Tutorial: Publishing a WFS-T service
Tutorial: Publishing a WFS-T service |
|
| Release 9.3 |
|
This tutorial will show you how to publish a WFS service with read-write access by enabling Transactions (WFS-T) using ArcGIS Server Manager. A WFS service with transactions (WFS-T) allows WFS clients to apply edits (inserts, deletes and updates) to the data in the source database through the WFS service. In order to apply changes through WFS-T, the data must be from an ArcSDE geodatabase, it must be versioned and the service must be published from a non-default version.
When a map service or geodata service is published with WFS capabilities, the data can be accessed by OGC compliant WFS clients, including the Data Interoperability extension in ArcCatalog and ArcMap. These WFS clients can also see the latest changes made to the data. If you're new to WFS services and want to learn more about it before attempting this tutorial, see WFS services.
If you've just installed ArcGIS Server, you need to complete some preparatory steps before you can log into Manager or publish services. You can find these steps in the Getting started after install section of this help system.
In order to create a map service or geodata service, you need to place the map document (mxd), geodatabase (File or Personal) or SDE connection file in a shared location visible to all server object container (SOC) machines in your GIS server. The SOC Account you created during the post install must also have permissions to read the map document and all of the data it references (map service), or all of the data in the geodatabase that you wish to publish (geodata service).
WFS services support simple features from ESRI sources, such as shapefiles and geodatabases. However, if you are going to enable transactions on the service (WFS-T), all data that you wish to edit must be stored within an ArcSDE geodatabase.
With WFS services you have the option of publishing a geodata service or a map service. There are a few differences to be aware of when selecting the type of service you are going to create. The following sections summarize the functionality available with geodata and map services to help you identify which type of service best suits your requirements.
Geodata services
A WFS geodata service allows you to access a geodatabase through the internet or any OGC compliant WFS client. A geodata service may be created for any type of geodatabase including ArcSDE geodatabases, personal geodatabases and file geodatabases. When creating a WFS service from a geodata service, it is important to keep in mind that all of the feature classes in the geodatabase will be exposed in the service.
Geodata services are useful in situations where you need to access geodatabases in remote locations. For example, a company may want to set up ArcSDE geodatabases to manage data in its Los Angeles and New York offices. Once created, each office can publish its ArcSDE geodatabase on the Internet using a geodata service.
Map services
A WFS map service represents a map document (mxd) that you've made available to others through the internet or any OGC compliant WFS client. Map services with WFS functionality give you a lot of control over the data that is published through the service. Here are some common reasons why you might set up a map service.
There are also some limitations associated with WFS map services. Consider the following things when publishing a WFS service from a map document:
Before creating a WFS service with read and write access there are some initial requirements to set up your data:
Follow these steps to prepare your data for a WFS-T service:
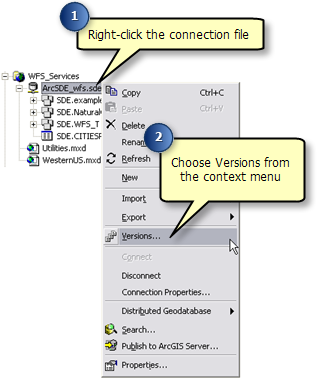
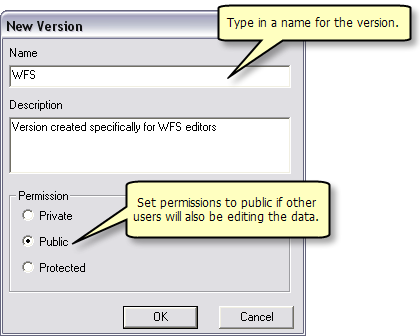
In the version manager dialog, right-click on the version you wish to create a child version of and click New. This creates a new version that can be used by WFS editors.
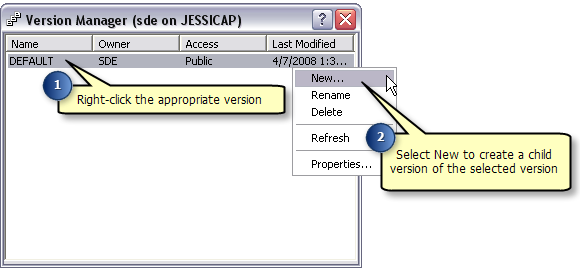
Type in a name for the new version. If users other than the creator will be editing the data, the Permission option must be set to Public.
