A raster is a set of cells arranged in rows and columns and is a commonly used dataset in GIS. Users typically employ many raster files, yet many users see an increasing need to manage raster data along with their other geographic information in a DBMS. The geodatabase provides a very effective means for raster data management in both file and ArcSDE geodatabases.
Raster management strategies
Two data management strategies for rasters are important:
- Raster provisioning. Getting raster datasets quickly "into play" with your GIS means you will most likely use them as is, typically as a series of raster files. This can be a series of independent files, or you can use a technology like the Image Server extension to ArcGIS Server to manage and serve these existing datasets as a collection.
- Rasters in the geodatabase. This strategy is useful when you want to manage rasters, add behavior, and control the schema; when you want to manage a well-defined set of raster datasets as part of your DBMS; when you need to get high performance without loss of content and information (no compression); and when you want one data architecture for managing all of your content.
Geographic properties of raster data
Four geographic properties are typically recorded for all raster datasets. These become useful for georeferencing and help explain how raster data files are structured. This concept is important to understand. It helps explain how rasters are stored and managed in the geodatabase.
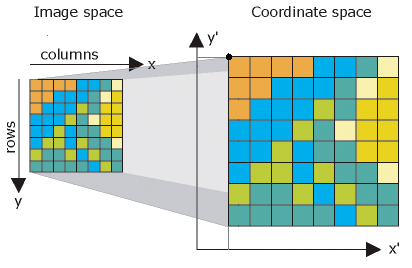
Raster datasets have a special way for defining geographic location. Once the cells or pixels can be accurately georeferenced, then it's easy to simply have an ordered list of all the cell values in a raster. This means that each raster dataset typically has a header record holding its geographic properties, and the body of the content is simply an ordered list of cell values.
Geographic properties for a raster typically include
- Its coordinate system
- A reference coordinate or x,y location (typically the upper left or the lower left corner of the raster)
- A cell size
- The count of rows and columns
This information can be used to find the location of any specific cell. By having this information available, the raster data structure simply lists all the cell values in order from the upper left cell along each row to the lower right cell as illustrated below.

