Common topology tasks
Common topology tasks
|
| Release 9.3 |
   |
Note: This topic was updated for 9.3.1.
A number of modifications can be made to a topology. In some cases, such as when renaming a topology, the change has no effect on the state of the topology. However, in other cases, the change may require that the topology be revalidated. For example, changes such as adding new feature classes or rules or changing the cluster tolerance may create new dirty areas and error features and necessitate that the topology be revalidated.
Adding a new feature class to a topology
Using ArcCatalog
Here are the steps to add a new feature class to an existing topology using ArcCatalog.
- In ArcCatalog, right-click the topology and click Properties.
- Click the Feature Classes tab.
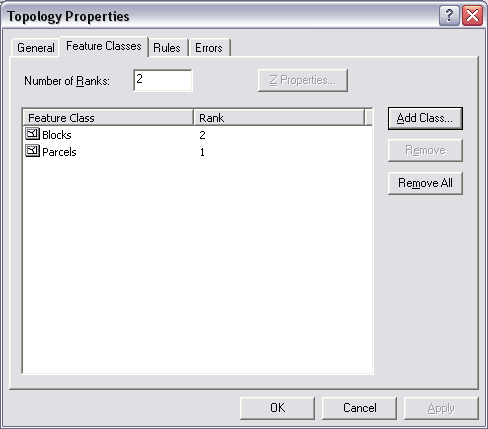
- Click Add Class.
- Click the feature class that you want to add to the topology and click OK.
Only feature classes that are within the feature dataset and that are not currently participating in a topology or geometric network can be added.
- Set the coordinate rank for the added feature class.
- Add any additional rules on the rules tab.
- Click OK, and the new feature class and rules will be added to the topology.
Changing the topology schema means the whole topology will be flagged as dirty.
- The final step is to validate the changed topology.
Using geoprocessing
You can also use geoprocessing topology tools to add feature classes and rules to an existing topology. Two commands are available in the Topology toolset in the Data Management toolbox:
- Add Feature Class To Topology
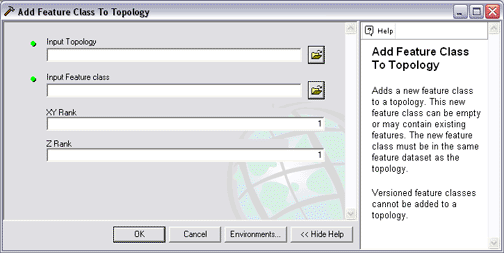
- Add Rules To Topology
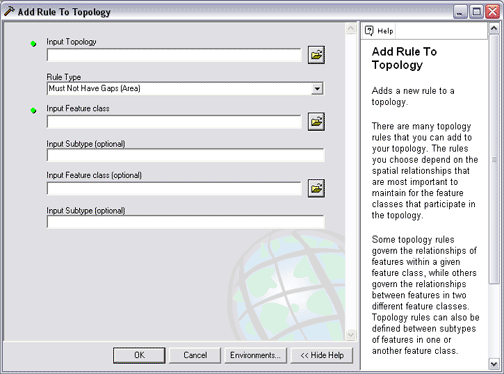
NOTE: Changing the topology schema means the whole topology will be flagged as dirty. The final step is to validate the changed topology.
A number of modifications can be made to a topology. In some cases, such as when renaming a topology, the change has no effect on the state of the topology. However in other cases, the change may require that the topology be revalidated. For example, changes such as adding new feature classes or rules or changing the cluster tolerance may create new dirty areas and error features, and the topology must be revalidated.
Creating new polygons from lines
Sometimes, you need to create polygon features from line feature data. For example, you might have a digitized set of boundary features (spaghetti) that you want to convert to polygons. Or, you may have only been able to obtain line features from a data provider.
In ArcCatalog
- In ArcCatalog, right-click the dataset, point to New, and click Polygon Feature Class From Lines.
- Type a name for the new polygon feature class.
- Optionally, change the .
- Check the feature classes that you want to be considered when finding closed areas.
If you check more than one feature class, then areas that are enclosed by lines from any of the feature classes will become polygon features.
If you check a polygon feature class, the boundaries of the polygons will be considered the same as lines.
- Optionally, select a point feature class that will be used to assign attributes to the new polygons.
Polygons that enclose a point will be given the attributes of the point.
