You will define the GIS functionality in your Web
applications by selecting and configuring tasks. Tasks encapsulate
specific functionality for your application, such as querying
or editing. Manager includes the following set of tasks:
You can also use the developer libraries included with the Web
ADF to create custom tasks. See the Developer Help for more
instructions.
Some tasks require that you define supporting services in order
for them to run. For example, the Find Address task requires you to
select an existing ArcGIS Server geocoding service or an ArcIMS
service enabled for geocoding.
For each task that you add to your application, Manager
lets you customize the specific look and behavior of the task.
The following sections describe the available tasks in more
detail.
Editor task
The Editor task provides a suite of tools for Web-based editing
of features in a geodatabase. This task requires an ArcGIS Server
map service that contains at least one layer from a versioned or
non-versioned geodatabase. If the geodatabase layer/feature class
is versioned, a non-pooled ArcGIS Server map service is required.
If the geodatabase feature class is non-versioned, the Editor task
can use either a pooled or non-pooled ArcGIS Server map
service.
When you add the Editor task to an application, users can use
its various tools to edit data and save their edits. The Editor
task includes tools for creating, moving, copying, splitting,
merging, and deleting features. Additionally, you can view and edit
the locations of feature vertices. When you configure the Editor
task for your application, you can select which versions and layers
users will be able to edit. When editing, users of your application
can adjust the snapping and selection options.
You cannot use the Editor task to create multipoint features. However, you can move, copy, or delete existing multipoint features with the Editor task. You can also use the Editor task to edit the attributes of existing multipoint features.
Only one Editor task can be configured per application using the ArcGIS Web Manager. However, the Editor task can be configured to work with all the editable resources that have been added to the web application.
The Editor task configuration page contains the following items
- Task Name - The name as seen by users in the Web Mapping Application.
- Service – A list of editable services that have been added to the application. The connection to the service must be a local connection and the service should have at least one versioned or non-versioned layer from an enterprise geodatabase. If no services appear then there may not be any services that are available for editing.
- Edit Data In – A list of editable workspaces in a particular map service. A workspace is a combination of the host (ArcSDE Server name), port, database, username, and the name of the editable version. If any one of these parameters is different between the layers in the map service, they are considered to be different workspaces.
- "Add Configuration" – Click this to create a new editing configuration. Each editing configuration has three property tabs, described in the following sections.
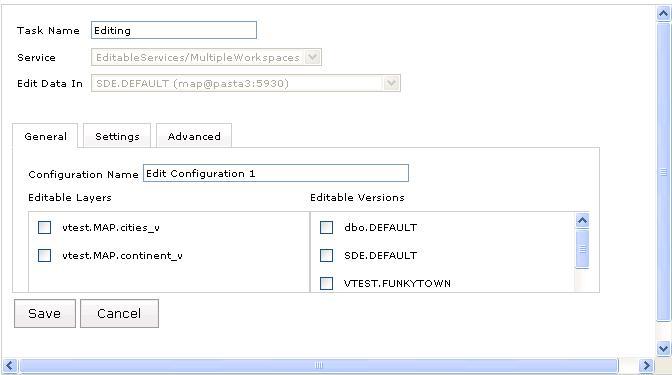
General Tab
- Configuration Name - The name that uniquely identifies the editing configuration. When you open the Editor task in the Web Mapping application, this name will be used to list the configurations available for editing.
- Editable Layers – The list of editable layers in the selected workspace.
- Editable Versions – The list of available versions if the selected workspace has versioned data.
Settings Tab
- Edits Allowed
- Add Features - New features can be added if this box is checked.
- Edit Attributes - The fields associated with a feature can be edited if this box is checked.
- Edit Features - The geometry of features can be edited if this box is checked.
- Tolerance - This tolerance value applies to selection of feature components like vertices. A value that is too small will make it hard for users to select a feature component like a vertex. A value that is too large can be confusing to users since there may be many feature components within that distance.
- Snapping Tolerance - The tolerance in pixels used to determine if a moved vertex should snap to an existing vertex, edge, or end.
- Highlight Color - The color used for features that have been selected for editing. The color is specified by three numbers between 0 and 255 that represent red, green, and blue values in that order. The default color is yellow.
- Vertices Color - the color used for newly added vertices. The color is specified by three numbers between 0 and 255 that represent red, green, and blue values in that order. The default color is red.
- Snapping Rules - When making edits, vertices can snap to either a vertex, an edge, or an end. An edge would be a line that forms a boundary for the feature. An end is a vertex that has only one edge connecting to it. The Edit Task will snap to the nearest vertex, edge, or end depending on whether these options are selected.
