When creating a new domain, you specify a name that will describe the parameter it governs.
The characters ' and `, a single quote and an apostrophe, may not be used when naming a domain.
After a domain is created, when you open the properties dialog box for a feature class or table, the domain name is displayed in the domain drop-down box when choosing a domain to associate with a given field. The description is a small sentence describing the purpose of the domain.
The field type is the type of attribute field with which the domain can be associated. The field type can be set to any of the following:
- Short—Short integers
- Long—Long integers
- Float—Single-precision floating point numbers
- Double—Double-precision floating point numbers
- Text (Coded domains only)—Alphanumeric characters
- Date—Date and time data
Once the field type is set, the name of the domain will appear in the domain drop-down list for any field of that type in the properties dialog box.
Learn more about field types.
When you create a domain, you must specify which type of domain you want to use. There are two types of attribute domains:
- Range domains—A range domain specifies a valid range of values for a numeric attribute. When creating a range domain, you enter a minimum and maximum valid value. A range domain can be applied to short-integer, long-integer, float, double, and date attribute types.
For example, in a feature class for water mains, you could have subtypes for transmission, distribution, and bypass water mains. Distribution water mains can have a pressure between 50 and 75 psi. For a distribution water main object to be valid, its pressure value must be entered as some value between 50 and 75 psi.
Range domains are validated through the use of the Validate Features command.Learn more about Editing with default values and attribute domains.
- Coded domains—A coded value domain can apply to any type of attribute—text, numeric, date, and so on. Coded value domains specify a valid set of values for an attribute.
For example, water mains may be buried under different types of surfaces as signified by a GroundSurfaceType attribute field: pavement, gravel, sand, or none (for exposed water mains). The coded value domain includes both the actual value that is stored in the database (for example, 1 for pavement) and a more user-friendly description of what that value actually means.
Validation for coded value domains is accomplished by restricting the user to choose field values from a drop-down list.
Often, when editing data, a single
is split into two features or two separate features are combined, or merged, into a single feature. For example, in a land base database, a land parcel may be split into two separate land parcels due to rezoning. Similar zoning changes may require two adjacent parcels to be merged into a single parcel.
While the result of these types of edit operations on the feature's geometry is easily predictable, their effects on the attribute values are not. The behavior of an attribute's values when a feature is split is controlled by its
. When two features are merged, an attribute's value is controlled by its
.
Each attribute domain has both a split policy and a merge policy. When a feature is split or merged, the geodatabase looks to these policies to determine what values the resulting feature or features have for a particular attribute.
Split policies
An attribute for any given table, feature class, or subtype can have one of three split policies that control the value of an attribute in the output object:
- Default value—The attributes of the two resulting features take on the default value for the attribute of the given feature class or subtype.
- Duplicate—The attributes of the two resulting features take on a copy of the original object's attribute value.
- Geometry ratio—The attributes of resulting features are a ratio of the original feature's value. The ratio is based on the ratio in which the original geometry is divided. If the geometry is divided equally, each new feature's attribute gets one-half of the value of the original object's attribute. Geometry ratio policies only apply to domains for numeric field types.
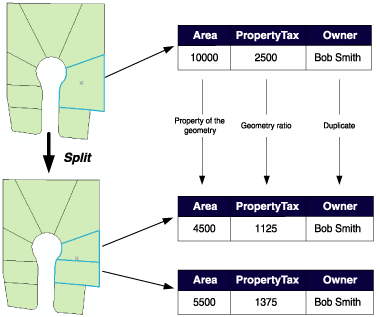
In the parcel example above, when a parcel is split, the Area attribute is automatically assigned as a property of the resulting geometry. The value for Owner is copied to the new objects (in this database, splitting a parcel does not affect its ownership). PropertyTax is calculated based on the area, or size, of a parcel. To calculate PropertyTax for each of the new objects, the split policy divides the PropertyTax of the original parcel proportionally among the new features according to their area.
Merge policies
When two features are merged into a single feature, merge policies control the value of attributes in the new feature. An attribute for any given feature class or subtype can have one of three merge policies:
- Default value—The attribute of the resulting feature takes on the default value for the attribute of the given feature class or subtype. This is the only merge policy that applies to nonnumeric fields and coded value domains.
- Sum values—The attribute of the resulting feature takes on the sum of the values from the original features' attribute.
- Geometry weighted—The attribute of the resulting feature is the weighted average of the values of the attribute from the original features. This average is based on the original feature's geometry.
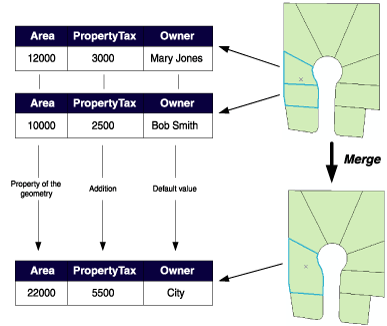
In the parcel example above, when two parcels are merged, the Area attribute is automatically assigned as a property of the resulting geometry. Owner is assigned its default value. As the PropertyTax for the merged feature is the sum of the original features' PropertyTax, its merge policy is to sum the values.
Note that merge policies are not evaluated when merging features in the Editor. However, developers can take advantage of merge policies when writing their own merge implementations.
The coded value section is only available for coded domains. It contains the coded values for a domain as well as an associated description of what that value represents.
The following graphic displays a method of using abbreviated text as coded values to represent categories of a feature. In this instance, LandUse categories are represented by suitable abbreviations:
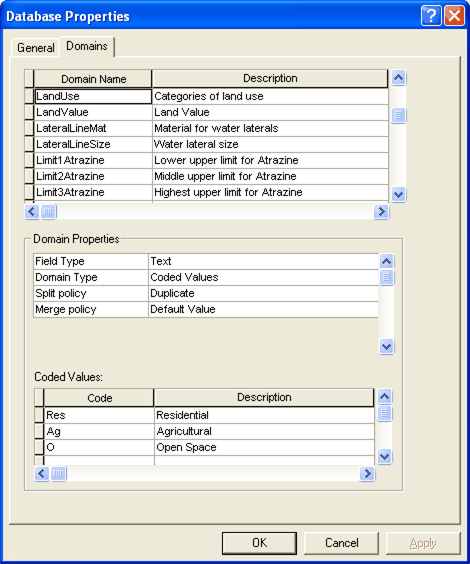
When entering coded values, the code must match the associated field type. In the above example, you could not enter an integer to represent the Residential category since the LandUse domain is associated with the Text data type.




 When entering coded values, the code must match the associated field type. In the above example, you could not enter an integer to represent the Residential category since the LandUse domain is associated with the Text data type.
When entering coded values, the code must match the associated field type. In the above example, you could not enter an integer to represent the Residential category since the LandUse domain is associated with the Text data type.