The raster block table in the geodatabase
Raster data is typically much larger in size than features and requires a side table for storage. For example, a typical orthoimage can have as many as 6,700 rows by 7,600 columns (more than 50 million cell values).
To get high performance with these larger raster datasets, a geodatabase raster is cut up into smaller tiles (referred to as blocks) with a typical size of around 128 rows by 128 columns or 256 x 256. These smaller blocks are then held in a side table for each raster. Each separate tile is held in a separate row in a block table as shown below.
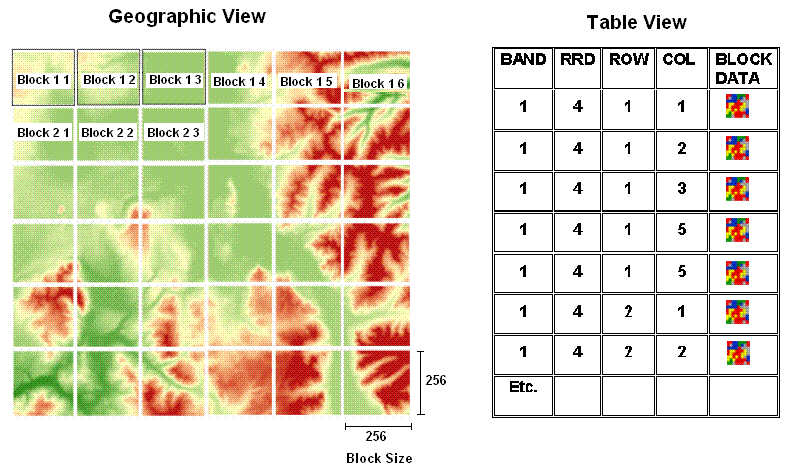
This simple structure means that only the blocks for an extent need to be fetched when they are needed instead of the entire image. In addition, resampled blocks used to build raster pyramids can be stored and managed in the same block table as additional rows.
This enables rasters of enormous sizes to be managed in a DBMS and to produce very high performance and multiuser, secure access.
Rasters are heavily and increasingly used in GIS applications. The geodatabase can manage rasters for many purposes: as individual datasets, as logical collections of datasets, and as picture attributes in tables.
A number of geodatabase capabilities enable users to extend how they manage their raster information as follows:
Working with rasters in the geodatabase| Use |
If you need to |
|---|
| Raster Datasets
|
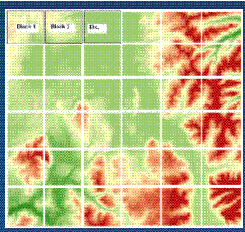
Manage very large, continuous image datasets and image mosaics.
|
| Raster Catalogs
|
Accomplish a number of purposes, including
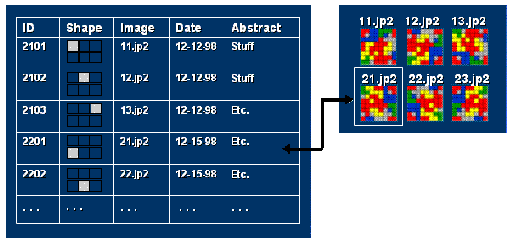
- Manage a tiled image layer, where each tile is a separate image.
- Manage any series of images in a DBMS.
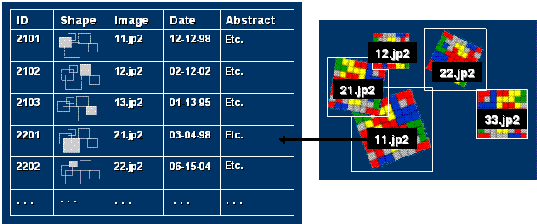
- Manage a raster time series.
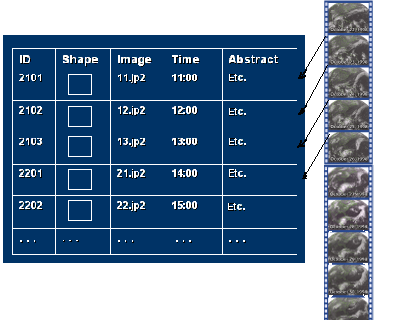
|
| Raster Attribute Columns in Tables
|
Store pictures or scanned documents as attributes in tables.
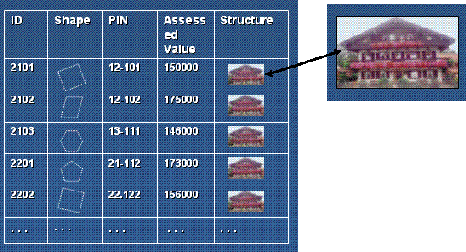
|
| Image Service Definition |
Publish image services for raster data collections in files on disk, in image catalogs, and in geodatabases.
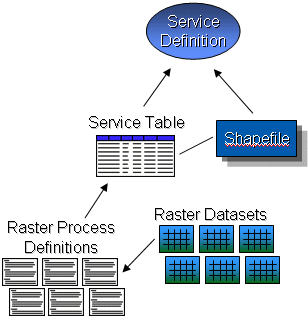
|


 Raster datasets are commonly used for representing and managing imagery, digital elevation models, and numerous other phenomena. Often rasters are used as a way to represent point, line, and polygon features. In the example below, you can see how a series of polygons would be represented as a raster dataset.
Raster datasets are commonly used for representing and managing imagery, digital elevation models, and numerous other phenomena. Often rasters are used as a way to represent point, line, and polygon features. In the example below, you can see how a series of polygons would be represented as a raster dataset.
 Rasters are interesting for at least two reasons: one, they can be used to represent all geographic information (features, images, and surfaces) and two, they have a rich set of analytic geoprocessing operators. Therefore, in addition to being a universal data type for holding imagery in GIS, rasters are also heavily used to represent features enabling all geographic objects to be used in raster-based modeling and analysis.
Rasters are interesting for at least two reasons: one, they can be used to represent all geographic information (features, images, and surfaces) and two, they have a rich set of analytic geoprocessing operators. Therefore, in addition to being a universal data type for holding imagery in GIS, rasters are also heavily used to represent features enabling all geographic objects to be used in raster-based modeling and analysis.

 This simple structure means that only the blocks for an extent need to be fetched when they are needed instead of the entire image. In addition, resampled blocks used to build raster pyramids can be stored and managed in the same block table as additional rows.
This enables rasters of enormous sizes to be managed in a DBMS and to produce very high performance and multiuser, secure access.
This simple structure means that only the blocks for an extent need to be fetched when they are needed instead of the entire image. In addition, resampled blocks used to build raster pyramids can be stored and managed in the same block table as additional rows.
This enables rasters of enormous sizes to be managed in a DBMS and to produce very high performance and multiuser, secure access.