- Click OK. The new feature class is created in the feature dataset.
Using geoprocessing
The
Feature To Polygon tool generates new polygon features from input line and polygon features. You can specify a point feature class that will supply attributes for the new polygon features.
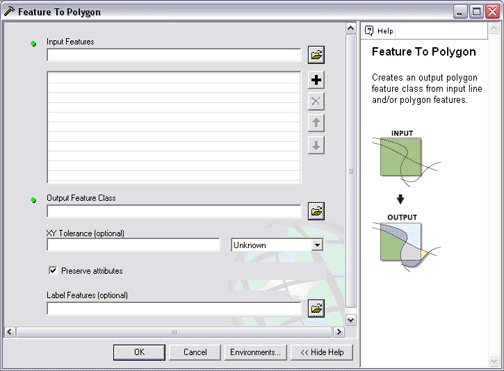
The Feature To Polygon tool is found in the Data Management Tools toolbox.
Using subtypes in a topology
When you design a geodatabase, you should be aware of the options for using feature class subtypes in your topology.
About subtypes
Subtypes allow you to model real-world objects more effectively by building subclasses of the features within a feature class. For example, in a parcel feature class, you might have subclasses of normal parcels (which cannot overlap) and condo parcels (which are allowed to overlap). Further, the default value for zoning might be different for each parcel subtype (for example, Single Family residential versus Multifamily residential).
To learn more about subtypes and the geodatabase, see
Subtypes.
Subtypes within a topology
Subtypes in topologies can have different rules applied to each subtype and can have different coordinate ranks as well. This allows you to create rules that apply only to specific subtypes, for example, structures built before the subdivision was created.
For example, consider building footprints; you could model a situation where a small percentage of buildings legitimately cross parcel boundaries by creating subtypes of buildings and only creating the Must Be Covered By rule for the subtypes that cannot extend across a parcel.
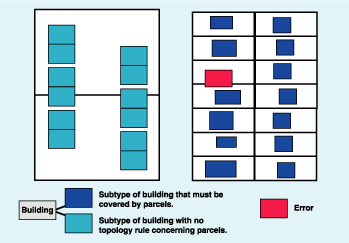
You could also apply different coordinate ranks to each subtype. For example, parcels whose boundaries were entered using COGO tools might have a higher coordinate rank than other parcels in a different subtype that were entered using digitizing.
In ArcCatalog
- Click the Feature Classes tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click the feature class you want to remove.
- Click Remove.
NOTE: Removing a feature class also removes all the topology rules associated with that feature class.
NOTE: Removing a feature class will require the topology to be validated again.
Viewing topology properties
- Right-click the topology and click Properties.
In ArcCatalog
- Click the General tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click in the Name text box and type a new name.
- Click OK.
NOTE: Renaming a topology does not affect its state, and the topology need not be revalidated.
Changing the cluster tolerance
In ArcCatalog
- Click the General tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click in the Cluster Tolerance text box and type a new value.
- Click OK.
NOTE: Changing the cluster tolerance of a topology will require the topology to be revalidated. The larger the cluster tolerance, the greater the likelihood that features in your data will be moved from their current positions. If the cluster tolerance is too large, the shapes will change.
Changing coordinate ranks
There are a number of ways to change rank settings in a topology that are described here.
Changing the number of ranks
- Click the Feature Classes tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click the Number of Ranks text box and type a number of ranks.
A topology can support up to 50 ranks to which feature classes may be assigned.
NOTE: Changing the number or ranks alone will not require the topology to be revalidated.
Changing the rank of a feature class
- Click the Feature Classes tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click and change the current rank of the feature class.
NOTE: Changing the rank of any feature class requires the topology to be revalidated.
Querying and navigating a topology graph
The ArcGIS developer tools known as ArcObjects provide programmer access to the topology graph. Here are some useful example scripts that can be used to work with the topology graph in geodatabase topologies:
- Topological queries command—This custom command allows for the selection of features based on their topological relationships to other features. The command allows for queries such as "select the features that share edges with the selected features" or "select lines that don't have polygons on the left or right."
- Determine adjacent command—This custom command calculates attribute values on a line layer based on the Object IDs of polygons to the left and right. The command will calculate the same information the LPOLY and RPOLY fields in a coverage maintained. The advantage of geodatabase topology is that you could calculate this information for different sets of polygons.
