Image services properties can be used to request an image from the server. The properties do not change the image on the server, they do control how it is sent from the server.
To set image service properties
- Right click on the image service layer in the contents window and click Properties.
- Adjust the properties as desired and click OK.
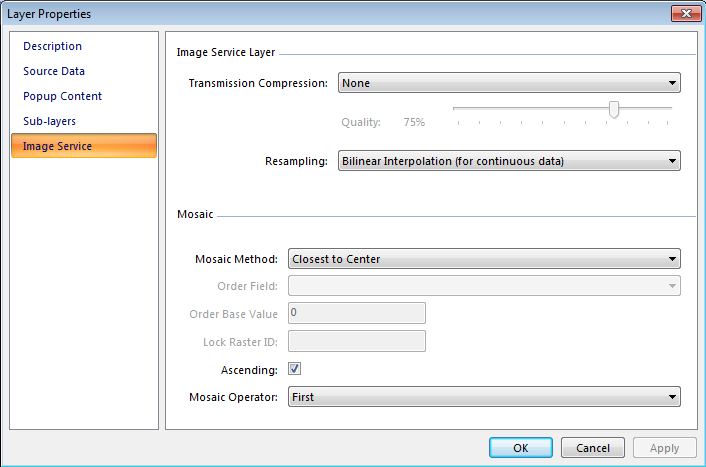
Transmission Compression A drop-down menu and text box to specify the compression applied to transmitted data. This transmission compression can be preset in the source to an image service, but you can always change this. A highly compressed image is transmitted faster than an uncompressed image; however, the image quality may not be as good.
- None - No compression is applied to the imagery, which provides the highest quality but results in the maximum volume of data transfer across the network.
- LZ77 - An efficient lossless compression method that is primarily for imagery with similar cells, such as scanned maps or results of classifications.
- JPEG - An efficient compression method that can often compress imagery by about three to eight times with little degradation of the image quality. When choosing the JPEG method, you can also edit the quality by typing a value from 0 to 100.
Resampling A drop-down menu that allows you to choose which resampling method will be used on the imagery that is displayed. The options include nearest neighbor, bilinear interpolation, cubic convolution, and majority.
Resampling your raster dataset alters the way in which the raster dataset is displayed. Resampling is the process of extrapolating new cell values while transforming your raster dataset when it undergoes a geoprocessing function or when it changes coordinate space.
The four resampling techniques are nearest neighbor, bilinear interpolation, cubic convolution, and majority.
For discrete raster datasets, such as those found in classified imagery including land-use maps or soil maps, the nearest neighbor and majority resampling algorithms are most appropriate. Nearest neighbor assigns the closest cell value to the pixel. Majority assigns the most popular value within the filter window, giving a smoother look.
For continuous raster datasets, such as a satellite image, an elevation model, or aerial photos, bilinear interpolation or cubic convolution are more appropriate. Bilinear interpolation creates a smooth-looking result. Cubic convolution creates a sharper-looking result but takes more processing time.
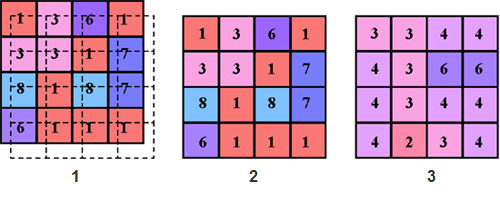
The diagram below shows an example of display resampling. Image 1 shows the original raster and the new position of the raster (outline of the raster). Image 2 shows how the nearest neighbor resampling technique would resample the data. Image 3 shows how bilinear interpolation would resample the raster.
The mosaicked image displayed from a mosaic dataset can be created from a number of input rasters. The mosaic method defines how the mosaicked image display is created from these rasters. For example, when using the By Attribute method, the values in an attribute field are used to sort the images, and when using Closest to Center, the image closest to the center of the display is positioned as the top image in the mosaic. Additionally, the mosaic operator allows you to define how to resolve the overlapping cells, such as choosing a blending operation.
The mosaic methods are defined as part of the mosaic dataset properties, but all may not be available. The mosaic methods include the following:
- Closest to Center—Enables rasters to be sorted based on a default order where rasters that have their centers closest to the view center are placed on top.
- Closest to Nadir—Enables rasters to be sorted by the distance between the nadir position and view center. This is similar to the Closest to Center method but uses the nadir point to a raster, which may be different than the center, especially for oblique imagery.
- Closest to Viewpoint—Orders rasters based on a user-defined location and nadir location for the rasters using the Viewpoint tool.
- By Attribute—Enables raster ordering based on a defined metadata attribute and its difference from a base value.
- North-West—Enables raster ordering in a view-independent way, where rasters with their centers to the northwest are displayed on top.
- Seamline—Cuts the raster using the predefined seamline shape for each raster using optional feathering along the seams.
- Lock Raster—Enables a user to lock the display of a single or multiple rasters based on an ID or name.
When using a date field with the By Attribute mosaic method, the base value must be entered using one of the following:
- yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss.s
- yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss
- yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm
- yyyy/MM/dd HH
- yyyy/MM/dd
- yyyy/MM
- yyyy
The mosaic operators include the following:
- First—The overlapping areas will contain the cells from the first raster dataset listed in the source.
- Last—The overlapping areas will contain the cells from the last raster dataset listed in the source.
- Min—The overlapping areas will contain the minimum cell values from all the overlapping cells.
- Max—The overlapping areas will contain the maximum cell values from all the overlapping cells.
- Mean—The overlapping areas will contain the mean cell values from all the overlapping cells.
- Blend—The overlapping areas will be a blend of the cell values that overlap; this blend value relies on an algorithm that is weight based and dependent on the distance from the cells to the edge within the overlapping area.
Generally, the mosaicked image is created using the following process:
- A spatial query defines the potential images.
- The current scale is compared with the minimum and maximum pixel values of the potential images.
- The qualified images are selected and sorted according to the mosaic method (the sorting order can be ascending or descending).
- The overlap area is resolved by the mosaic operator.
When the Lock Raster mosaic method is specified, the first two steps above are not used.
- Click the Mosaic Method drop-down arrow and choose a method.
- If you choose By Attribute, you can specify a field and base value.
- If you choose Lock Raster, you can specify a raster ID value to which the mosaic dataset will be locked.
- Optionally, uncheck Sort Ascending.
This reverses the ordering method.
- Optionally, click the Mosaic Operator drop-down arrow and choose a different operator for calculating overlapping cell values.
 Feedback
Feedback
 E-mail this topic
E-mail this topic
 Print this topic
Print this topic
 Feedback
Feedback
 E-mail this topic
E-mail this topic
 Print this topic
Print this topic