If you are creating a Geodata service, continue to step 6. If you are creating a map service, skip to step 8.
For Geodata services
To ensure that the geodata service publishes the appropriate data when it is created, the connection properties of the Geodatabase must be updated so that they reference the new WFS version that has been created.
To do this, right click on the geodatabase connection file and choose Connection Properties.
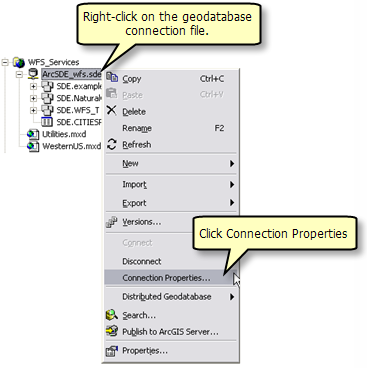
Under the section Connection Details click the Change button
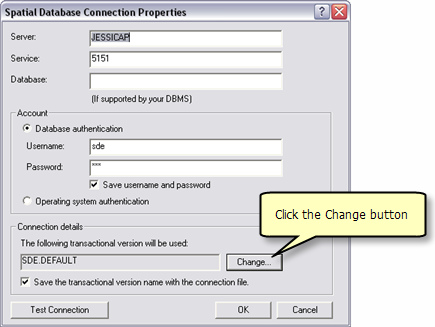
Select the version dedicated to WFS users and click OK
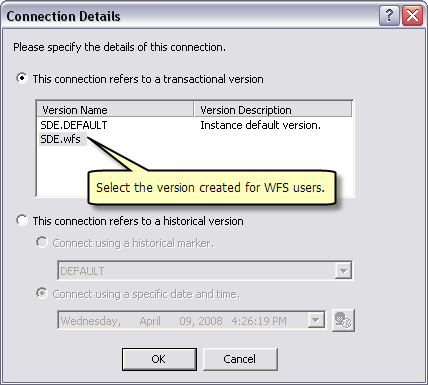
For map services
Right click on the geodatabase and select Change Version. This opens the Version Manager dialog.
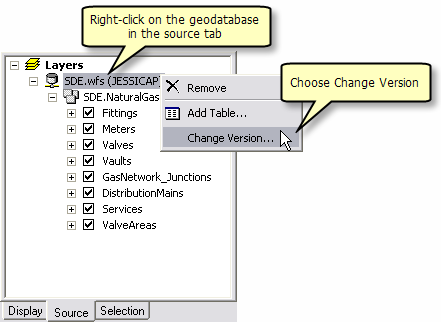
In the Version Manager dialog select the version dedicated to WFS users and click OK.

Follow these steps to create your geodata or map service:
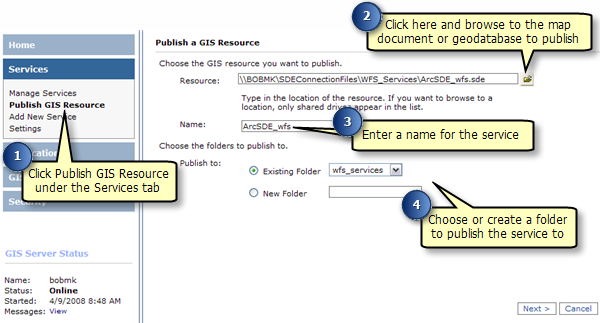
If you have an existing service that does not have WFS capabilities enabled, follow these steps to enable it:
After a WFS service has been published there is an option called Transactions (WFS-T) which must be enabled to allow WFS users to edit and apply changes to the data in the source database.
