and Microsoft Virtual Earth™.
The Web application JavaScript option is useful for combining information from a range of GIS servers.
-
ArcGIS JavaScript™ API. Using the ArcGIS JavaScript API, you can embed maps and tasks from any ArcGIS Server into your own custom Web page.
-
ArcGIS JavaScript Extension for the Google Maps API. You can combine your organization's GIS content hosted in ArcGIS Server on top of Google Maps using JavaScript.
-
ArcGIS JavaScript Extension for the Virtual Earth API. Using JavaScript, you can combine your organization's GIS content hosted in ArcGIS Server with content on top of the Microsoft Virtual Earth™ base maps that support both 2D and 3D visualization. Here are some example mash ups in 2D and 3D that integrate GIS data into Virtual Earth™.
In addition to GIS mapping, you can use JavaScript to add your own custom GIS tools and buttons for access to more advanced GIS functions from ArcGIS Server. In the example below, some simple editing tools have been added to digitized points, lines, and polygons into the base map.
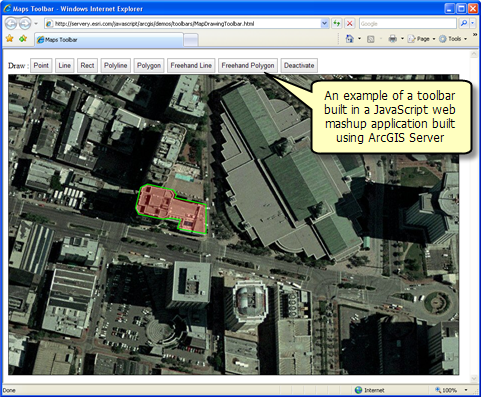
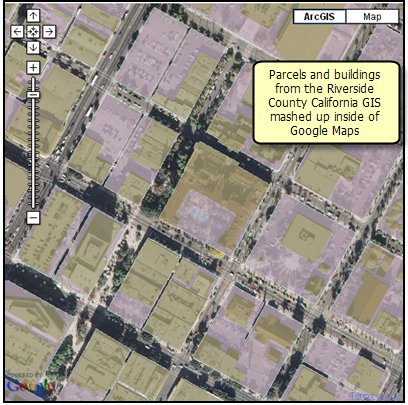
Image courtesy of Google Maps(TM)
ArcGIS geoprocessing services can be accessed from Google Maps™. For example, here is a drive-time calculation accessed and performed from Google Maps™. This enables you to add task-based GIS services into the Google Maps™ framework.
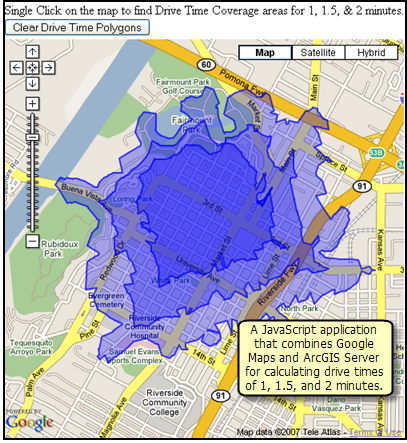
Image courtesy of Google Maps(TM)
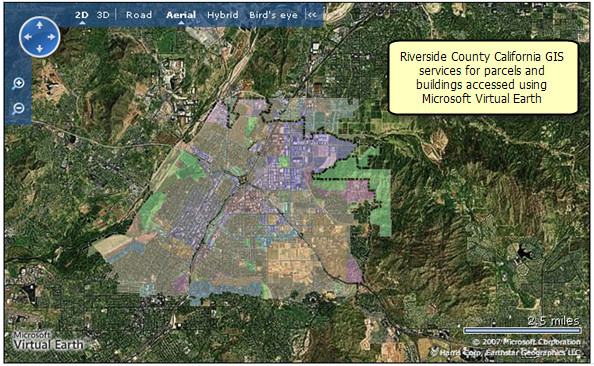
Image courtesy of Microsoft Virtual Earth(TM)
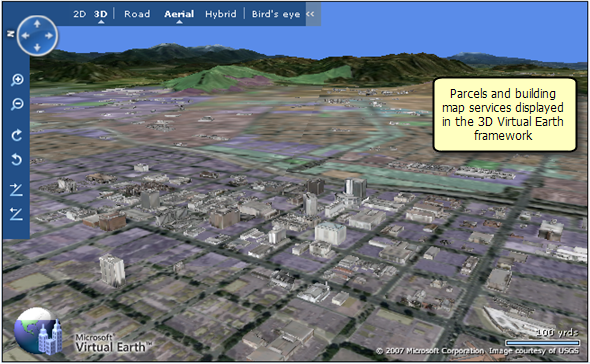
Image courtesy of Microsoft Virtual Earth(TM)
| Usage notes | Users access the Web mashup application through their Web browsers.
