The FME Workbench interface supports batch execution and batch script creation. For example, you can apply an existing workspace transformation to a large number of input files, and produce separate outputs for each.
Open your existing workspace and select Batch Deploy from the File menu. The Create Batch Translation Wizard appears.
Note: If the File>Batch Deploy option is disabled, it is because there is no source or destination dataset in the workspace.
Select the source type from the drop-down list.
Choose the dataset to use for the batch translation.
If you have specified more than one output destination, this pane will appear for each destination.
Batch deploy this writer
Check this box, and enter or browse to the destination location.
Retain Source Dataset Basename in Destination Path
The output dataset name is always taken from the source name, for example: roads.dgn becomes roads.gml. However, this doesn't always make sense when using folder-based datasets. For example:
C:\myData\ShapeFiles\roads.shp
converted to MIF/MID and pointed to a MIFFiles folder would become
C:\myData\MIFFiles\ShapeFiles\roads.mif
This is because the "ShapeFiles" portion is treated by FME as the name of the source dataset, and is therefore included in the output. Because of this, you have an option to drop the source dataset name from the output.
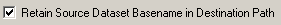
The Retain Source Dataset Basename in Destination Path box is checked by default to ensure backwards compatibility. To drop the source dataset name, uncheck this box. If you uncheck the box, and reference the above example, the destination would now be:
C:\myData\MIFFiles\roads.mif
Note that before using this option, you should be aware of the difference between file- and folder-based datasets.
You can also Type the optional suffix to append to your destination dataset (for example, a file-type suffix).
Select when you want to run the batch translation:
Run Now: Execute the batch translation immediately, from within Workbench.
Save scripts to run outside of Workbench: Type or browse for the location of the batch translation file. Note that batch files consist of both a .tcl file and a .bat file. Both files are needed to run the batch translation. To run the scripts outside of Workbench, go to the Windows DOS prompt and:
type the name of the .bat file, or
type fme tclfilename.tcl
Click the Finish button to run the batch translation.