Follow these steps to enable transactions on a WFS service:
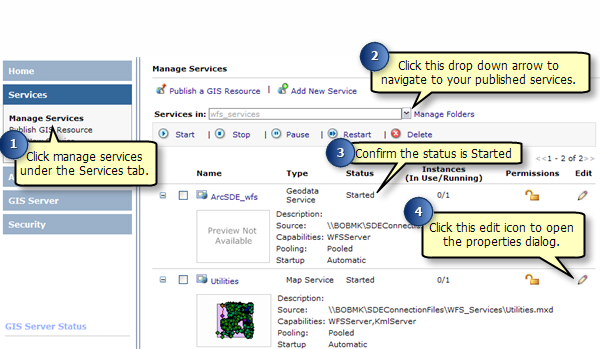
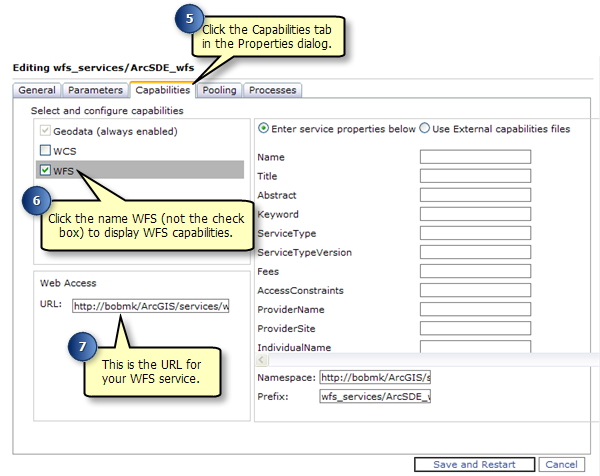
Once you have published a WFS service it can be used in any client that supports WFS 1.1 and the Simple Features profile of GML including web browsers. You can also use the Data Interop extension in ArcCatalog and ArcMap to work with WFS services. The following sections will show you how to access WFS services through a web browser and the Data Interop extension in ArcCatalog.
A Web browser is one of the simplest clients of a WFS service. You can request information through HTTP and the responses or exceptions are returned through the browser.
To connect to your service you need to know the WFS URL which can be located in the service's Properties under the Capabilities tab in ArcGIS Server Manager or ArcCatalog. Once you have the URL you can use OGC standard operations to request information about the service through HTTP. Some examples of operations that you can use to request information include:
This request will return all feature types and functionality available through the service in GML format. To use the GetCapabilities operation in a web browser copy and paste the WFS URL into the address bar and add "?request=getCapabilities" to the end, as shown in the example and screen shot below.
URL example: http://bobmk/arcgis/services/wfs_services/ArcSDE_wfs/GeoDataServer/WFSServer?request=getcapabilities
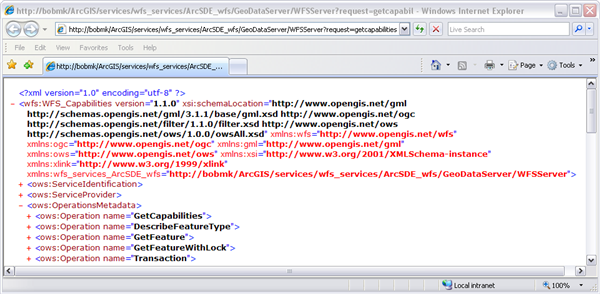
The following graphic is an example of functionality returned by the GetCapabilities operation:
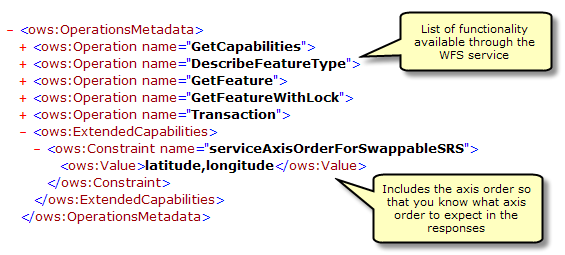
GetCapabilities also returns a list of all available feature classes and tables:

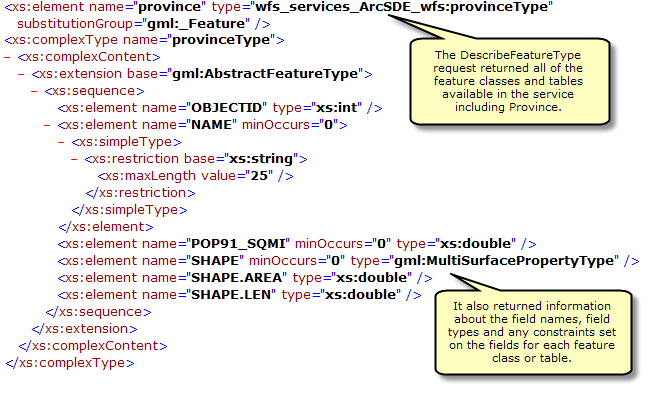
This request describes the field information about one or more features in the WFS service. This includes the field names, field types, allowed minimum and maximum field values and any other constraints set on a field of the feature classes or tables.
