If you want to create more than one geodatabase in the same SQL Server instance when using the single spatial database model, you create multiple SQL Server databases, create a geodatabase in each one, authorize each geodatabase, and create separate ArcSDE services for each one (if you will be using ArcSDE services to connect to the geodatabases).
The following graphic illustrates that there are two separate databases, Database1 and Database2, on one SQL Server instance and that each database contains a complete geodatabase.
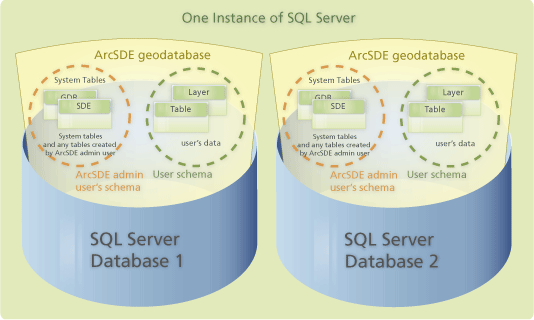
The databases can have any unique name that follows SQL Server rules for identifiers, does not start with a number, and is not sde.
You can use the ArcSDE for SQL Server Post Installation wizard to create additional databases and geodatabases. Run through all steps of the Post Installation wizard, making sure to provide a unique database name, ArcSDE service name, and ArcSDE service number. Since users are created at the instance level then added to the database in SQL Server, be sure to use the same password for the ArcSDE administrator when prompted.
If clients only use direct connections to each separate geodatabase, you do not need to create an ArcSDE service and can skip the last step of the Post Installation wizard. However, if clients will connect using an ArcSDE service, you need to create an additional service for each additional geodatabase. As mentioned, this can be done through the Post Installation wizard; just be sure to specify a different service name, port number, and the correct database name on the ArcSDE service information dialog box.
Be aware that if you plan to use different settings in the dbtune.sde, giomgr.defs, or dbinit.sde files, these changes must be made
before running the Post Installation wizard.
- To specify different geodatabase storage information for the second geodatabase, make copies of your giomgr.defs and dbtune.sde files, giving them different names. For example, you could name them giomgr2.defs and dbtune2.sde. Alter the contents of these new files. When you run the Post Installation wizard, you will specify these custom files.
- To set variables in the dbinit.sde file to connect to the second geodatabase, make a copy of your dbinit.sde file, giving it a new name. This name must include the name of the new ArcSDE service. For example, if the new service name is sdesql2, name the dbinit file dbinit_sdesql2.sde. Add the appropriate variables to the new dbinit file. When running the Post Installation wizard, specify the new dbinit file.
Client connections can be made to one geodatabase at a time. When connected to one single spatial database geodatabase on a SQL Server instance, you cannot query information from another geodatabase on the SQL Server instance through that same connection.
For instance, in ArcCatalog, you could create a spatial database connection to Database1. When you add data to ArcMap through that connection, you cannot view the data in Database2. To access the data in Database2, you would set up a second spatial database connection in ArcCatalog, this time specifying Database2 in the Database field and Database2's port number in the Service field.
For information on setting up spatial database connections in ArcCatalog, see
Creating spatial database connections in the "Data management with ArcCatalog" section of the help.For connection syntax, see
ArcSDE connection syntax.
NOTE: ArcSDE geodatabases licensed through ArcGIS Server Enterprise only
Prior to ArcSDE 9, geodatabases in SQL Server were always stored using the multiple spatial database model. For ArcSDE 9 and later releases, you should use the single spatial database model. However, since the multiple spatial database model is still supported (though not recommended), the following is a description this model.
In the multiple spatial database model, the ArcSDE repository is stored in a database called SDE. User-defined data, such as feature classes, raster, and nonspatial tables, reside in other databases. The ArcSDE repository in the SDE database stores references to the location of all the user-defined data for a particular instance of ArcSDE. The SDE database and any other related databases form
a single geodatabase. This data storage model is known as the multiple spatial database model because it takes multiple SQL Server databases to make one ArcSDE geodatabase.
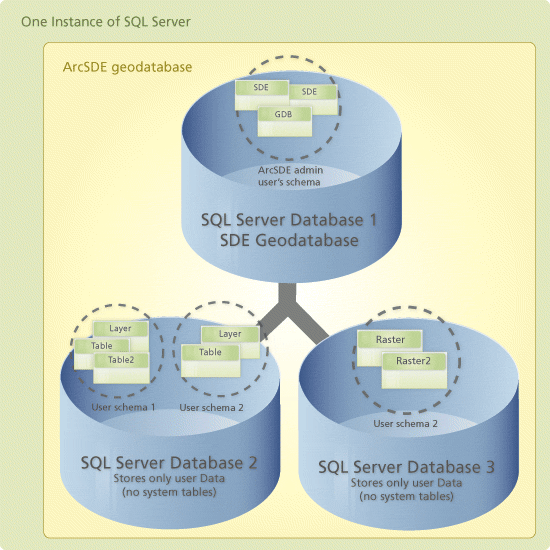
The single spatial database model explained in the previous section is the recommended way to store your geodatabases. However, if you would like to use the multiple spatial database model, the following are rules and guidelines for its use and creation.
Rules for using a multiple spatial database instance
- The database that stores the ArcSDE metadata must be named SDE. Additional databases that store user-defined data can have any name that follows SQL Server rules for identifiers and do not start with a number.
- Each instance of SQL Server can only host one multiple spatial database instance. SQL Server database names must be unique and can, therefore, only support one database named SDE. If you want to store multiple geodatabases in the same SQL Server instance, you can have one multiple spatial database instance and several single spatial database instances.