Mashup applications can support a few simple GIS tasks that are accessed and executed on GIS servers. The base map for your mashup application is very often provided by a server from Google Maps™, Microsoft Virtual Earth™, or ESRI ArcGIS Online. These Web applications are frequently used for information delivery to a broad range of users. No special development environment needs to be installed for building and using JavaScript applications. The Web applications are easy to manage and deploy within an ArcGIS Server system. |
| Who uses this application type? |
|
| Typical tasks |
|
For more information on building Web mashup applications to access ArcGIS Server content, see Building geospatial mashups and JavaScript applications.
The Web Mapping Application included with ArcGIS Server
ArcGIS Server includes a browser-based Web Mapping Application that can be readily deployed using ArcGIS Server. The Web Mapping Application is used to build advanced applications with high-end GIS capabilities. The ArcGIS Web Mapping Application runs inside of most Web browsers and can be customized using either the .NET or Java versions of the Web Application Development Framework (Web ADF).
Here are some example uses of the Web Mapping Application that are included with ArcGIS Server.
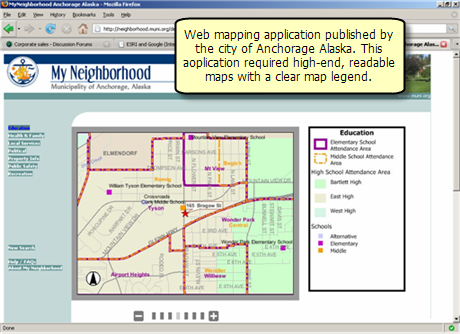
Image courtesy of My Neighborhood, Municipality of Anchorage, Alaska
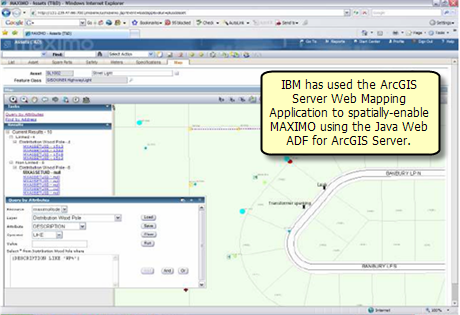
Image courtesy of IBM
Many ArcGIS Server users build custom applications or extend the out-of-the-box Web mapping application using the Web ADF. Developer kits are included for both .NET and Java developers.
-
.NET Web Application Development Framework (ADF). The .NET Web ADF is an AJAX-enabled framework for building Web applications built on ASP .Net AJAX. It includes both server side and client side controls and libraries.
-
Java Web Application Development Framework (ADF). The Java Web ADF is an AJAX-enabled framework for building Web applications built on JSF and JEE. It includes server-side controls with client side behavior in JavaScript and libraries that you can use in various Java application development frameworks systems such as Eclipse.
| Usage notes | Users access the Web mapping application through their Web browsers.
This is a very useful for information delivery to a broad range of users. The Web mapping application runs as part of the Web server tier in your Web environment It can support a series of focused GIS tasks that are accessed and executed on the ArcGIS server. The Web mapping application also supports more involved editing and analytical tasks via direct connections to geodatabases and application servers. It is easy to add advanced customization to the Web mapping application using the ADF via either .NET or Java. The Web Mapping Application is easy to deploy within an ArcGIS Server system |
| Who uses this application type? |
|
| Typical tasks |
|
For more information, see Building Web applications with ArcGIS Server using the Web ADF.
GIS explorer applications
Hundreds of thousands of users are beginning to use Google Earth™ and Microsoft Virtual Earth™ for accessing Web maps in 2D and 3D. Many are also accessing GIS content to add as map layers in these geospatial explorer applications.
ArcGIS users can publish content into any or all of these applications (e.g., using KML). In addition, many users want a GIS explorer that integrates more closely with their GIS base map content and their advanced analytical functions.
ArcGIS Explorer is one of these GIS explorer client applications. It is ESRI's free GeoExplorer for use on the Web. In addition to accessing imagery, transportation, and places of interest, ArcGIS Explorer can be used to access a multitude of 3D digital base maps and analytical tasks published by the ArcGIS Server community. Using ArcGIS Server, you can author and serve GIS explorer maps in 2D and 3D as well as to publish advanced analytical models and tasks that can be accessed using ArcGIS Explorer.
ArcGIS Explorer is a free application from ESRI that you can sahre with any of your users.
GIS explorer applications utilize maps that are placed onto the globe and that can be tilted up to create a 3D view of the information. They enable 3D GIS mapping and interaction and can integrate many information sets. Geospatial explorers typically rely on globe- and map-based Web services for GIS exploration.