To use the DescribeFeatureType operation in a web browser copy and paste the WFS URL into the address bar and add "?SERVICE=WFS&VERSION=1.1.0&REQUEST=DescribeFeatureType&VERSION=1.1.0" to the end of the URL. This will return all of the field information about each of the feature types and tables available in the feature service, as seen in the screen shot below.
URL Example: http://bobmk/arcgis/services/wfs_services/ArcSDE_wfs/GeoDataServer/WFSServer?SERVICE=WFS&VERSION=1.1.0&REQUEST=DescribeFeatureType&VERSION=1.1.0
Adding filters
You can also specify a single feature class or table that you want the field information for by appending the following request to the end of the URL with the name of the feature type or table. "?SERVICE=WFS&VERSION=1.1.0&REQUEST=DescribeFeatureType&TypeName=[enter feature type here]&VERSION=1.1.0"
In the example below the DescribeFeatureType request is used to identify the field information for the feature type called cities.
URL example: http://bobmk/arcgis/services/wfs_services/ArcSDE_wfs/GeoDataServer/WFSServer?SERVICE=WFS&VERSION=1.1.0&REQUEST=DescribeFeatureType&TypeName=cities&VERSION=1.1.0

This request returns information about specific feature types available through the WFS service. Additionally, filters can be used to refine the information that is returned. For more information about the different filters available with WFS services see WFS Services.
To use the GetFeature operation in a web browser copy and paste the WFS URL into the address bar and add "?request=getFeature&typename=[enter feature type here]" to the end of the URL. This will return all of the attribute and geometry information about each feature or row in the feature type.
URL example: http://bobmk/arcgis/services/wfs_services/ArcSDE_wfs/GeoDataServer/WFSServer?request=getfeature&typename=cities

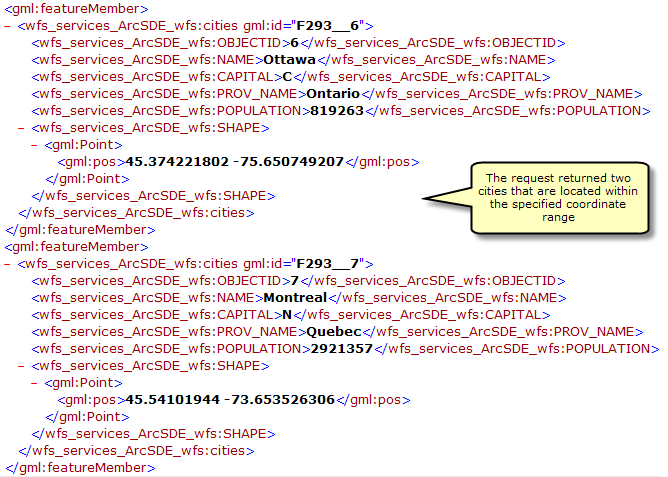
You can also add filters in the request to refine the results that are returned. For example you can request all of the cities that are within a specified coordinate range. In the example below two cities are located within a specified coordinate range.
URL Example: http://bobmk/arcgis/services/wfs_services/ArcSDE_wfs/GeoDataServer/WFSServer?request=getfeature&typename=cities&BBOX=46.90,-76.21,42.12,-72.88
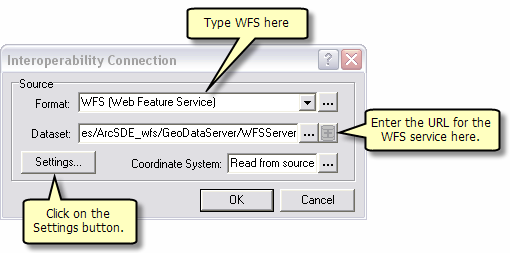
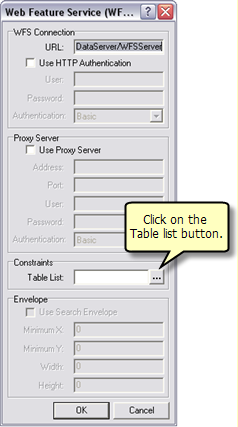
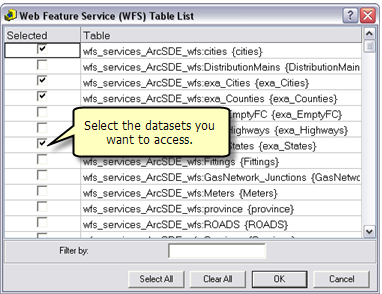
The Data Interoperoperability Extension allows you to read and write data in non-ArcGIS data formats. You can use the Interoperability Connection tool located in ArcCatalog to connect directly to external ESRI data formats, including WFS services. Once the connection is made, the data source will appear underneath the Interoperability Connection entry in the Catalog Tree. A connection is just like any other dataset in that you can add it to ArcMap or use it in geoprocessing tools.