Advanced Tab
The Advanced tab contains auto-reconciliation options to resolve conflicts between edits made by two different users. The Editor task auto-reconciles conflicts based on two important settings:
- Are conflicts defined by object (row) or by attribute (column)? If two users edit different attributes of the same feature, is this considered a conflict? If you've chosen to define conflicts by object (row), this situation is treated as a conflict and only one of the users' edits can be applied. However, if you've chosen to define conflicts by attribute (column), both edits may be applied. In this case, a conflict would only occur if the two users edited the same attribute.
- Are conflicts resolved in favor of the database or the edit session? If someone else edits the same feature as you and saves his or her edits first, what happens when you save? If you've chosen to resolve conflicts in favor of the database, your edits will not be applied. This setting can be thought of as "First in wins". If you've chosen to resolve conflicts in favor of the edit session, your changes will overwrite the other user's edits. Resolving conflicts in favor of the edit version can be thought of as "Last in wins".
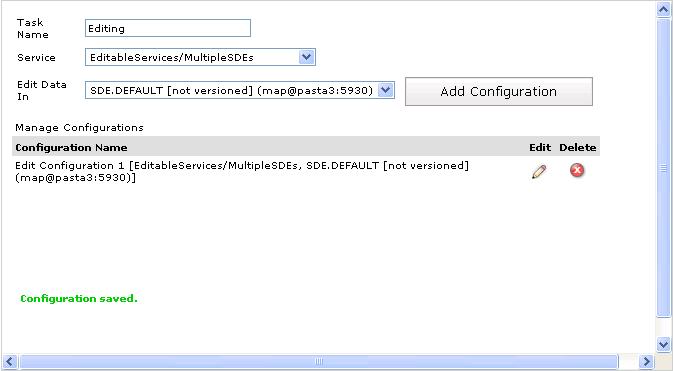
Once saved, all available editing configurations are listed as shown in the screenshot below. Click the 'Edit' icon to update an existing editing configuration or click the 'Delete' icon to remove it from the Editor task.
Find Address task
The Find Address task prompts the user for an address, then
displays the resulting address on the map. It can be configured
with an ArcGIS Server geocode service or an ArcIMS service with
geocoding enabled.
ArcGIS Services
The Find Address task is based on a Geocode Service. Once you add
a Find Address task to your Current Tasks list, you need to
specify the Gecode Service using the Supporting Services link in the right panel.
The text you see in the user interface for the Find Address task
comes from the Geocode Service's locator file. You can change this text by opening
the locator (.loc) in a text file before publishing it to the
server.
ArcIMS Services
If you are using an ArcIMS service, you must
select a supporting service that supports geocoding, then
configure the task.
- Create the Find Address task, select the task in the left panel, and then click the Services link in the right panel to specify your service. Any service that has a geocode extension is listed.
- After selecting the service, specify the task name - this is the name that users will see in the Web Mapping Application for this task.
- Specify the button text and help tip that tells users to run the task.
- Select the Find Address task, and click Add.
- Click on the results tab to configure how results will appear on the map.
- By default map tips are enabled which means geocoded address will appear on the map with an interactive display. If you wish to turn these, off uncheck the check box on the results tab.
- If you wish to use a special symbol for the results of this task, select special symbols. If no symbols are specified the defaults for the layer will be used.
- When done, click Apply.
Find Place task
The Find Place Task used ArcWeb Services to locate user-defined places. Because ArcWeb Services was deprecated earlier in 2009, it is recommended that you use the Find Address Task or the Search Attributes Task to achieve similar functionality.
ESRI has made available a geocode service on ArcGIS Online that you can use to add place finding capabilities in your Web applications. The locator references a geodatabase of over 6 million places worldwide. You can connect to this service in Manager and use it as a supporting service to the Find Address Task. To do this, you'll need to connect to http://tasks.arcgisonline.com/arcgis/services and browse to the Locators folder > ESRI_Places_World.
Geoprocessing task
With the Geoprocessing task, you can make use of services that
run ArcGIS geoprocessing jobs on the server and send the results
back to the client application. The geoprocessing task requires an
ArcGIS Server geoprocessing service, which you specify using
the Supporting Resources tab. Geoprocessing services are based
on models and can be published from either a toolbox or a map
document containing a tool layer. See the topic "Geoprocessing
services" in the ArcGIS Server Help for more information on how to
create one.
Task configuration
To configure a Geoprocessing task for a Web application,
you can follow these general steps:
- After specifying a resource from within the 'Create a Web Application' wizard, click Next to choose the tasks for your application.
- Select 'Geoprocessing Task' in the list of available tasks and either double-click it or click the 'Add' button to add it to the list of current tasks.
- Select the 'Supporting Resources' tab.
