WMS services
WMS services |
|
| Release 9.3.1 |
|
The Open Geospatial Consortium, Inc. (OGC) Web Map Service (WMS) specification is an international specification for serving and consuming dynamic maps on the Web. WMS services are useful if you want to make your maps available online in an open, recognized way across different platforms and clients. Any client built to support the WMS specification can view and work with your service. Four versions of the WMS specification have been published so far. They are v1.0.0, v1.1.0, v1.1.1, and v1.3.0 (most recent).
Client applications work with a WMS service by appending parameters to the service's URL. WMS services published with ArcGIS Server support the following three operations:
It is not necessary for a WMS service to support all the operations. But one must support at least GetCapabilities and GetMap operations to be a "Basic WMS", and support optional GetFeatureInfo operation to be a "Queryable WMS".
The maps returned by a WMS service are images only. They do not contain actual data. To expose your data as vector features through OGC specifications, publish a WFS service instead. To expose data as raster layers, publish a WCS service. You can publish both WFS and WCS services using ArcGIS Server 9.3.
You can learn more about WMS services at the Open Geospatial Consortium Web site. ESRI also maintains an Interoperability and Standards Web page detailing its support for OGC services in ArcGIS.
There are two ways you can publish a WMS service using ArcGIS Server:
You can use either ArcGIS Server Manager or ArcCatalog to publish the service. If you need help with this step, see Publishing a GIS resource to the server.
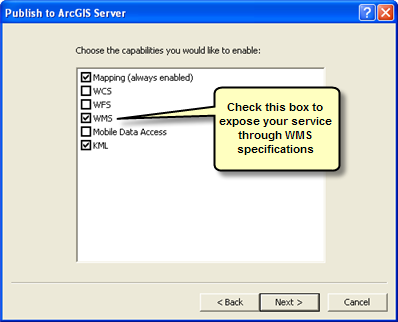
When you publish your map or image service, you should enable the WMS capability by checking the box in the Capabilities list.
Notes:
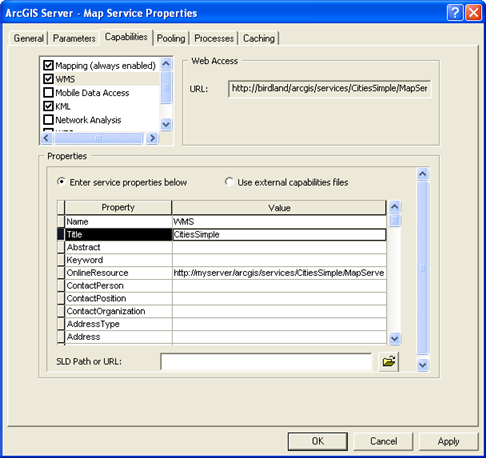
After you publish the service, you can set further properties for the WMS service on the Capabilities tab of the Service Properties dialog box.
For a detailed walk-through of the process of creating a WMS service, see Tutorial: Publishing a WMS service.
A WMS service's properties are reflected in its capabilities files so that whoever consumes the service can have a better understanding of the service publisher. When publishing a WMS service with system generated capabilities files (the default), it is recommended you populate the WMS service properties except for Name, Title and OnlineResource. The Name and Title service properties are pre-filled in with WMS and the name of the map service or image service, and OnlineResource is pre-filled in with the URL of the WMS service. In most cases you should not change those three properties.
To populate or modify WMS service properties, do the following:
Note: The OnlineResource field is necessary for a WMS client to communicate correctly with your WMS service. Usually its value is a URL and it should show up in the Web Access box of the Capabilities tab.
The following characters cannot be included in any of the service properties: &, <, >, ", '. If you need to use one of these characters, you must substitute the appropriate escape sequence from the table below:
| & | & |
| < | < |
| > | > |
| " | " |
| ' | ' |
The security for an ArcGIS Server WMS service is managed by controlling the security of its parent map or image service. If a particular role, for example Planners, is denied access to a map, then Planners will not be able to access the map no matter whether they try to consume it through SOAP, representational state transfer (REST), or OGC (for example, WMS) interfaces. ArcGIS Server supports a number of different authentication schemes including HTTP-based authentication (Basic and Digest), Integrated Windows Authentication, and ArcGIS Server managed token-based authentication.
Services that are expected to be accessed via WMS interfaces should be secured using HTTP Basic, HTTP Digest or Integrated Windows Authentication. Most WMS clients (both non-ESRI as well as ESRI clients) will understand and work with these widespread standard authentication schemes.
Although not recommended, a WMS service can still be secured using ArcGIS Server managed token-based authentication by using this type of authentication on its parent map or image service. Most third-party WMS clients will not be able to connect to WMS services secured in this way; but to make raw requests to WMS services protected by a token, you can get a valid token from the token service and append the token string as an extra parameter to the requests you send out. In other words, requests to a token-secured WMS service must use the following format: http://<WMS_service_url>?<standard WMS parameters>&token=<valid_tokenString>
To connect to a WMS service, you need to know the URL. WMS services published with ArcGIS Server have this URL format:
http://<Web server machine name>/<ArcGIS Server instance name>/services/<folder name (if applicable)>/<service name>/<service type (can be MapServer or ImageServer)>/WMSServer?
Remember that the WMS capability is available for both map services and image services. This is why there are two options for the service type.
For example, if you have a folder Japan containing the map service Tokyo, running on myServer with the default instance arcgis, the URL of your WMS service would look like this:
http://myServer/arcgis/services/Japan/Tokyo/MapServer/WMSServer?
If you have an image service IdahoImages running on myServer with the instance name of PublicLands, your URL for the WMS service would look like this:
http://myServer/PublicLands/services/IdahoImages/ImageServer/WMSServer?
A Web browser is the simplest client of a WMS service. WMS requests can be issued through HTTP, and the responses or exceptions are returned through the browser. WMS services support three operations: GetCapabilities, GetMap, and GetFeatureInfo. Through URL parameters, a client can use these operations to obtain metadata, maps, and feature information from the WMS service. These operations and parameters are detailed in the OGC WMS specifications.
ESRI WMS clients include ArcGIS Desktop (ArcCatalog and ArcMap), ArcExplorer, ArcGIS Server Web Application Developer Framework (ADF) for .NET, ArcGIS Server Web ADF for Java, and ESRI GIS Portal Toolkit Map Viewer.