- In multiple spatial database instances, the ArcSDE repository must reside on the SDE schema. These instances do not support ArcSDE repositories on a dbo schema. Consult ArcSDE for SQL Server dbo-schema geodatabases if you would like to see an explanation of storing ArcSDE repositories in the dbo schema.
- The ArcSDE geodatabase system tables must be owned by a user named SDE. (In SQL Server 2005 or later releases, make sure the SDE user's default schema is also named SDE.)
- The SDE user must be granted access to every database that will store user-defined ArcSDE data.
- All users who connect to this geodatabase instance must be added to the SDE database, even if user-defined data is not stored in the SDE database. If the users will store data in the SDE database, a new schema must be created for that user in the SDE database. Again, the user name and schema name must be the same.
- Cross-database queries are permitted. ArcSDE views can reference data from multiple databases.
- SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE (also known as data manipulation language (DML)) statements can be used across database boundaries. For example, if you connect to the public_works database, you can display and edit data from the planning database. However, you cannot execute CREATE, ALTER, and DROP (DDL) statements across database boundaries.
- The collection of the SDE database and other related databases forms a single geodatabase. One set of ArcSDE geodatabase system tables supports all the user-defined data that it references. Therefore, backup and restore operations must apply to the entire geodatabase. If all databases are not backed up and restored simultaneously, you risk geodatabase corruption.
- The SDE and other related databases must use the same collation.
- All spatial databases that will contain an ArcSDE XML column must have their own full text catalog.
- To see a list of the permissions necessary for the SDE and other users, see User permissions for geodatabases in SQL Server.
Guidelines for creating a multiple spatial database instance
Here are some guidelines for creating a database to store spatial data.
- Use the ArcSDE Post Installation wizard to create the database that will store the ArcSDE repository. The wizard will create the SDE database, grant the SDE login access to it, and install the ArcSDE system tables. Make sure you call this database SDE.
- Give the data files a large initial size, then use the Enterprise Manager or SQL Server Management Studio to increase the autogrowth increment of both the database and transaction log file. At this time, make an initial backup.
- To create additional databases that store user-defined data, use SQL Server tools such as the Enterprise Manager, Query Analyzer, or Management Studio. The SDE user must be added to each additional database you create. This user requires no special permissions in these databases. Permissions are automatically granted to the SDE user when datasets are created or registered as versioned.
Migrating from the multiple to the single spatial database model
As mentioned above, the single database model is the recommended model to use for your geodatabases. If you have an existing geodatabase stored using the multiple database model and want to migrate to the single database model, follow the steps below:
- Create a full database backup of all ArcSDE databases.
- Create a new single database model geodatabase using the Post Installation wizard. Be sure to run the Post Installation wizard for the same release you are using. For example, if you are using the multiple database model with ArcSDE 9.1 and want to move to the single database model, run the 9.1 Post Installation wizard to create the single geodatabase. Also, be sure to perform these steps within the same instance of SQL Server.
NOTE: If you are currently using ArcSDE 8.3, first upgrade to at least ArcSDE 9, then migrate to the single database model.
- Use the ArcCatalog interface to transfer data to your new single database model geodatabase.
The Post Installation wizard creates a new database in SQL Server, so create a service or set up a direct connection with which to access the new geodatabase. Then, start ArcCatalog and make a connection to both the old multiple database model and the new single database model. Next, transfer data between the geodatabases using copy/paste, import, export, or various other methods of migrating data.


 The databases can have any unique name that follows SQL Server rules for identifiers, does not start with a number, and is not sde.
You can use the ArcSDE for SQL Server Post Installation wizard to create additional databases and geodatabases. Run through all steps of the Post Installation wizard, making sure to provide a unique database name, ArcSDE service name, and ArcSDE service number. Since users are created at the instance level then added to the database in SQL Server, be sure to use the same password for the ArcSDE administrator when prompted.
If clients only use direct connections to each separate geodatabase, you do not need to create an ArcSDE service and can skip the last step of the Post Installation wizard. However, if clients will connect using an ArcSDE service, you need to create an additional service for each additional geodatabase. As mentioned, this can be done through the Post Installation wizard; just be sure to specify a different service name, port number, and the correct database name on the ArcSDE service information dialog box.
Be aware that if you plan to use different settings in the dbtune.sde, giomgr.defs, or dbinit.sde files, these changes must be made before running the Post Installation wizard.
The databases can have any unique name that follows SQL Server rules for identifiers, does not start with a number, and is not sde.
You can use the ArcSDE for SQL Server Post Installation wizard to create additional databases and geodatabases. Run through all steps of the Post Installation wizard, making sure to provide a unique database name, ArcSDE service name, and ArcSDE service number. Since users are created at the instance level then added to the database in SQL Server, be sure to use the same password for the ArcSDE administrator when prompted.
If clients only use direct connections to each separate geodatabase, you do not need to create an ArcSDE service and can skip the last step of the Post Installation wizard. However, if clients will connect using an ArcSDE service, you need to create an additional service for each additional geodatabase. As mentioned, this can be done through the Post Installation wizard; just be sure to specify a different service name, port number, and the correct database name on the ArcSDE service information dialog box.
Be aware that if you plan to use different settings in the dbtune.sde, giomgr.defs, or dbinit.sde files, these changes must be made before running the Post Installation wizard.
 The single spatial database model explained in the previous section is the recommended way to store your geodatabases. However, if you would like to use the multiple spatial database model, the following are rules and guidelines for its use and creation.
The single spatial database model explained in the previous section is the recommended way to store your geodatabases. However, if you would like to use the multiple spatial database model, the following are rules and guidelines for its use and creation.