- Here, if you haven't already, add the ArcGIS Server that is hosting your Geoprocessing toolbox. After connecting, expand the host node to see the Geoprocessing service. You can hover the mouse cursor over it to review its service type. It should read 'Service Type = GP'.
- Double-click it or select it and hit the 'Add' button to add it to the list of Selected Services. NOTE: you can chose more than one. Click Next.
- Here, you will configure the task to determine its behavior and user experience while running withing the Web application. Select the Geoprocessing Task from the pull-down.
- Specify a Task Name. This will be the label for the task in the Web application UI. There is a default name, which you can keep. Changing it is optional.
- Select the Geoprocessing service to be used in this task. This is the service that you chose as the Supporting Resource.
- Select the Geoprocessing Task. This is a tool that lives within the toolbox that your Geoprocessing service was configured with.
- You can check Show Job Messages if you wish to display the Geoprocessing messages from within the running application during the execution of the task.
- Enter the button text for the task. 'Run' will be the text by default.
- Click 'Apply'. This is not optional. You must click Apply before clicking the Next button or else your configuration will not be reflected in your application. You should see a message at the top of the page in green that confirms the success of configuring your task.
Runtime experience
An end user who opens a geoprocessing task will see a pallette
of tools that allow for specification of the model parameters. For
example, if the underlying model requires a line feature class as
input, tools will be available in the task for drawing lines.
When the user has specified all of the parameters, he or she can
then invoke the model by clicking a button on the task. As the
job runs, the end user can see any messages from the task in the
Results Control. If the geoprocessing service has an associated map
service which was added to the application at design time, the
results will also be visible on the map.
Geoprocessing services have a property that determines whether
they run synchronously or asynchronously. If the service is
configured to run asynchronously, the user has the option of
viewing the results of the task even after closing the web
application. If the task had not finished executing before the user
closed the browser, and if the user has cookies enabled, the
results will be retrieved automatically when the user next visits
the web application. Otherwise, the user can click the Save link on
the results node and save out result information to a file and use
this file to check task results in another session. The Save link
will only be available if the VirtualDirectory property of the
geoprocessing task is set. If the service is configured to run
synchronously, there will be no Save link available and the user
will have to keep the session alive to view the results until they
are available.
Query Attributes task
The Query Attributes task helps users select or view certain
data on the map, based on that data's attributes. When you
configure the Query Attributes task, you create an
easy-to-understand form that will guide the user through the
process of making the query. This way, users of your application
will not have to know the details about the dataset, nor will they
have to construct a Structured Query Language (SQL) statement, in
order to query the data.
- Under the Select Tasks tab, select Query Attributes and click Add.
- Click Next to go to the Configure Tasks page.
- On the Configure Tasks page, select the Query Attributes task from the pick list.
- In the dialog, change the title name, if desired.
- Change the tool tip message, if desired. This provides more detailed instructions when the end user puts the mouse over the text box.
- Change the label text, if desired. You can phrase the label text any way you'd like such as "Search for rivers" or "Enter the last name of a parcel owner".
- Change the Find button text, if desired. The Find button is what users click after they have added query criteria.
- Select which service you want your users to search on. Only one service is allowed per query task.
- Select which layer in the service you want your users to search on. Only one layer is allowed per query task.
- Select a field you want your users to query on.
- Select the comparison operator you want to use.
- Set a default value, if desired.
- Select which fields you want returned in the response.
- When done, click Apply.
Search Attributes task
The Search Attributes task allows a user to enter some text that
will be used to search the attributes of the layers on the map.
This kind of search is similar to the simple Web search that
sites like Yahoo and Google provide. The Results control lists the
features on the map whose attributes match the search. The user can
then select, zoom to, or pan to any of these features.
To configure the Search Attributes task, you must specify the
display settings, the search fields, and how you want the results
to appear.
- Under the Select Tasks tab, select Search Attributes and click Add.
- Click Next to go to the Configure Tasks page.
- On the Configure Tasks page, select the Search Attributes task from the pick list.
- In the dialog, change the title name, if desired.
- Change the tool tip message, if desired. This provides more detailed instructions when the end user puts the mouse over the text box.
- Change the label text, if desired. You can phrase the label text any way you'd like such as "Search for rivers" or "Enter the last name of a parcel owner".
- Change the Find button text, if desired. The Find button is what users click after they have added search criteria.
- Select which service you want your users to search on. Only one service is allowed per search task.
- Select which layer in the service you want your users to search on. Only one layer is allowed per search task. The selected layer must have one or more text or string fields. If the layer has no text fields, no values are listed in the Search Fields box.
- Select which fields you want your users to search on. You can select one or more of the fields listed.
- Select which fields you want returned in the response. This list does not need to be the same as the previous list.
- When done, click Apply.







