Steps
- In the ArcCatalog tree, right-click the database in which you want to create a new table, point to New, and Click Table. A wizard for defining a new table will appear.
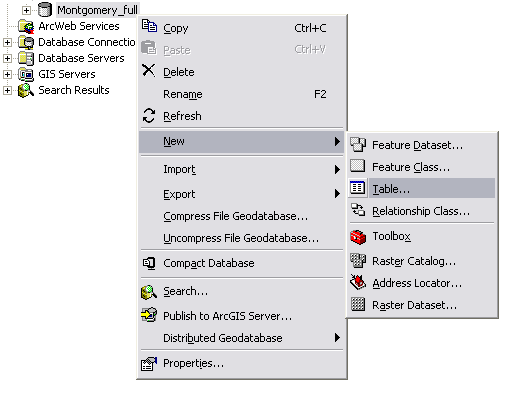
- Type a name for the table. To create an alias for this table, type the alias. Click Next.
-
NOTE: If your geodatabase is not a file or ArcSDE geodatabase, skip this step.
If you are creating a new table within a file geodatabase, you can choose an optional configuration keyword for setting up your table to manage text fields in various languages. Using the DEFAULTS keyword, in most cases, is a reasonable and intelligent choice.
NOTE: If you want to store Asian characters such as Japanese or Chinese in text fields within your table in a file geodatabase, you may want to choose the TEXT_UTF16 keyword choice for file geodatabases.
For more information, refer to Configuration keywords for file geodatabases and Configuration keywords for ArcSDE geodatabases.
- To add a field to the table, click the next blank row in the Field Name column and type a name.
- Click in the Data Type column next to the new field's name, then click its data type.
- To create an alias for this field, click the field next to Alias and type the alias for this field.
- To prevent nulls from being stored in this field, click the field next to Allow nulls, click the drop-down arrow, then click No.
- To associate a default value with this field, click the field next to Default value and type the value.
- To associate a domain with this field, click the field next to Domain, click the drop-down arrow to see a list of the domains that apply to this field type, and click the domain.
- To set other properties specific to the type of field, either click the property in the drop-down list or type the property.
- Repeat steps 8 through 14 until all the table's fields have been defined.
- Click Finish.
NOTE:
- All simple tables in the geodatabase require an ObjectID type field. The ObjectID field uniquely identifies each object stored in the table in the database.
- When creating a new table, you can use another table as a template. Click Import, navigate to the table that contains the field definitions you want to copy, then click OK. Now you can edit the field names and their data types.
- If you have entered a field that you don't want included in the new table, select it by clicking its tab in the grid, then press the Delete key.
Steps
- In ArcToolbox, you can find the Create Table tool in the toolbox named Data Management Tools. It is contained in the Tables toolset.

- Specify the name of the geodatabase in which the new table is to be created or specify the name of the output workspace (file folder) in which a new dBASE table is to be created.
- Provide the new table name and an optional table whose fields can be used as a template for the fields in the new table.
- Set a configuration keyword if necessary for managing text fields in various languages. If you are creating a new table within a file geodatabase, you can choose an optional configuration keyword for setting up your table. Using "Defaults" in most cases is a reasonable and intelligent choice.
NOTE: If you want to store Asian characters such as Japanese or Chinese in text fields within your table in a file geodatabase, you may want to choose the TEXT_UTF16 keyword choice.
For more information, refer to Configuration keywords for file geodatabases.


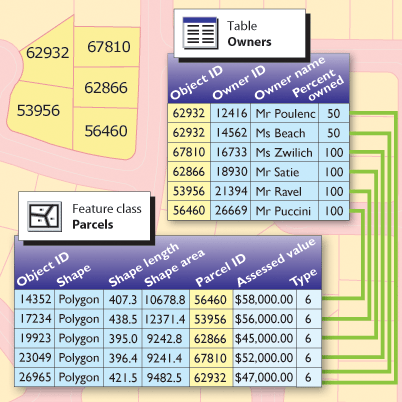 ArcGIS users work with tables in many formats and sources including
ArcGIS users work with tables in many formats and sources including

