NOTE: Client and server release compatibility varies depending on the method of connection you use. See the "ArcSDE service" and "Direct connections" sections of this topic for details.
NOTE: Applies to geodatabases created with an ArcGIS Server Enterprise license only
The ArcSDE service, also known as an application server or a three-tiered architecture, conveys spatial data between GIS applications and a database. The database may be any of the supported database management systems (DBMSs)—Oracle, SQL Server, Informix, DB2, or PostgreSQL.
Most of the supported DBMSs allow more than one database on a server. Each database must have its own ArcSDE service, but multiple client connections can be made to the database using that ArcSDE service.
For ArcSDE service connections, the release of the client software must be the same or greater than the release of the ArcSDE geodatabase. For example, you can connect from a 9.2 ArcGIS Desktop client to a 9.1 ArcSDE geodatabase, but you cannot connect from a 9.1 ArcGIS Desktop client to a 9.2 ArcSDE geodatabase.
The only exception to this is ArcGIS Desktop 9.2 service pack 5 or later 9.2 service pack releases; they can connect with an ArcSDE service to an ArcSDE 9.3 geodatabase.
Defining properties of the ArcSDE service
- The giomgr process
This is the ArcSDE service monitor. Each ArcSDE service has one giomgr process. This process listens for user application connection requests, spawns gsrvr processes, and cleans up disconnected user processes. The giomgr will not start if a valid server license has not been installed.
- The gsrvr process
The giomgr process spawns a gsrvr process for each application connected to the ArcSDE service. The gsrvr process is dedicated to a single user/application connection. It communicates with the database on behalf of the connected application. The gsrvr process responds to the queries and edit requests the application sends to the database.
Learn how ArcIMS map services use gsrvr connections.
- The TCP/IP service name and port number
The ArcSDE service, through the giomgr process, listens for application connection requests on a dedicated Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) service name and port number. The gsrvr process, in turn, communicates with the application on the same TCP/IP service and port number. These are stored in the services.sde file; the operating system's service file; and, on Windows, in the Windows Registry.
How the ArcSDE service works
When you connect to the database with an ArcSDE service (also called an ArcSDE application server), each ArcSDE service listens for user connections on a dedicated TCP/IP service name and port number through the giomgr process. The default service name is esri_sde and the default port number is 5151.
On UNIX or Linux systems, the service name and port number can be found in the $SDEHOME/etc/services.sde file.
Learn more about the services.sde file.
On Windows systems, the ArcSDE service is created as a Windows service during the ArcSDE postinstallation setup. This ArcSDE service is set to automatically start when the server host is rebooted. Like all Windows services, the ArcSDE service is usually started and stopped from the Windows Services menu. The postinstallation wizard automatically enters the service name and port number for the default service name in the registry and both the Windows and ArcSDE services files.
What happens when a client application connects using an ArcSDE service?
The following sequence of events takes place when an ArcSDE client application connects to an ArcSDE geodatabase using an ArcSDE service:
- The giomgr process listens for connections on its TCP/IP port.
The giomgr must be in a listening state before it can process a connection request. Make sure the ArcSDE service is started and listening.
On UNIX and Linux, use sdemon –o status to determine the state of the giomgr process.
On Windows, examine the state of the ArcSDE application service from the Services menu. Open the Windows Administrative tools. Double-click the Services icon to invoke the Services menu. The ArcSDE service should have a status of STARTED under the status field.
On Windows, you can also use the sdemon –o status command from an MS-DOS command tool.
- Applications submit connection requests to the ArcSDE service.
The giomgr process responds to connection requests serially. Depending on the underlying DBMS, the giomgr process may require anywhere from 1 to 5 seconds to validate a connection request. It's possible that if many applications are trying to obtain an ArcSDE connection at the same time, some may exceed the standard TCP/IP 75-second time-out.
- The giomgr compares the application computer's clock time with its host's clock time.
If the application computer's clock time is more than MAXTIMEDIFF seconds from the server's clock time, the giomgr process does not allow the application to connect. MAXTIMEDIFF is set in the SERVER_CONFIG table. See The giomgr.defs file and the SERVER_CONFIG system table and ArcSDE initialization parameters for details.
- The giomgr compares the client application's release with the ArcSDE service's release.
If the client application's release is older than the application server's release, the connection is refused, except in the case of ArcGIS 9.2 SP5 or later 9.2 service pack clients.
In general, ArcSDE applications are downward compatible. For example, applications developed with the ArcSDE 9.2 application programming interface (API), such as ArcGIS Desktop 9.2, can connect to an ArcSDE 9.1 or lower geodatabases with an ArcSDE service.
Applications built with an earlier version of the ArcSDE API cannot connect to ArcSDE 9.2 application servers; for example, ArcGIS Desktop 9.0 cannot connect to an ArcSDE 9.2 geodatabase. Check the ESRI support site for supported ArcSDE releases.
- The giomgr process starts a gsrvr process that will serve the application.
The giomgr process must be able to spawn a gsrvr process. If the maximum number of processes determined by current operating system restrictions has been reached, this operation will fail and no gsrvr process will be created.
- The gsrvr process attaches to shared memory.