Who uses GIS explorers?
- Google Earth™ and Microsoft Virtual Earth™ users
- ArcGIS Explorer users
- Decision makers and executives
- Professional workers with computers on their desks
- Specialists with GIS-based tasks
- Citizens
- Casual GIS users
- Users who want to use a free GIS explorer on their computers
Some common tasks performed with GIS explorers
- Map navigation and visualization of integrated map layers (e.g., via KML).
- Invoking focused tasks that are hosted and executed on a server (e.g., address geocoding, routing and transportation modeling, accessing GIS modeling and analysis operations on a server, users who need to visualize, and understand their results, etc.)
- Map interaction to provide a common operational picture to many users
- Simple edit tasks (e.g., making attribute updates, adding map notes, etc.)
| Supported Web map explorers | Usage notes | Links to more information |
|
Google Earth™
|
|
See KML support in ArcGIS
|
| Microsoft Virtual Earth™ |
|
See Using the ArcGIS JavaScript Extension for the Virtual Earth API |
| ArcGIS Explorer |
|
See the ArcGIS Explorer Resource Center
|
Mobile GIS applications
ArcGIS Server includes tools for building mobile applications for accessing ArcGIS Server in the field. These capabilities are known as ArcGIS Mobile, and include an out-of-the-box ArcGIS Mobile application as well as a Mobile Developer's Kit for building custom mobile applications in the Windows Mobile development environment.

With ArcGIS Mobile applications, you can use mobile devices to:
- View and navigate maps and features
- Collect and update GIS features
- Synchronize the contents in a mobile application with the GIS server (e.g., receive map updates from the server, send observations and edits to the server directly from the field).
- Perform field inspection and mobile data collection
A range of mobile devices is supported -- such as those that support Windows Mobile and Windows Vista.
| Usage notes | Supports field maps that run on Pocket PC's, Smart phones, and Tablet PC's.
Frequently enabled with GPS, which can be used to find locations and features on the map, for map navigation, and for data entry in the field. The use of GPS-based field data collection and inspection is increasing and becoming more widely deployed to non-GIS users. This solution can be used to address this community. Useful for using maps in the field. Maps can be periodically synchronized with a host server via a wireless or a wired connection. ArcGIS Mobile enables users to build custom applications in which GIS is an integral part of the work, but not the central field task. This supports the creation of applications that help the mobile worker's perform his or her job and workflow. |
| Who uses this application type? |
|
| Typical tasks |
|
See An overview of ArcGIS Mobile for more information.
OGC applications
ArcGIS includes support for a range of OGC standards and specifications including:
- The OGC and ISO simple features specification
- GML
- WMS, including SLD support
- WFS, including WFS-T support
- WCS
- CSW
This enables ArcGIS to openly publish content to many external applications such as OGC-centric applications like Gaia. ArcGIS Server can also be used to access and consume OGC Web services within the ArcGIS system for generating map displays, performing data updates, and GIS database management.
For more information on OGC support, see An overview of OGC and ISO support.
Custom ArcGIS Engine applications
What is ArcGIS Engine?
ArcGIS Engine is a core set of cross platform ArcObjects components compatible with multiple API's such as .NET, Java, Visual Basic 6, and C++. Developers can use these embeddable components to build custom GIS mapping applications.
ArcGIS Engine applications can be built and deployed on Microsoft Windows, Sun Solaris, and Linux platforms. Typical applications vary from simple map viewers to custom GIS editing programs.
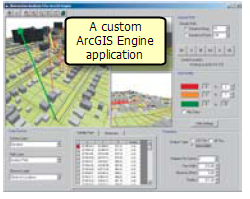
In addition to the ArcObjects software libraries, ArcGIS Engine used for building custom applications for ArcGIS users. The vast majority of these are custom map applications that are built to operate in the Microsoft Windows environment.
The developer's kit for ArcGIS Engine includes a number of user interface controls and tools that can be embedded in applications and forms for custom applications.
These are examples of controls that you can drag and drop into your custom applications. Once you create an ArcMap mxd or an ArcGobe 3dd document (3dd), you can simply drop them into your custom application and write custom code to perform specialized tasks.
| Usage notes | Using ArcGIS Engine, you can programmatically embed a map interface with focused tools into another application or build a custom application.
ArcGIS Engine is primarily employed for focused uses -- for example, create a laptop PC map with focused editing tasks. Map controls and software objects are used by programmers to build custom applications. |
| Who uses this application type? |
|
| Typical tasks |
|
For more information about using ArcGIS Engine to build and deploy custom applications, visit the ArcGIS Engine resource center.