Follow the steps below to connect to a WFS service through the Interoperability Connection tool.

It is important to create an efficient workflow for managing edits made through a WFS-T service. Assuming you have followed the recommended method of creating a separate WFS version for WFS-T editors to work with, the system that you have set up should look similar to the diagram below:
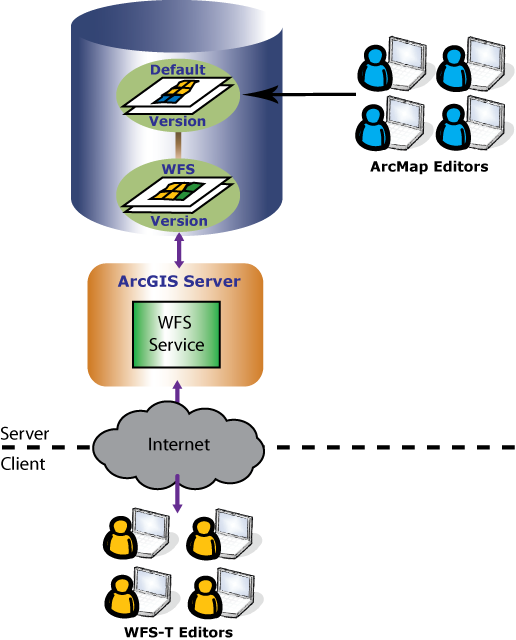
In this example, WFS-T editors and ArcMap editors use versions so that each group can have their own isolated view of the geodatabase to work with. ArcMap editors are directly editing the Default version through ArcMap. WFS-T editors are accessing the WFS service over the internet. This allows WFS-T editors to make edits on the WFS version that was created as a child of Default. To learn more about versions, see Understanding versioning in the desktop help system.
To keep the two versions in sync, a process can be run regularly to update the WFS version with edits from the Default version, and also to update the Default version with the edits from the WFS version. This is a two step process in the editing workflow of any versioned system called reconcile and post. This process can be automated or it can be administered by an editor (depending on their permissions) or database administrator. To learn more about the reconcile and post process see An Overview of the version editing process
When run, the reconcile operation will pull updates from the Default version into the current editing session on the WFS version. Conflicts may occur if edits have been made to the same features in both versions. You can either setup conflict resolution to be automatic, or you can choose to resolve each conflict manually through the conflict resolution dialog.
After handling any conflicts the post operation can be run. This process merges changes from the WFS version into the Default version
The whole reconcile and post process is summarized in the diagram below. Here the WFS version pulls updates from the Default version during reconcile. After incorporating the changes, the WFS version posts its updates to the Default version using the post operation. At this point the Default and WFS versions both have the same content.
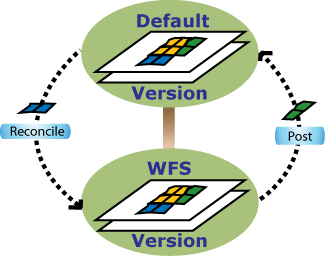
Once the reconcile and post process is complete, both versions are up to date with the most current representation of the features, and WFS editors can continue making edits again.
It is important to note that if there are outstanding locks when reconcile and post is run, the system will not allow the process to succeed. This is a safeguard to prevent conflicts between features locked by WFS-T clients and features changed through the reconcile and post process. Also, running reconcile and post will lock the WFS-T version to prevent any lock and transaction calls from being made by WFS-T editors during the reconcile and post process.
To accommodate this safeguard, it is recommended that the reconcile and post process be run at well established times which all WFS-T editors have prior knowledge of. This will allow the editors to get their changes posted to the database. Administrators may also need to manually remove locks from the locks table before the reconcile and post.
To learn more about the WFS-T locking scheme, see WFS services.