- Create Shortest Path Feature Task—This custom script creates a new polyline feature that corresponds to the Shortest Path between the two input points. The sample uses the Dijkstra algorithm with a weight corresponding to the Euclidean distance between nodes of the graph. The Planar Graph used is the Topology Graph.
- Draw Adjacent sample script by Kirk Kuykendall—This sample draws lines separating polygons with the same attributes.
Working with topology rules
There are many tasks to work with rules within a topology. You can
- Add or remove rules from an existing topology.
- Save rules as a rule set file that can be shared and reused.
- View rule descriptions and diagrams.
Adding rules to a topology
- Click the Rules tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click Add Rule to add a new rule from the drop-down list.
- Optionally, you can check the Show Errors text box to view graphic examples of each rule.
- Click OK.
NOTE: After adding a new rule, you must revalidate your topology.
Removing a rule from a topology
- Click the Rules tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click the rule that you want to remove.
- Click Remove.
NOTE: Removing a rule will require the topology to be revalidated.
Saving topology rules to a Rule Set file
- Click the Rules tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click Save Rules.
- Navigate to where you want to save the rules that you've defined for the topology.
- Type a name for the rule set.
- Click Save to save all the rules for the topology to the file.
Loading topology rules from a Rule Set file
- Click the Rules tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click Load Rules.
- Navigate to the place where the rule set that you want to load is saved.
- Click the rule set.
- Click Open.
The Load Rules Feature Class Mapping dialog box appears.
If the rule set was created from a topology that had the same feature class names as the feature classes in the new topology you're defining, the feature classes named in the rule set should be correctly matched to the feature classes in the new topology.
If the names are different, you will need to match the feature classes mentioned in the rule set to their corresponding feature classes in the new topology.
- For each Source feature class that is not mapped, click in the Target column and click the feature class to which it corresponds in the new topology.
- Click OK.
- Click OK on the Topology Properties dialog box to load the rule set.
NOTE: Loading a rule set into a topology with previously specified rules will append the rules from the rule set to the existing rules.
NOTE: Loading a rule set will require the topology to be revalidated.
NOTE: If there are feature classes specified in a rule set that cannot be matched to feature classes in the new topology, rules involving the unmatched feature classes will not be loaded.
Getting the description of a topology rule
- Click the Rules tab on the Topology Properties dialog box.
- Click the rule for which you want to see a description.
- Click Description.
NOTE: You can also view the description of a topology rule for which errors have been detected using the Show Rule Description item in the Fix Topology Error context menu.
Summarizing topology errors
You can view a summary of the number of errors in a topology from the Topology Properties dialog box. The summary tells you how many errors and exceptions exist for each of the topology rules.
You can save the summary as a text file to create a record of the state of the topology at a given time. This can be a useful way to document and monitor progress on a large topology editing project.
Summarizing topology errors in ArcCatalog
- Right-click the topology in the ArcCatalog tree and click Properties to open the Topology Properties dialog box.
Click the Errors tab on the Topology Properties dialog box and click Generate Summary.
- Optionally, click Export To File if you want to save a text file of the error summary report.
Summarizing topology errors in ArcMap
ArcMap includes a number of tools to identify and correct individual topology errors.
One task you can perform is similar to ArcCatalog. You can right-click the topology layer in ArcMap and click Properties to view an error summary.
Also, once you start editing in ArcMap, you can use the Topology Editing toolbar and its Error Inspector tool to generate an error report and focus on applying fixes for each individual error.
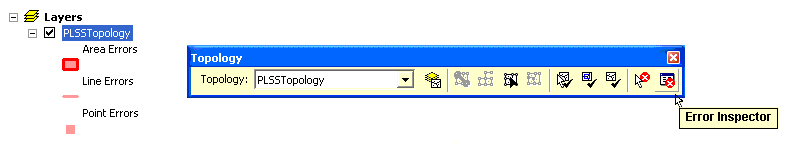
See the
Topology Error Inspector for more information.





 The Feature To Polygon tool is found in the Data Management Tools toolbox.
The Feature To Polygon tool is found in the Data Management Tools toolbox.

 See the Topology Error Inspector for more information.
See the Topology Error Inspector for more information.