Sufficient memory must be available on the ArcSDE service's host computer; otherwise, the application connection will fail with a shared memory error. Should this happen, make more memory available to the gsrvr processes by reconfiguring either the ArcSDE service or the DBMS server to use less memory. If possible, add more physical memory to the host computer.
- The gsrvr process connects to the DBMS.
The client application must provide a valid user name, password, and database name (database name not needed for Oracle DBMSs) when it submits the connection request to the giomgr process. Invalid entries are rejected with a -9 SE_INVALID_USER error.
- The giomgr process attaches the application to the gsrvr process.
Once the giomgr process has attached the application to the gsrvr process, it resumes listening for new connections and performing other ArcSDE service management tasks. All application communication with the DBMS is conducted through the gsrvr process.
With a direct connection, also known as a two-tiered architecture, client machines are configured to communicate directly with the DBMS. Since the client gets the data directly from the database, most of the data processing takes place on the client machine. For ArcSDE geodatabases licensed with ArcGIS Server Enterprise, you still need to install the ArcSDE component to have access to certain required files. You also need to complete all the postinstallation setup steps, except for the creation of an ArcSDE service.
For most client/server combinations, your connecting client must be running the same release of the software as your ArcSDE geodatabase to use a direct connection. For instance, you cannot connect from an ArcGIS Desktop 9.0 client to an ArcSDE 9.2 geodatabase. However, beginning with ArcGIS 9.3, you can make a direct connection from an ArcGIS Desktop 9.3 client to a 9.2, 9.1, or 9.0 release ArcSDE geodatabase. To do this, you must use the ArcGIS pre 9.3 geodatabase direct connect setup provided on your ArcGIS Desktop installation media. This setup gives you the option to install direct connect drivers that will allow you to connect from an ArcGIS 9.3 client to a 9.2, 9.1, or 9.0 ArcSDE geodatabase.
It should be noted, however, that this does not apply to ArcSDE for Informix due to differences in the client SDK necessary to make direct connections, or ArcSDE for Oracle8
i, since that release of the DBMS is no longer supported by Oracle.
Additionally, beginning with ArcGIS 9.2 service pack (SP) 5, you will be able to make a direct connection from a 9.2 SP5 or later 9.2 service pack client to an ArcSDE 9.3 geodatabase. This requires the installation of ArcSDE 9.3 libraries on the client machine. These libraries are included in an installation (ArcGIS 9.3 geodatabase direct connect for 9.2 clients setup) that can be downloaded from the
ESRI support site.
What happens when a client application makes a direct connection to the DBMS in which an ArcSDE geodatabase is stored?
The following sequence of events occur when an ArcSDE client application connects directly to the DBMS:
- The DBMS server listens for local or remote connections.
Each of the DBMSs supported by ArcSDE has its own method of accepting the connections of client applications. Make sure you are entering the connection information correctly if you are using an ESRI application.
If you still cannot get connected, test the connection using the DBMS' native SQL utility.
- The client application makes sure the ArcSDE license has been installed.
If the client application queries a valid ArcGIS Server license (stored in the SERVER_CONFIG table), it acquires a connection to the database.
To learn more about direct connections, see
Properties of a direct connection to an ArcSDE geodatabase. To learn how to set up your client machines to connect to an ArcSDE geodatabase with a direct connection, see
Setting up clients for a direct connection.


 To administer ArcSDE geodatabases for SQL Server Express, you can also connect to these geodatabases by first making a connection to a database server, then connecting to the geodatabase, as shown below.
To administer ArcSDE geodatabases for SQL Server Express, you can also connect to these geodatabases by first making a connection to a database server, then connecting to the geodatabase, as shown below.
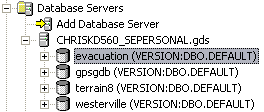 This is the action of connecting to the geodatabase. For your users to connect to the geodatabase from ArcGIS Desktop software, you must provide them with connection information. For details on the specific information you must provide to users so they can connect to an ArcSDE geodatabase from ArcCatalog, see Creating spatial database connections in the "Data management with ArcCatalog" section of the help. For information on connecting to a database server to administer geodatabases, see Adding an ArcSDE database server.
The type of connection you make—a direct connection or through an ArcSDE service—is the connection method. For geodatabases created using an ArcGIS Server Enterprise license, you may choose to use just one type of connection at your site, or you can use both. For example, you could use an ArcSDE service for your ArcGIS Desktop clients and a direct connection for your ArcIMS server.
This is the action of connecting to the geodatabase. For your users to connect to the geodatabase from ArcGIS Desktop software, you must provide them with connection information. For details on the specific information you must provide to users so they can connect to an ArcSDE geodatabase from ArcCatalog, see Creating spatial database connections in the "Data management with ArcCatalog" section of the help. For information on connecting to a database server to administer geodatabases, see Adding an ArcSDE database server.
The type of connection you make—a direct connection or through an ArcSDE service—is the connection method. For geodatabases created using an ArcGIS Server Enterprise license, you may choose to use just one type of connection at your site, or you can use both. For example, you could use an ArcSDE service for your ArcGIS Desktop clients and a direct connection for your ArcIMS server.